|
Petrolia Oil Field (Texas)
Petrolia Oil Field is a North Texas segment of land located in Clay County, Texas and the Great Plains. The hydrocarbon exploration site was geographically within of the Red River of the South. The oil and gas reservoir was located between Texas State Highway 79 and Texas State Highway 148 converging at Petrolia, Texas. The sandstone geology was discovered in 1904 as having deposits of fossil fuels. On December 17, 1910, a crude oil deposit was struck at . The Dorthulia Dunn No. One blowout produced . The Clay County oil reservoir reached peak production in 1914 yielding . By 1915, the oil field had received national recognition as the first natural gas reservoir producing a light non-flammable inert gas known as helium. The Petrolia sandstone plain was the premier producer of helium culminating in the United States Bureau of Mines and United States Department of War constructing a helium extraction plant near Petrolia, Texas. Global Helium Demand and World War I The North Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bend Arch–Fort Worth Basin
The Bend Arch–Fort Worth Basin Province is a major petroleum producing geological system which is primarily located in North Central Texas and southwestern Oklahoma. It is officially designated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) as Province 045 and classified as the Barnett-Paleozoic Total Petroleum System (TPS). Introduction Oil and Natural gas, gas in Province 045 are produced from Carbonate rock, carbonate and clastic rock reservoirs ranging in age from the Ordovician to the Permian. The 1995 USGS Assessment of undiscovered, technically recoverable oil and gas identified six conventional plays in Province 045, which are listed below in Table 1:Ball, 1996 One continuous unconventional play, the "Mississippian age, Mississippian Barnett Shale" (4503), was also considered. The cumulative mean of undiscovered resource for conventional plays was: of oil, of natural gas liquids, associated gas, and non-associated gas. Table 1 Notes: 1. Assessment unit number also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands. In a valley, a plain is enclosed on two sides, but in other cases a plain may be delineated by a complete or partial ring of hills, by mountains, or by cliffs. Where a geological region contains more than one plain, they may be connected by a pass (sometimes termed a gap). Coastal plains mostly rise from sea level until they run into elevated features such as mountains or plateaus. Plains are one of the major landforms on earth, where they are present on all continents, and cover more than one-third of the world's land area. Plains can be formed from flowing lava; from deposition of sediment by water, ice, or wind; or formed by erosion by the agents from hills and mountains. Biomes on plains include grassland (temperate or subtropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
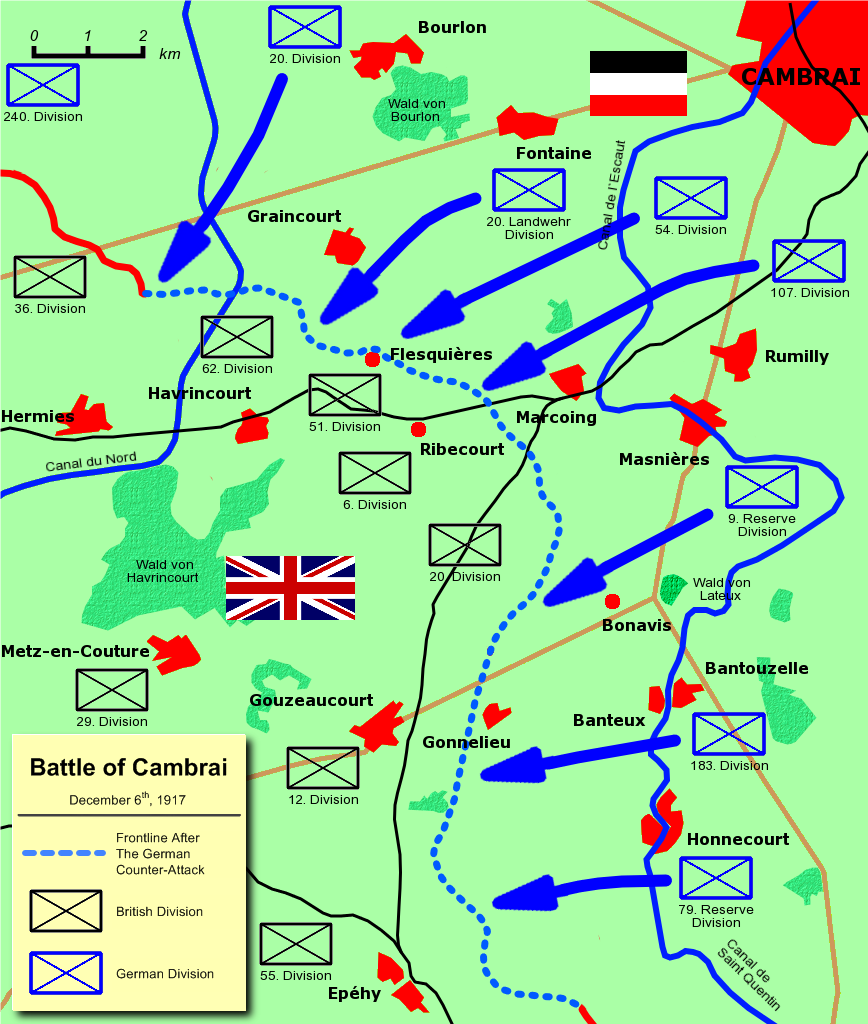
Counter-offensive
In the study of military tactics, a counter-offensive is a large-scale strategic offensive military operation, usually by forces that had successfully halted the enemy's offensive, while occupying defensive positions. The counter-offensive is executed after exhausting the enemy's front line troops and after the enemy reserves had been committed to combat and proven incapable of breaching defenses, but ''before'' the enemy has had the opportunity to assume new defensive positions. Sometimes the counter-offensive can be of a more limited operational maneuver nature, with more limited objectives rather than those seeking attainment of a strategic goal. A counter-offensive as considered by Clausewitz to be the most efficient means of forcing the attacker to abandon offensive plans.p.540, Briggs Counter-offensives can be executed not only on land, but also by the naval forces and air forces. Strategic counter-offensives have been recorded by military historians in many wars throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
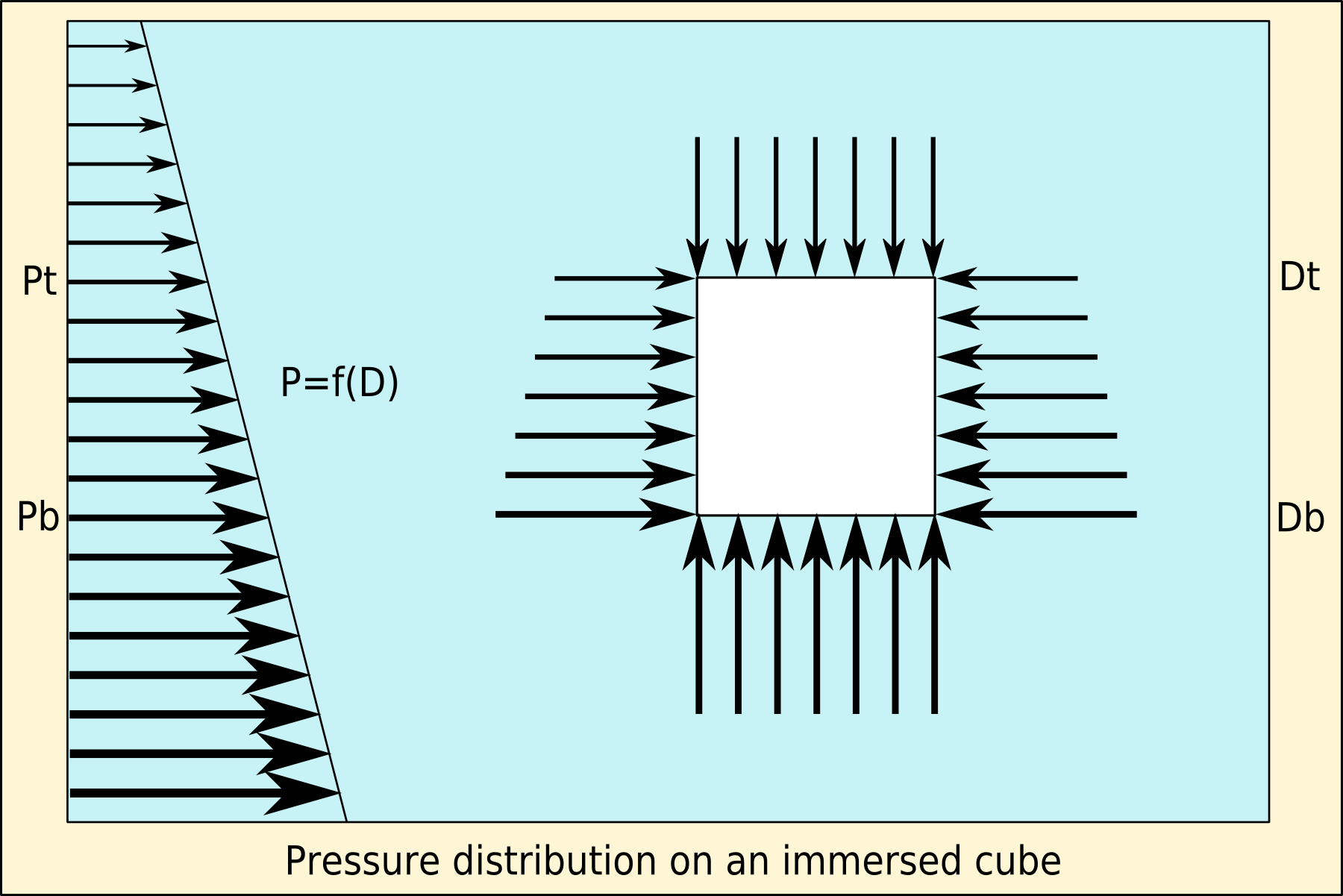
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifting Gas
A lifting gas or lighter-than-air gas is a gas that has a density lower than normal atmospheric gases and rises above them as a result. It is required for aerostats to create buoyancy, particularly in lighter-than-air aircraft, which include free balloons, moored balloons, and airships. Only certain lighter than air gases are suitable as lifting gases. Dry air has a density of about 1.29 g/L (gram per liter) at standard conditions for temperature and pressure (STP) and an average molecular mass of 28.97 g/mol, and so lighter-than-air gases have a density lower than this. Gases used for lifting Hot air Heated atmospheric air is frequently used in recreational ballooning. According to the Ideal gas law, an amount of gas (and also a mixture of gases such as air) expands as it is heated. As a result, a certain volume of gas has a lower density as the temperature is higher. The average temperature of air in a hot air balloon is about . Hydrogen Hydrogen, being the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, and their colonies during the First World War (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of France, Britain, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and after proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although France, Britain, Russia, and Italy were also referred to as the Quadruple Enten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Model
In economics, a model is a theoretical construct representing economic processes by a set of variables and a set of logical and/or quantitative relationships between them. The economic model is a simplified, often mathematical, framework designed to illustrate complex processes. Frequently, economic models posit structural parameters. A model may have various exogenous variables, and those variables may change to create various responses by economic variables. Methodological uses of models include investigation, theorizing, and fitting theories to the world. Overview In general terms, economic models have two functions: first as a simplification of and abstraction from observed data, and second as a means of selection of data based on a paradigm of econometric study. ''Simplification'' is particularly important for economics given the enormous complexity of economic processes. This complexity can be attributed to the diversity of factors that determine economic activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In macroeconomics, as well, the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model has been used to depict how the quantity of total output and the aggregate price level may be determined in equilibrium. Graphical representations Supply schedule A supply schedule, depicted graphically as a supply curve, is a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied by producers. Under the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World War I, World WarI (1914–1918) and World War II, World WarII (1939–1945), although historians have also described other global conflicts as world wars, such as the Seven Years' War and the Cold War. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' cited the first known usage in the English language to a Scotland, Scottish newspaper, ''The People's Journal'', in 1848: "A war among the great powers is now necessarily a world-war." The term "world war" is used by Karl Marx and his associate, Friedrich Engels, in a series of articles published around 1850 called ''The Class Struggles in France''. Rasmus B. Anderson in 1889 described an episode in Teutonic mythology as a "world war" (Swedish: ''världskrig''), justifying this description by a line in an O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six naturally occurring noble gases are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn). Oganesson (Og) is a synthetically produced highly radioactive element. Although IUPAC has used the term "noble gas" interchangeably with "group 18" and thus included oganesson, it may not be significantly chemically noble and is predicted to break the trend and be reactive due to relativistic effects. Because of the extremely short 0.7 ms half-life of its only known isotope, its chemistry has not yet been investigated. For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas State Historical Association
The Texas State Historical Association (TSHA) is a non-profit educational organization, dedicated to documenting the history of Texas. It was founded in Austin, Texas, on March 2, 1897. , TSHA moved their offices from Austin to the University of North Texas in Denton. In 2015, the offices were relocated again, to the University of Texas at Austin. Overview The chief executive officer is Jesús F. de la Teja and the chief historian is Walter L. Buenger. The association president (2018-2019) is Sarita Hixon; the preceding president is (2017-2018) Paula Mitchell Marks. Other past presidents include Steve Cook (2016-2017), Lynn Denton (2015-2016), John L. Nau III (2014-2015), Gregg Cantrell (2013-2014), Watson Arnold (2012-2013), Merline Pitre (2011-2012), Dianne Garrett Powell (2010–2011) and Walter L. Buenger (2009-2010). Other past presidents are the late Robert A. Calvert (1989–1990) of Texas A&M, Alwyn Barr (1992-1993) of Texas Tech University, and Jerry D. Thompson (2001– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |