|
Phlogiston Theory
The phlogiston theory, a superseded scientific theory, postulated the existence of a fire-like element dubbed phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burning up''), from (''flame''). The idea of a substance was first proposed in 1667 by Johann Joachim Becher and later put together more formally in 1697 by Georg Ernst Stahl. Phlogiston theory attempted to explain chemical processes such as combustion and rusting, now collectively known as oxidation. The theory was challenged by the concomitant mass increase and was abandoned before the end of the 18th century following experiments by Antoine Lavoisier in the 1770s and by other scientists. Phlogiston theory led to experiments that ultimately resulted in the identification (), and naming (1777), of oxygen by Joseph Priestley and Antoine Lavoisier, respectively. Theory Phlogiston theory states that ''phlogisticated'' substances contain phlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
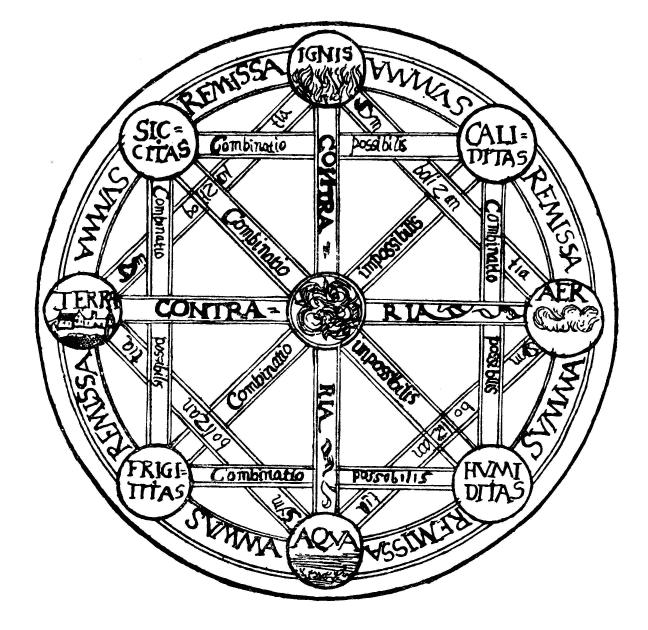
Classical Elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the elements to be divisible into infinitely small pieces without changing their nature. While the classification of the material world in ancient India, Hellenistic Egypt, and ancient Greece into air, earth, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcination
Calcination is thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), generally for the purpose of removing impurities or volatile substances and/or to incur thermal decomposition. The root of the word calcination refers to its most prominent use, which is to remove carbon from limestone (calcium carbonate) through combustion to yield calcium oxide (quicklime). This calcination reaction is CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g). Calcium oxide is a crucial ingredient in modern cement, and is also used as a chemical flux in smelting. Industrial calcination generally emits carbon dioxide (). A calciner is a steel cylinder that rotates inside a heated furnace and performs indirect high-temperature processing (550–1150 °C, or 1000–2100 °F) within a controlled atmosphere. Etymology The process of calcination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Science
Popular science (also called pop-science or popsci) is an interpretation of science intended for a general audience. While science journalism focuses on recent scientific developments, popular science is more broad ranging. It may be written by professional science journalists or by scientists themselves. It is presented in many forms, including books, film and television documentaries, magazine articles, and web pages. History Before the modern specialization and professionalization of science, there was often little distinction between "science" and "popular science", and works intended to share scientific knowledge with a general reader existed as far back as Greek and Roman antiquity. Without these popular works, much of the scientific knowledge of the era might have been lost. For example, none of the original works of the Greek astronomer Eudoxus (4th century BC) have survived, but his contributions were largely preserved due to the didactic poem '' Phenomena'' writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Pott
Johann Heinrich Pott (6 October 1692 – 29 March 1777) was a Prussian physician, chemist, and a glass and porcelain technologist. He is considered a pioneer of pyrochemistry. He examined the elements bismuth and manganese apart from attempting improvements to glass and porcelain production. Biography Pott was born in Halberstadt, son of the royal councillor Johann Andreas Pott (1662–1729) and Dorothea Sophia daughter of Andreas Machenau. He studied at the cathedral school in Halberstadt and Francke's pedagogium before studying theology at the University of Halle. He then shifted to study medicine and chemistry under Georg Ernst Stahl. In 1713 he studied assaying at Mansfield under mining master Lages. He spent two years along with two of his brothers as travelling evangelists for the Community of True Inspiration but he left the sect in 1715 and returned to study chemistry at Halle, receiving a doctorate in 1716 on sulfur under Friedrich Hoffmann. He worked as a physician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern charcoal briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. The early history of wood charcoal production spans ancient times, rooted in the abundance of wood in various regions. The process typically involves stacking wood billets to form a conical pile, allowing air to enter through openings at the bottom, and igniting the pile gradually. Charcoal burners, skilled professionals tasked with managing the delicate operation, often lived in isolation to tend their wood piles . Throughout histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Of Sulphur
Liver of sulfur is a loosely defined mixture of potassium sulfide, potassium polysulfide, potassium thiosulfate, and likely potassium bisulfide. Synonyms include hepar sulfuris, sulfur, sulfurated potash and sulfurated potassa. There are two distinct varieties: "potassic liver of sulfur" and "ammoniacal liver of sulfur". Overview Liver of sulfur is mainly used in metalworking to form a brown or black patina on copper and silver as well as many (though not all) copper alloys and silver alloys (brass, for example— a copper alloy— does not react with sulfur compounds). It is sold as a yellow brittle solid (a "lump" which must be mixed with water before use) as well as a pre-mixed liquid and a gel form. The solid is believed to have the longest shelf life, though all liver of sulfur tends to decompose with time. Modern gel forms contain stabilizers that allow the reactivity to last much longer. Liver of sulfur that is kept dry, sealed from air, out of the light, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulphate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry of the isolated anion is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. Soot is considered a hazardous substance with carcinogenic properties. Most broadly, the term includes all the particulate matter produced by this process, including black carbon and residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke classified as cokes or char. It can include polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals like mercury. Soot causes various types of cancer and lung disease. Terminology Definition Among scientists, exact definitions for soot vary, depending partly on their field. For example, atmospheric scientists may use a different definition compared to toxicologists. Soot's definition can also vary across time, and from paper to paper even among scientists in the same field. A common feature of the definitions is that soot is composed largely of carbon based particles resulting from the incomplete burni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Halle
Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (), also referred to as MLU, is a public research university in the cities of Halle and Wittenberg. It is the largest and oldest university in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. MLU offers German and international (English) courses leading to academic degrees such as BA, BSc, MA, MSc, doctoral degrees, and habilitation. The university was created in 1817 through the merger of the University of Wittenberg (founded in 1502) and the University of Halle (founded in 1694). MLU is named after Protestant reformer Martin Luther, who was a professor in Wittenberg. Today, the university campus is located in Halle, while ''Leucorea Foundation'' in Wittenberg serves as MLU's convention centre. History University of Wittenberg (''Universität Wittenberg'') was founded in 1502 by Frederick the Wise, Elector of Saxony to propagate the principles of Renaissance humanism. The foundation of the university was heavily criticized, especially wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |