|
Pharnabazus (5th Century BC)
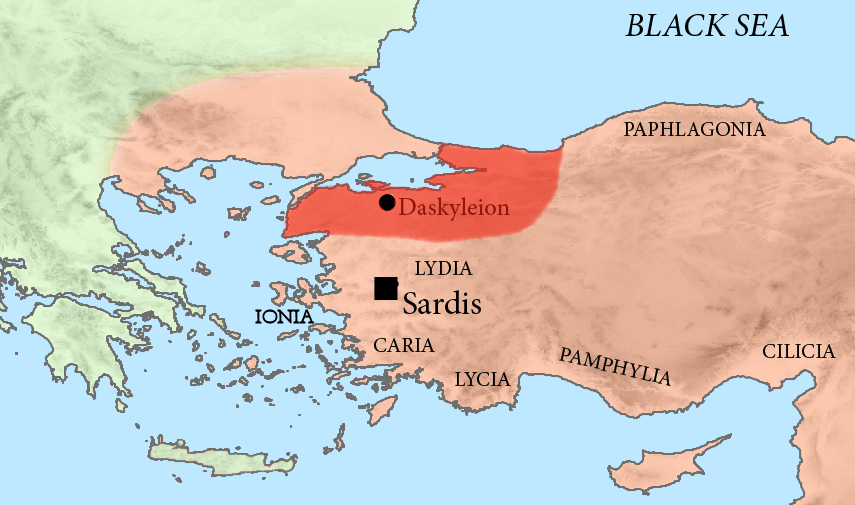
Pharnabazus II (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Achaemenid Empire, Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I of Phrygia, Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazos I of Phrygia, Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus of Phrygia, Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine. According to research by Theodor Nöldeke, he was descended from Otanes, one of the associates of Darius the Great, Darius in the murder of Smerdis. Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia War with Sparta against Athens (c.413-404 BC) Athens was the dominant power in the Aegean Sea, Aege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empires. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. A satrap served as a viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and its modern usage is a pejorative and refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian languages, Old Iranian . In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median language, Median form is reconstructed as . Its Sanskrit cognate is (). The Biblical Hebrew form is , as found in Esther 3:12. In the Parthian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnacid Dynasty
The Pharnacid dynasty was a Persian Empire, Persian dynasty that ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty from the 5th until the 4th century BCE. It was founded by Artabazos I of Phrygia, Artabazus, son of satrap Pharnaces I of Phrygia, Pharnaces I (younger brother of Hystaspes (father of Darius I), Hystaspes, who was born shortly before 565 BCE), son of Arsames (died ca. 520 BCE). They were directly related to the Achaemenid dynasty itself. The last member of the dynasty was Pharnabazus, son of Artabazus, Pharnabazus III. Before the Pharnacids, Mitrobates (ca. 525–522 BCE) had ruled Hellespontine Phrygia for Cyrus the Great and Cambyses II, before being killed and his territory absorbed by the satrap of Lydia, Oroetes. Following the reorganization of Darius I, Mitrobates was succeeded by Oebares II (c.493), son of Megabazus, before Artabazus became satrap circa 479 BCE and started the Pharnacid dynasty, which would rule Hellespontine Phrygia unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenian Empire
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (''Symmachia (alliance), symmachia'') of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies". While Sparta excelled as Greece's greatest power on land, Athens turned to the seas becoming the dominant naval power of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. Following Sparta's withdrawal from the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Persian Invasion Of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece (492–490 BC) at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes. The invasion began in spring 480 BC, when the Persian army crossed the Hellespont and marched through Thrace and Macedon to Thessaly. The Persian advance was blocked at the pass of Thermopylae by a small Allied force under King Leonidas I of Sparta; simultaneously, the Persian fleet was blocked by an Allied fleet at the straits of Artemisium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The Dodecanese, located to the southeast, includes the islands of Rhodes, Kos, and Patmos; the islands of Delos and Naxos are wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smerdis
Bardiya or Smerdis ( ; ; possibly died 522 BCE), also named as Tanyoxarces (; ) by Ctesias, was a son of Cyrus the Great and the younger brother of Cambyses II, both Persian kings. There are sharply divided views on his life. Bardiya either ruled the Achaemenid Empire for a few months in 522 BCE, or was impersonated by a magus called Gaumata ( ), whose name is given by Ctesias as Sphendadates (; ), until he was toppled by Darius the Great. Name and sources The prince's name is listed variously in the historical sources. In Darius the Great's Behistun inscription, his Persian name is Bardiya or Bardia. Herodotus calls him Smerdis, which is the prevalent Greek form of his name; the Persian name has been assimilated to the Greek (Asiatic) name ''Smerdis'' or ''Smerdies'', a name which also occurs in the poems of Alcaeus and Anacreon. Bardiya is called ''Tanyoxarces'' by Ctesias, who also names Gaumāta as ''Sphendadates'';Ctesias ''Persica'' 8 he is called ''Tanooxares'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius The Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West Asia, parts of the Balkans (Skudra, Thrace–Achaemenid Macedonia, Macedonia and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia) and the Caucasus, most of the Black Sea's coastal regions, Central Asia, the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, Indus Valley in the far east, and portions of North Africa and Northeast Africa including History of Persian Egypt, Egypt (), eastern ancient Libya, Libya, and coastal The Sudans, Sudan. Darius ascended the throne by overthrowing the Achaemenid monarch Bardiya (or ''Smerdis''), who he claimed was in fact an imposter named Gaumata. The new king met with rebellions throughout the empire but quelled each of them; a major event in Darius's life was his expedition to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otanes
Otanes (Old Persian: ''Utāna'', ) is a name given to several figures that appear in the ''Histories'' of Herodotus. One or more of these figures may be the same person. In the ''Histories'' Otanes, son of Pharnaspes He was regarded as a Persian nobleman, being among the few with highest ranks in the kingdom, who was also a political philosopher. ''Histories'' 3.68.1, 3.68.3, 3.69.6 has an Otanes as the son of the Achaemenid Pharnaspes, as the father of Phaidyme (or Phaedyma), who in turn is a wife of Cambyses II, and later a wife of the Gaumata alias Smerdis. Herodotus gives this Otanes a role in the overthrow of the false Smerdis, and ''this'' Otanes is therefore generally assumed to be identical to a known co-conspirator of Darius I, mentioned in Darius's own list of his helpers at overthrowing Gaumata (DB IV 83). The Behistun inscription has this Otanes as the son of Thukhra, in which case he could not have been the son of Pharnaspes, and so cannot have been a brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Nöldeke
Theodor Nöldeke (; born 2 March 1836 – 25 December 1930) was a German orientalist and scholar, originally a student of Heinrich Ewald. He is one of the founders of the field of Quranic studies, especially through his foundational work titled '' Geschichte des Qorāns'' (''History of the Quran'')''.'' His research interests also ranged over Old Testament studies, and his command of Semitic languages ranging across Arabic, Hebrew, Aramaic, Syriac, and Ethiopic allowed him to write hundreds of studies across a wide range of Oriental topics, including a number of translations, grammars, and works on literatures found in various languages. Among the projects Nöldeke collaborated on was Michael Jan de Goeje’s published edition of al-Tabari's ''Tarikh'' ("Universal History"), for which he translated the Sassanid-era section. This translation remains of great value, particularly for the extensive supplementary commentary. His numerous students included Charles Cutler Torrey, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barsine
Barsine (; c. 363–309 BC) was the daughter of a Persian father, Artabazus, satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia, and a Greek Rhodian mother, the sister of mercenaries Mentor of Rhodes and Memnon of Rhodes. Barsine became the wife of her uncle Mentor, and after his death married her second uncle, Memnon. In 334 BC, the year of Alexander's invasion of Asia, she and her children were sent by Memnon to the king Darius III as hostages for his fidelity; and in the ensuing year, when Damascus was betrayed to the Macedonians, she fell into the hands of Alexander, by whom it is said that she became the mother of Heracles. Twelve years after Alexander's death in 323, Nearchus, who was Barsine's son-in-law, unsuccessfully advocated for Heracles' claim to the throne, who was, then, seventeen, which meant he was born about five years after Barsine and Alexander supposedly met in Damascus, in 333 BC. From a comparison of the accounts of Diodorus and Justin, it appears that he was brou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |