|
Philosophy Of Color
The philosophy of color is a subset of the philosophy of perception that is concerned with the nature of the perceptual experience of color. Any explicit account of color perception requires a commitment to one of a variety of ontological or metaphysical views, distinguishing namely between externalism/internalism, which relate respectively to color realism, the view that colors are physical properties that objects possess, and color fictionalism, the view that colors possess no such physical properties. History Philosophical concerns about the nature of color can be traced back at least as far as Anaxagoras (5th century BCE), who favoured color realism in his sophism: "Snow is frozen water. But water is dark in color. Therefore, snow is dark in color." Anaxagoras claimed that our perception deviated from the truth "...owing to the feebleness f the senses" Later, Democritus (circa 400 BCE) would say, "By convention sweet, by convention bitter, by convention hot, by convention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
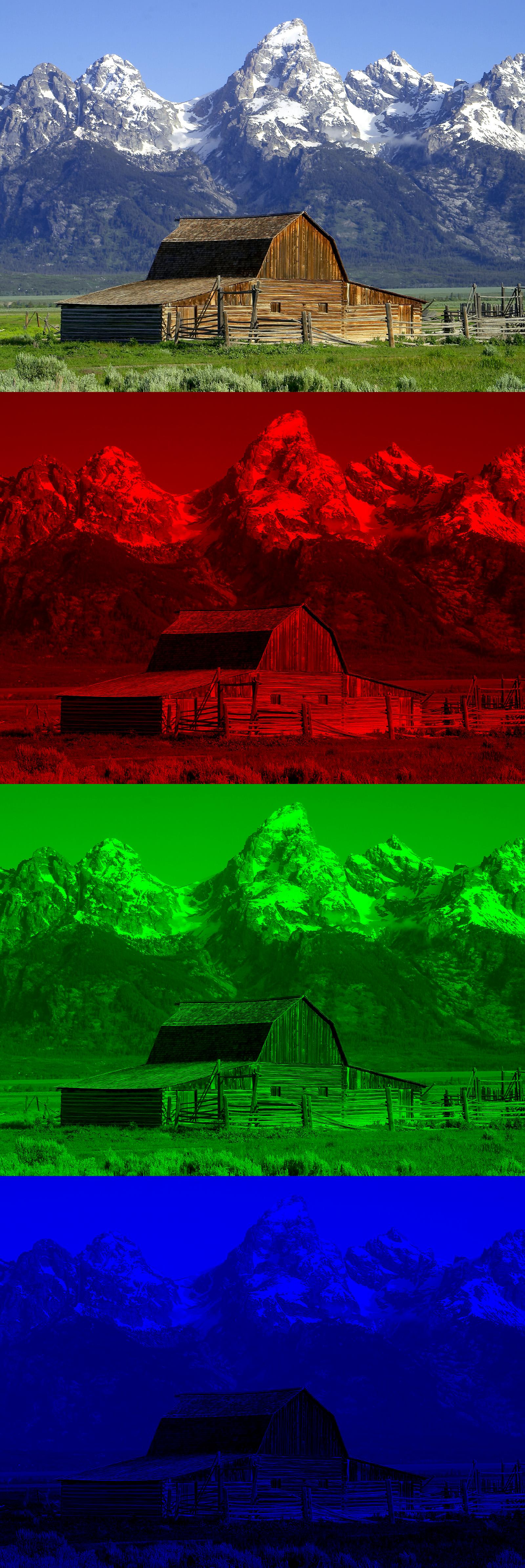
RGB Color Wheel
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography and colored lighting. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the same device over time. Thus an RGB value does not define t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Churchland
Paul Montgomery Churchland (born October 21, 1942) is a Canadian philosopher known for his studies in neurophilosophy and the philosophy of mind. After earning a Ph.D. from the University of Pittsburgh under Wilfrid Sellars (1969), Churchland rose to the rank of full professor at the University of Manitoba before accepting the Valtz Family Endowed Chair in Philosophy at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) and joint appointments in that institution's Institute for Neural Computation and on its Cognitive Science Faculty. As of February 2017, Churchland is recognised as Professor Emeritus at the University of California, San Diego, UCSD, and is a member of the Board of Trustees of the Moscow Center for Consciousness Studies of Moscow State University. Churchland is the husband of philosopher Patricia Churchland, with whom he collaborates closely. Early life and education Paul Montgomery Churchland was born in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, on October 21, 1942. Note, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Terms
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, emission spectra, emission, Reflection (physics), reflection and Transmittance, transmission. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelengths, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain. Colors have perceived properties such as hue, colorfulness (saturation), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realism (visual Arts)
Realism in the arts is generally the attempt to represent subject-matter truthfully, without artificiality, exaggeration, or speculative or supernatural elements. The term is often used interchangeably with naturalism, although these terms are not necessarily synonymous. Naturalism, as an idea relating to visual representation in Western art, seeks to depict objects with the least possible amount of distortion and is tied to the development of linear perspective and illusionism in Renaissance Europe. Realism, while predicated upon naturalistic representation and a departure from the idealization of earlier academic art, often refers to a specific art historical movement that originated in France in the aftermath of the French Revolution of 1848. With artists like Gustave Courbet capitalizing on the mundane, ugly or sordid, realism was motivated by the renewed interest in the commoner and the rise of leftist politics. The realist painters rejected Romanticism, which had c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualia
In philosophy of mind, qualia (; singular: quale ) are defined as instances of subjective, conscious experience. The term ''qualia'' derives from the Latin neuter plural form (''qualia'') of the Latin adjective '' quālis'' () meaning "of what sort" or "of what kind" in relation to a specific instance, such as "what it is like to taste a specific this particular apple now". Examples of qualia include the perceived sensation of ''pain'' of a headache, the ''taste'' of wine, and the ''redness'' of an evening sky. As qualitative characteristics of sensations, qualia stand in contrast to propositional attitudes, where the focus is on beliefs about experience rather than what it is directly like to be experiencing. C.S. Peirce introduced the term ''quale'' in philosophy in 1866, and in 1929 C. I. Lewis was the first to use the term "qualia" in its generally agreed upon modern sense. Frank Jackson later defined qualia as "...certain features of the bodily sensations especially, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictionalism
Fictionalism is a view in philosophy that posits that statements appearing to be descriptions of the world should not be construed as such, but should instead be understood as cases of "make believe", thus allowing individuals to treat something as literally true (a "useful fiction"). Concept Fictionalism consists in at least the following three theses: # Claims made within the domain of discourse are taken to be truth-apt; that is, true or false. # The domain of discourse is to be interpreted at face value—not reduced to meaning something else. # The aim of discourse in any given domain is not truth, but some other virtue(s) (e.g., simplicity, explanatory scope). Two important strands of fictionalism are: modal fictionalism developed by Gideon Rosen, which states that possible worlds, regardless of whether they exist or not, may be a part of a useful discourse, and mathematical fictionalism advocated by Hartry Field. Modal fictionalism is recognized as further refinement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Television
Color television (American English) or colour television (British English) is a television transmission technology that also includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improves on the monochrome or black-and-white television technology, which displays the image in shades of gray (grayscale). Television broadcasting stations and networks in most parts of the world upgraded from black-and-white to color transmission between the 1960s and the 1980s. The invention of color television standards was an important part of the history of television, history and technology of television. Transmission of color images using mechanical scanners had been conceived as early as the 1880s. A demonstration of mechanically scanned color television was given by John Logie Baird in 1928, but its limitations were apparent even then. Development of electronic scanning and display made a practical system possible. Monochrome transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience concerned with the functions of the nervous system and their mechanisms. The term ''neurophysiology'' originates from the Greek word ''νεῦρον'' ("nerve") and ''physiology'' (which is, in turn, derived from the Greek ''φύσις'', meaning "nature", and ''-λογία'', meaning "knowledge"). Neurophysiology has applications in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of many neurological and psychiatric diseases. Neurophysiological techniques are also used by clinical neurophysiologists to diagnose and monitor patients with neurological diseases. The field involves all levels of nervous system function, from molecules and cells to systems and whole organisms. Areas of study include: * The electrochemical properties of neurons * Function and regulation of proteins in neurons and glia * Metabolic reactions relevant to neural function * Cell signalling in the nervous system * Neurotransmission and synaptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
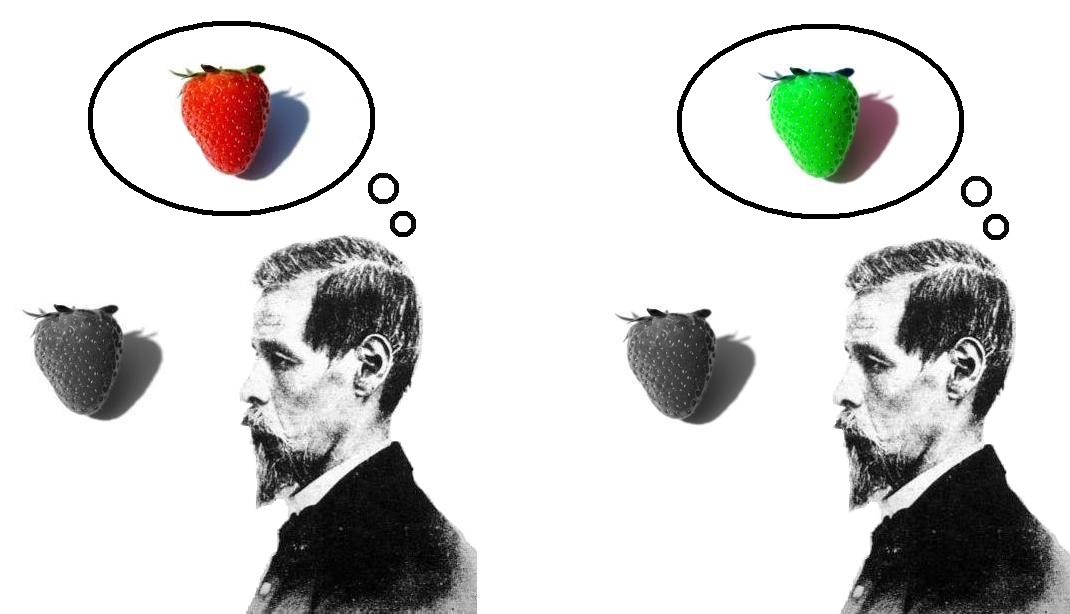
Knowledge Argument
The knowledge argument (also known as Mary's Room, Mary the Colour Scientist, or Mary the super-scientist) is a philosophical thought experiment proposed by Frank Jackson in his article "Epiphenomenal Qualia" (1982), and extended in "What Mary Didn't Know" (1986). The experiment describes Mary, a scientist who exists in a black-and-white world where she has extensive access to physical descriptions of color, but no actual perceptual experience of color. Mary has learned everything there is to learn about color, but she has never actually experienced it for herself. The central question of the thought experiment is whether Mary will gain new knowledge when she goes outside of the colorless world and experiences seeing in color. The experiment is intended to argue against physicalism—the view that the universe, including all that is mental, is entirely physical. Jackson says that the "irresistible conclusion" is that "there are more properties than physicalists talk about". Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Colour Scientist
Mary may refer to: People * Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name) Religion * New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below * Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blessed Virgin Mary * Mary Magdalene, devoted follower of Jesus * Mary of Bethany, follower of Jesus, considered by Western medieval tradition to be the same person as Mary Magdalene * Mary, mother of James * Mary of Clopas, follower of Jesus * Mary, mother of John Mark * Mary of Egypt, patron saint of penitents * Mary of Rome, a New Testament woman * Mary the Jewess, one of the reputed founders of alchemy, referred to by Zosimus. Royalty * Mary, Countess of Blois (1200–1241), daughter of Walter of Avesnes and Margaret of Blois * Mary of Burgundy (1457–1482), daughter of Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy * Queen Mary of Denmark (born 1972), wife of Frederik X of Denmark * Mary I of England (1516–1558), aka "Bloody Mary", Queen of England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualia
In philosophy of mind, qualia (; singular: quale ) are defined as instances of subjective, conscious experience. The term ''qualia'' derives from the Latin neuter plural form (''qualia'') of the Latin adjective '' quālis'' () meaning "of what sort" or "of what kind" in relation to a specific instance, such as "what it is like to taste a specific this particular apple now". Examples of qualia include the perceived sensation of ''pain'' of a headache, the ''taste'' of wine, and the ''redness'' of an evening sky. As qualitative characteristics of sensations, qualia stand in contrast to propositional attitudes, where the focus is on beliefs about experience rather than what it is directly like to be experiencing. C.S. Peirce introduced the term ''quale'' in philosophy in 1866, and in 1929 C. I. Lewis was the first to use the term "qualia" in its generally agreed upon modern sense. Frank Jackson later defined qualia as "...certain features of the bodily sensations especially, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |