|
Pharnaces (died 47 BCE), the son of Mithridates VI of Pontus, he tried to reconquer Pontus, but was crushed by Julius Caesar
{{hndis ...
Pharnaces ( el, Φαρνάκης, link=no) may refer to: * Pharnaces (fl. 550 BCE – 497 BCE), founder of the Pharnacid dynasty of satraps of Hellespontine Phrygia * Pharnaces II of Phrygia (fl. 430 BCE – 413 BCE), satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia * Pharnaces (Persian noble) (died 334 BCE), Persian commander in the battle of the Granicus * Pharnaces I of Pontus (fl. 2nd century BCE), first important ruler of the kingdom of Pontus * Pharnaces II of Pontus Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithrida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces I Of Pontus
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblings: a brother called Mithridates IV of Pontus and a sister called Laodice who both succeeded Pharnaces. He was born and raised in the Kingdom of Pontus. Life The date of his accession cannot be fixed with certainty; but it is certain, at least, that he was on the throne before 183 BC, in which year he succeeded in reducing the important city of Sinope, which had been long an object of ambition to the Kings of Pontus. The Rhodians sent an embassy to Rome to complain of this aggression, but without effect. About the same time Pharnaces became involved in disputes with his neighbour, King of Pergamon, Eumenes II, which led to repeated embassies from both monarchs to Rome, as well as to partial hostilities. But in the spring of 181 BC, withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces (satrap)
Pharnaces Ι ( el, Φαρνάκης; Elamite language, Elamite: ''Parnaka''; –497 BCE) was a son of Arsames. He was a younger brother of Hystaspes (father of Darius I), Hystaspes, and therefore an uncle of Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Emperor Darius I, son of Hystaspes. He was the founder of the Pharnacid dynasty that ruled over Hellespontine Phrygia. Mayor of the Palace According to the Persepolis Administrative Archives, fortification tablets found at Persepolis, Pharnaces was the chief economic official to Darius I between 506 and 497 BCE. He was a Mayor of the Palace, his statutory attribute being a short stick, probably made of a precious metal. He likely appears on some of the reliefs in Persepolis. Hellespontine Phrygia Pharnaces became involved at some point with Hellespontine Phrygia in Asia Minor (modern northwest Turkey), since Aristotle of Stagira mentions that Pharnaces introduced mules in the region. Pharnaces had a son named Artabazos I of Phrygia, Artabazu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnacid Dynasty
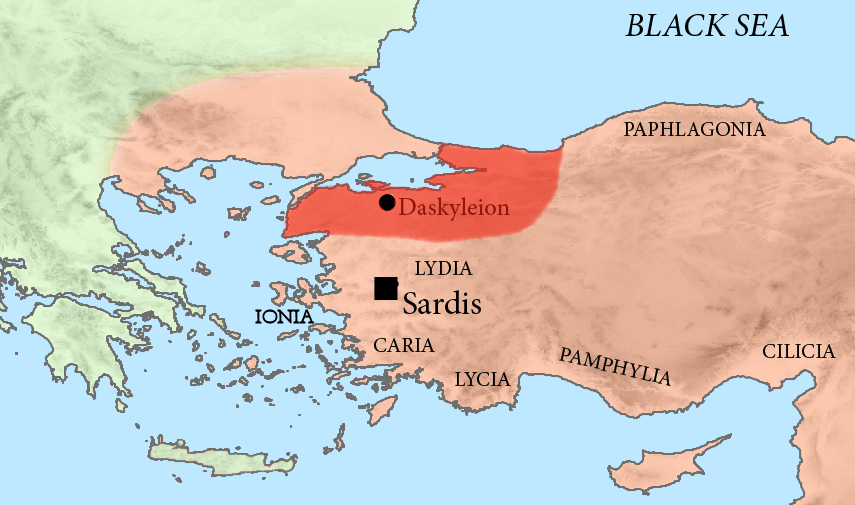
The Pharnacid dynasty was a Persian dynasty that ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty from the 5th until the 4th century BCE. It was founded by Artabazus, son of satrap Pharnaces I (younger brother of Hystaspes, who was born shortly before 565 BCE), son of Arsames (died ca. 520 BCE). They were directly related to the Achaemenid dynasty itself. The last member of the dynasty was Pharnabazus III. Before the Pharnacids, Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BCE) had ruled Hellespontine Phrygia for Cyrus the Great and Cambyses II, before being killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, Mitrobates was succeeded by Oebares II (c.493), son of Megabazus, before Artabazus became satrap circa 479 BCE and started the Pharnacid dynasty, which would rule Hellespontine Phrygia until the conquests of Alexander the Great (338 BCE). The residence of the Pharnacid Dynasty was at Dascylium (near moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces II Of Phrygia
Pharnaces II (Old Iranian: ''Farnaka''; floruit, fl. 430 BCE - 422 BCE) ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty of Persia. Hellespontine Phrygia (Greek: Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία) comprised the lands of Troad, Mysia and Bithynia and had its seat at Daskyleion, south of Cyzicus, Mysia (near modern-day Erdek, Balıkesir Province, Turkey). His grandfather, Artabazos I of Phrygia, was the founder of the Pharnacid dynasty. Pharnaces II followed as satrap either upon the death of his father, Pharnabazus I, or directly upon the death of his grandfather. He was succeeded by his son Pharnabazus II. File:MYSIA, Kyzikos. Circa 460-400 BC.jpg, Coinage of Hellespontine Phrygia at the time of Pharnaces II, Kyzikos, Mysia, circa 460-400 BC File:MYSIA, Kyzikos. Circa 450-400 BC.jpg, Coinage of Hellespontine Phrygia at the time of Pharnaces II, Kyzikos, Mysia, circa 450-400 BC See also *Pharnacid Dynasty Year of birth missing 422 BC deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces (Persian Noble)
Pharnaces (died 334 BC, el, Φαρνάκης) was a Persian noble of the 4th century BC apparently belonging to the Pontic-Cappadocian nobility. His sister was a wife of Darius III. Arrian ''Anabasis Alexandri'' 1.16.3 They had a son named Ariobarzanes and a daughter who married Mithridates and thus they were nephews of Pharnaces. Diodorus 17.20.2 (wrongly naming him "Spithrodates") He was one of the Persian commanders in the battle of the Granicus in 334 BC in Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...), and was killed during the battle. References Year of birth missing 334 BC deaths 4th-century BC Iranian people Achaemenid dynasty {{Iran-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of the Hellespont. Its capital was Dascylium, and for most of its existence it was ruled by the hereditary Persian Pharnacid dynasty. Together with Greater Phrygia, it made up the administrative provinces of the wider Phrygia region. History The satrapy was created in the beginning of the fifth century BC, during the time of administrative reorganisations of the territories in western Asia Minor, which were amongst the most important Achaemenid territories. The first Achaemenid ruler of Hellespontine Phrygia was Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BC), who was appointed by Cyrus the Great and continued under Cambises. He was killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of neighbouring Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use la, flōruit is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are wills attested by John Jones in 1204, and 1229, and a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)". The term is often used in art history when dating the care ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |