|
Persian Language In India
Before British colonisation, the Persian language was the lingua franca of the Indian subcontinent and a widely used official language in the northern India. The language was brought into South Asia by various Turkics and Afghans and was preserved and patronized by local Indian dynasties from the 11th century, such as Ghaznavids, Sayyid dynasty, Tughlaq dynasty, Khilji dynasty, Mughal dynasty, Gujarat sultanate, and Bengal sultanate. Initially it was used by Muslim dynasties of India but later started being used by non-Muslim empires too. For example, the Sikh Empire, Persian held official status in the court and the administration within these empires. It largely replaced Sanskrit as the language of politics, literature, education, and social status in the subcontinent. The spread of Persian closely followed the political and religious growth of Islam in the Indian subcontinent. However Persian historically played the role of an overarching, often non-sectarian language connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. (subscription required) Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often also used interchangeably to denote a wider region which includes, in addition, Bhutan, the Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, the "Indian subcontinent" is more of a geophysical term, whereas "South Asia" is more geopolitical. "South Asia" frequently also includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent even in extended usage.Jim Norwine & Alfonso González, ''The Third World: states of mind and being'', pages 209, Taylor & Francis, 1988, Quote: ""The term "South Asia" also signifies the Indian Subcontinent""Raj S. Bhopal, ''Ethnicity, race, and health in multicultural societies'', pages 33, Oxford University Press, 2007, ; Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyid Dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See: * M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill * The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion into South Asia, Journal of South Asian Studies, 4(1), pp. 91–109 * Sookoohy M., Bhadreswar – Oldest Islamic Monuments in India, , Brill Academic; see discussion of earliest raids in Gujarat The first ruler of the dynasty, Khizr Khan, who was the Timurid vassal of Multan, conquered Delhi in 1414, while the rulers proclaimed themselves the Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate under Mubarak Shah, which succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled the Sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty in 1451. Origins A contemporary writer Yahya Sirhindi mentions in his ''Tarikh-i-Mubarak Shahi'' that Khizr Khan was a descendant of Muhammad. Members of the dynasty derived their title, Sayyid, or the descendants of the Islamic prophet Muh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Asian English
South Asian English, informally Desi English, refers to English dialects spoken in most modern-day South Asian countries, inherited from British English dialect. Also known as Anglo-Indian English during the British Raj, the English language was introduced to the Indian subcontinent in the early 17th century. Today it is spoken as a second language by about 350 million people, 20% of the total population. Although it is fairly homogeneous across the subcontinent, sharing "linguistic features and tendencies at virtually all linguistic levels", there are some differences based on various regional factors. South Asian English is sometimes just called "Indian English", as British India included most of modern-day South Asia (except Afghanistan). But today, the varieties of English are officially divided according to the modern states: * Bangladeshi English * Indian English * Maldivian English * Nepalese English * Pakistani English * Sri Lankan English History British India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajam
(, ) is an Arabic word for a non-Arab, especially a Persian. It was historically used as a pejorative—figuratively ascribing muteness to those whose native language is not Arabic—during and after the Muslim conquest of Iran. Since the early Muslim conquests, it has been adopted in various non-Arabic languages, such as Turkish, Azerbaijani, Chechen, Kurdish, Malay, Sindhi, Urdu, Bengali, Punjabi, Kashmiri, and Swahili. Today, the terms and continue to be used to refer to anyone or anything Iranian, particularly in the Arab countries of the Persian Gulf. Communities speaking the Persian language in the Arab world exist among the Iraqis, the Kuwaitis, and the Bahrainis, in addition to others. A number of Arabs with Iranian heritage may have the surname (), which has the same meaning as the original word. Etymology According to traditional etymology, the word ''Ajam'' comes from the Semitic root ''ʿ-j-m''. Related forms of the same root include, but are not l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Iran
Greater Iran or Greater Persia ( ), also called the Iranosphere or the Persosphere, is an expression that denotes a wide socio-cultural region comprising parts of West Asia, the South Caucasus, Central Asia, South Asia, and East Asia (specifically the Tarim Basin)—all of which have been affected, to some degree, by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian languages. It is defined by having long been ruled by the dynasties of various Iranian empires, under whom the local populaces gradually incorporated some degree of Iranian influence into their cultural and/or linguistic traditions; or alternatively as where a considerable number of Iranians settled to still maintain communities who patronize their respective cultures, geographically corresponding to the areas surrounding the Iranian plateau. It is referred to as the "Iranian Cultural Continent" by ''Encyclopædia Iranica''. Throughout the 16th–19th centuries, Iran lost many of the territories that had been conquered under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In South Asia
Islam is the second-largest religion in South Asia, with more than 650 million Muslims living there, forming about one-third of the region's population. Islam first spread along the coastal regions of the Indian subcontinent and Sri Lanka, almost as soon as it started in the Arabian Peninsula, as the Arab traders brought it to South Asia. South Asia has the largest population of Muslims in the world, with about one-third of all Muslims living here. Islam is the dominant religion in half of the South Asian countries (Pakistan, Maldives, Bangladesh and Afghanistan). It is the second largest religion in India and third largest in Sri Lanka and Nepal. On the Indian subcontinent, Islam first appeared in the southwestern tip of the peninsula, in today's Kerala state. Arabs traded with Malabar even before the birth of Prophet Muhammad. Native legends say that a group of Sahaba, under Malik Ibn Deenar, arrived on the Malabar Coast and preached Islam. According to that legend, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
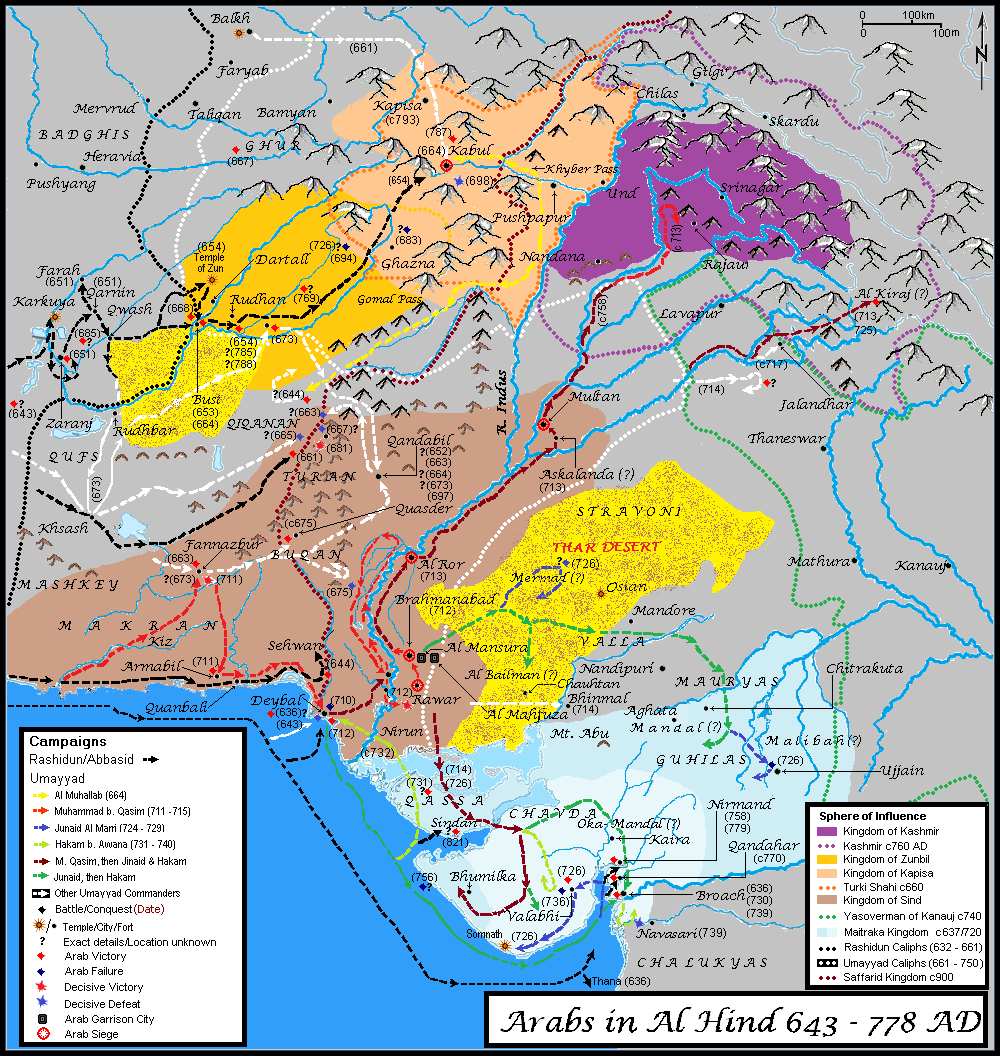
Muslim Conquests In The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place between the 13th and the 18th centuries, establishing the Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Indo-Muslim period. Early Muslim conquests, Earlier Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent include the invasions which started in the Northwest India (pre-1947), northwestern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Pakistan), especially the Umayyad campaigns in India, Umayyad campaigns during the 8th century. Mahmud of Ghazni, sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid caliph, Abbasid Caliphate and invaded vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat during the 11th century. After the capture of Siege of Lahore (1186), Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim rule in India in 1192. In 1202, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, British East India Company following the Second Anglo-Sikh War. At its peak in the mid-19th century the empire extended from Gilgit and Tibet under Qing rule, Tibet in the north to the Thar Desert, deserts of Sindh in the south and from the Khyber Pass in the west to the Sutlej in the east, and was divided into eight provinces. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 4.5 million in 1831 (making it the List of countries by population in 1800, 19th most populous state at the time), it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Raj, British Empire. In 1799, Ranjit Singh of Sukerchakia Misl captured Lahore from the Sikh triumvirate which had been ruling it Sikh period in Lahore#Sikh triumvirate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Sultanate
The Bengal Sultanate (Middle Bengali: , Classical Persian: ) was a Post-classical history, late medieval sultanate based in the Bengal region in the eastern South Asia between the 14th and 16th century. It was the dominant power of the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states in the Indian subcontinent, including parts of Odisha in the southwest, parts of Bihar in the northwest, parts of Assam in the northeast, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the eastern South Asia during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah. Its raids and conquests reached Kingdom of Nepal, Nepal in the north, Brahmaputra valley (modern-day Assam) in the east, and Jaunpur Sultanate, Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Sur Empire, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat Sultanate
The Gujarat Sultanate or Sultanate of Gujarat was a late medieval Islamic Indian kingdom in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat. The kingdom was established in 1394 when Muzaffar Shah I, the Governor of Gujarat, declared independence from the Tughlaq dynasty of Delhi. Following Timur's invasion of the Delhi Sultanate, Delhi was devastated and its rule weakened considerably, leading Muzaffar Shah to declare himself independent in 1394, and formally established the Sultanate in Gujarat. The next sultan, his grandson Ahmad Shah I, moved the capital to Ahmedabad in 1411. His successor Muhammad Shah II subdued most Rajput chieftains. The prosperity of the sultanate reached its zenith during the rule of Mahmud Begada. He also subdued most Gujarati Rajput chieftains and built a navy off the coast of Diu. In 1509, the Portuguese Empire wrested Diu from the Sultanate in the Battle of Diu (1509). The Mughal emperor Humayun attacked Gujarat in 1535 and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |