|
Peter K. Homer
Peter K. Homer (born 1961) of Southwest Harbor, Maine, won $200,000 from NASA for his entry in the Astronaut Glove Challenge. The competition was held on Thursday, May 3, 2007, with a total of five teams competing (two of which dropped out prior the commencement of the competition), and was one of NASA's seven Centennial Challenges. The gloves were rated on strength, flexibility and comfort. Homer's glove design performed better overall than the competition and NASA hopes it will help improve future astronaut gloves. He was unemployed at the time of his victory. When performing a space walk, NASA astronauts use their hands as their primary way to move around and complete tasks. After many hours of working inside the pressurized gloves, the force required by the astronauts to move their fingers and wrists back and forth repeatedly often results in blisters, abrasions and damaged fingernails. New technologies would reduce discomfort and make the astronauts' jobs easier and safer. . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Harbor, Maine
Southwest Harbor is a town in Hancock County, Maine, United States. Located on Mount Desert Island, the population was 1,756 at the 2020 census. The municipality contains within it the villages of Southwest Harbor, Manset, Seawall, Wonderland, and Pemetic Hills. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , of which is land and is water. Demographics 2010 census As of the census of 2010, there were 1,764 people, 835 households, and 483 families living in the town. The population density was . There were 1,484 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the town was 97.3% White, 0.2% African American, 0.5% Native American, 0.3% Asian, 0.3% from other races, and 1.4% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.0% of the population. There were 835 households, of which 24.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 44.2% were married couples living together, 10.1% had a femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glove
A glove is a garment covering the hand. Gloves usually have separate sheaths or openings for each finger and the thumb. If there is an opening but no (or a short) covering sheath for each finger they are called fingerless gloves. Fingerless gloves having one small opening rather than individual openings for each finger are sometimes called gauntlets, though gauntlets are not necessarily fingerless. Gloves which cover the entire hand or fist but do not have separate finger openings or sheaths are called mittens. Mittens are warmer than other styles of gloves made of the same material because fingers maintain their warmth better when they are in contact with each other; reduced surface area reduces heat loss. A hybrid of glove and mitten contains open-ended sheaths for the four fingers (as in a fingerless glove, but not the thumb) and an additional compartment encapsulating the four fingers. This compartment can be lifted off the fingers and folded back to allow the individual fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centennial Challenges
The Centennial Challenges are NASA space competition inducement prize contests for non-government-funded technological achievements by American teams. Origin NASA's Centennial Challenge Program (CCP) directly engages the public at large in the process of advanced technology development that is of value to NASA's missions and to the aerospace community. CCP offers challenges set up as competitions that award prize money to the individuals or teams to achieve the specified technology challenge. The prize contests are named "Centennial" in honor of the 100 years since the Wright brothers' first flight in 1903. The Wright Brothers' pioneering inventions embody the spirit of the challenges. The Centennial Challenges are based on a long history of technology prize contests, including the Longitude prize (won by John Harrison), the Orteig Prize (won by Charles Lindbergh), the Ansari X PRIZE (won by Scaled Composites), and the DARPA Grand Challenge (won by Stanford University in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Walk
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes ''spacewalks'' and lunar or planetary surface exploration (commonly known from 1969 to 1972 as ''moonwalks''). In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVA has been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China. On March 18, 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to perform a spacewalk, exiting the Voskhod 2 capsule for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to perform a moonwalk, outside his lunar lander on Apollo 11 for 2 hours and 31 minutes. On the last three Moon missions, astronauts also performed deep-space EVAs on the return to Earth, to retrieve film ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
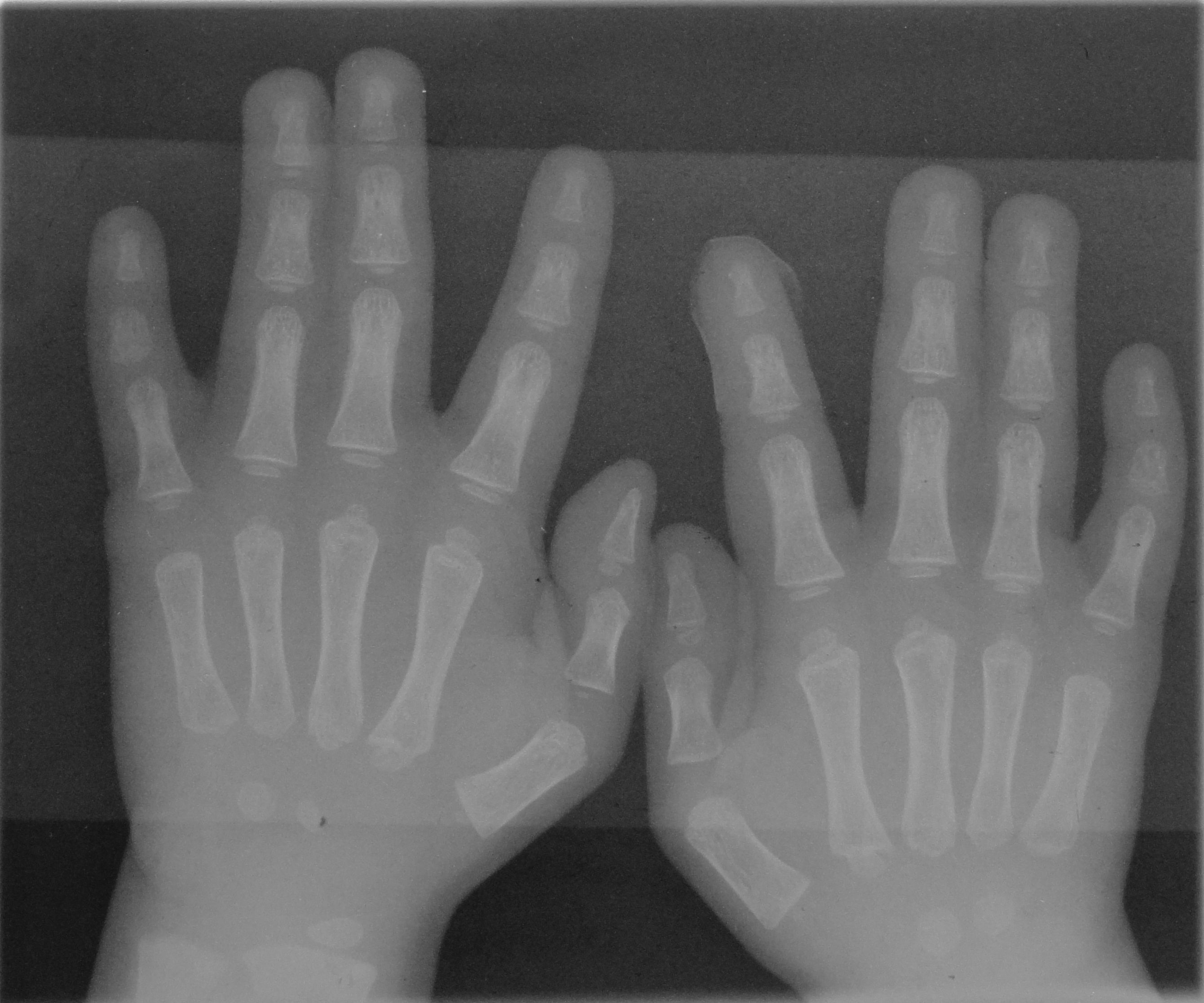
Hands
A hand is a prehensile, multi- fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: four fingers plus one thumb; these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, however, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly). Chambers 1998 p. 603 Oxford Illustrated pp. 311, 380 Land vertebrate fingers The five-rayed anterior limbs of terrestrial vertebrates can be derived phylogenetically from the pectoral fins of fish. Within the taxa of the terrestrial vertebrates, the basic pentadactyl plan, and thus also the fingers and phalanges, undergo many variations. Morphologically the different fingers of terrestrial vertebrates are homolog. The wings of birds and those of bats are not homologous, they are analogue flight organs. However, the phalanges within them are homologous. Chimpanzees have lower limbs that are specialized for manipulation, and (arguably) have fingers on their lower limbs as well. In the case of Primates in general, the digits of the hand a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrists
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingernails
A nail is a claw-like plate found at the tip of the fingers and toes on most primates. Nails correspond to the claws found in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called alpha-keratin, which is a polymer. Alpha-keratin is found in the hooves, claws, and horns of vertebrates. Structure The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. Parts of the nail The matrix, sometimes called the ''matrix unguis'', keratogenous membrane, nail matrix, or onychostroma, is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells, which harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate. It is the part of the nail bed that is beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph and blood vessels. The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail plate is determined by the size, length, and thickness of the matrix, while the shape of the fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Aerospace Engineers
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Mount Desert Island
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)




_1938.jpg)