|
Perpetual Bond
A perpetual bond, also known colloquially as a perpetual or perp, is a bond with no maturity date, therefore allowing it to be treated as equity, not as debt. Issuers pay coupons on perpetual bonds forever, and they do not have to redeem the principal. Perpetual bond cash flows are, therefore, those of a perpetuity. Perpetual bonds vs. equity * Although similar to equity, perpetual bonds do not have attached votes and, therefore, provide no means of control over the issuer. * Perpetual bonds are still fixed-income securities; therefore, paying coupons is mandatory whereas paying dividends on equity is discretionary. Examples * Consols that were issued by the United States and the UK governments. * War bonds issued by a number of governments to finance war efforts in the first and second world wars. * The oldest example of a perpetual bond was issued on 15 May 1624 by the Dutch water board of Lekdijk Bovendams and sold to Elsken Jorisdochter. Only about five such bonds from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a type of Security (finance), security under which the issuer (debtor) owes the holder (creditor) a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to provide cash flow to the creditor (e.g. repay the principal (i.e. amount borrowed) of the bond at the Maturity (finance), maturity date and interest (called the coupon (bond), coupon) over a specified amount of time.) The timing and the amount of cash flow provided varies, depending on the economic value that is emphasized upon, thus giving rise to different types of bonds. The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods. Thus, a bond is a form of loan or IOU. Bonds provide the borrower with external funds to finance long-term investments or, in the case of government bonds, to finance current expenditure. Bonds and Share capital, stocks are both Security (finance), securities, but the major difference between the two is that (capital) stockholders h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geert Rouwenhorst
K. Geert Rouwenhorst is a Dutch-American investor and professor of finance. He was hired at Yale University in 1990. In 2012, he was appointed the Robert B. and Candice J. Haas Professor at Yale School of Management and deputy director for International Financial Center at Yale. His work has traced the history of mutual funds through 18th century Netherlands. The International Financial Center at Yale also holds the oldest non-defaulted bond in the world. His work with Gary B. Gorton circa 2012 has been influential in establishing the idea of commodities as an asset class and has fueled the rise of commodity indices and exchange-traded funds. He has studied the relative performance of futures and the underlying commodities. Rouwenhorst is also a partner at SummerHaven Investment management, a smaller firm which focuses on commodities. Degrees *Ph.D. University of Rochester, 1991 *MS University of Rochester, 1988 *BLaw Erasmus University Rotterdam Erasmus University Rotte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpetual Subordinated Debt
Perpetual subordinated debt is subordinated debt in the form of a bond with no maturity date for the return of principal. Such a perpetual bond means it never needs to be redeemed by the issuer, and thus pay coupon interest continually until bought back (hence, "perpetual"). Like other subordinated debt, it has claims after senior debt (hence "subordinated") in the event of default. Perpetual subordinated debt is not "straight debt", rather it is close to, or in some cases identical to, preferred shares, paying a fixed-rate coupon similar to preferred shares' fixed-rate dividend. Perpetual debt comes in two types: cumulative and noncumulative. Interest on cumulative perpetual debt accrues if payments are missed. For noncumulative perpetual debt, if payments are missed, they do not accrue and the cash flow is lost.Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms, p. 529 Noncumulative perpetual debt is almost identical to typical preferred shares (most of which are noncumulative), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Bond
A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of Bond (finance), bond issued by a government to support government spending, public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called Coupon (finance), coupon payments'','' and to repay the face value on the Maturity (finance), maturity date. For example, a bondholder invests $20,000, called face value or principal, into a 10-year government bond with a 10% annual coupon; the government would pay the bondholder 10% interest ($2000 in this case) each year and repay the $20,000 original face value at the date of maturity (i.e. after 10 years). Government bonds can be denominated in a foreign currency or the government's domestic currency. Countries with less stable economies tend to denominate their bonds in the currency of a country with a more stable economy (i.e. a hard currency). All government bonds carry Default (finance), default risk; that is, the possibility that the government will be unable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Income
Fixed income refers to any type of investment under which the borrower or issuer is obliged to make payments of a fixed amount on a fixed schedule. For example, the borrower may have to pay interest at a fixed rate once a year and repay the principal amount on maturity. Fixed-income securities (more commonly known as bonds) can be contrasted with equity securities (often referred to as stocks and shares) that create no obligation to pay dividends or any other form of income. Bonds carry a level of legal protections for investors that equity securities do not: in the event of a bankruptcy, bond holders would be repaid after liquidation of assets, whereas shareholders with stock often receive nothing. For a company to grow its business, it often must raise money – for example, to finance an acquisition; buy equipment or land, or invest in new product development. The terms on which investors will finance the company will depend on the risk profile of the company. The company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security (finance)
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any form of financial instrument, even though the underlying legal and regulatory regime may not have such a broad definition. In some jurisdictions the term specifically excludes financial instruments other than equity and fixed income instruments. In some jurisdictions it includes some instruments that are close to equities and fixed income, e.g., equity warrants. Securities may be represented by a certificate or, more typically, they may be "non-certificated", that is in electronic ( dematerialized) or " book entry only" form. Certificates may be ''bearer'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights under the security merely by holding the security, or ''registered'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights only if they appear on a securi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
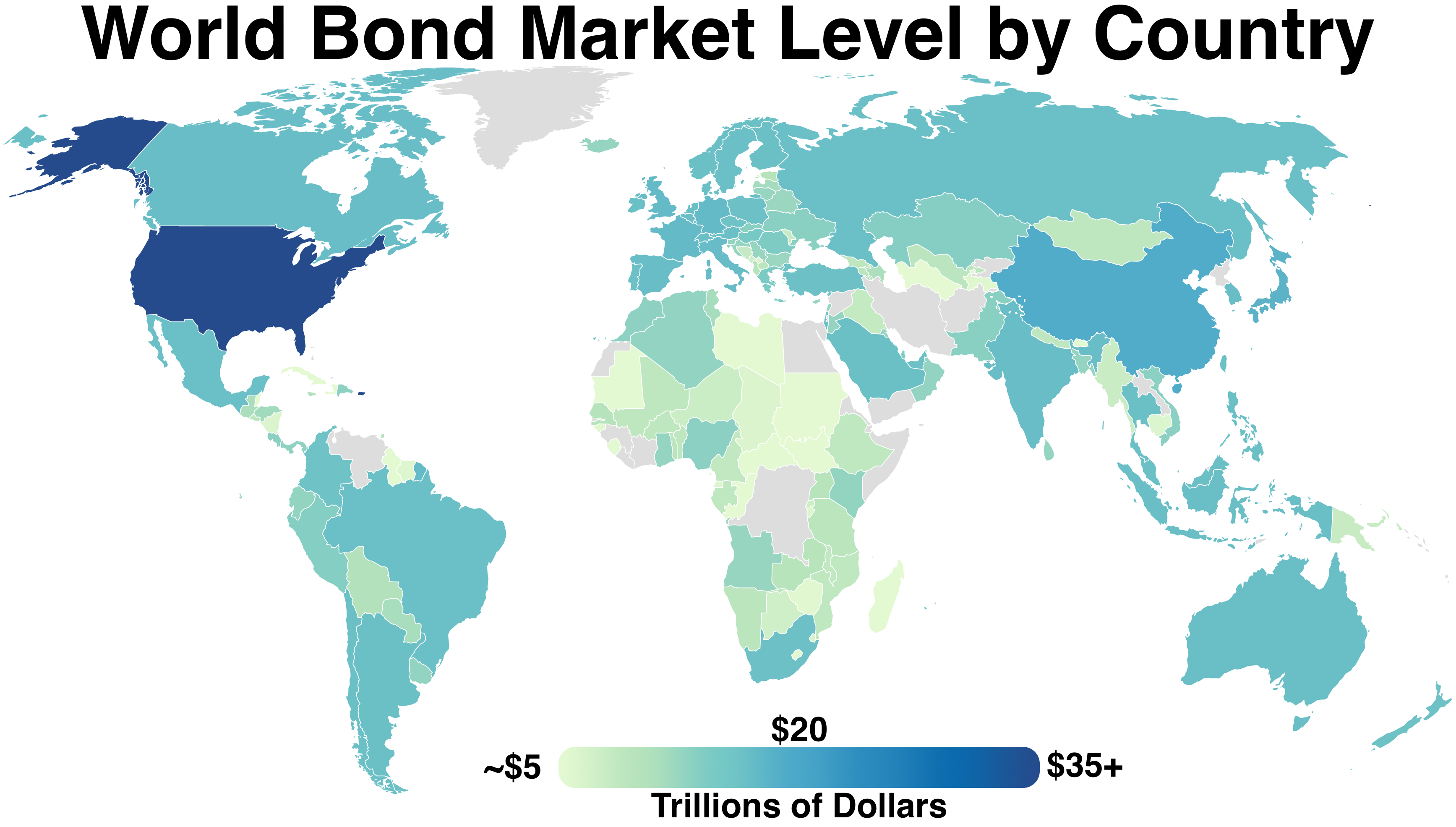
Bond Market
The bond market (also debt market or credit market) is a financial market in which participants can issue new debt, known as the primary market, or buy and sell debt security (finance), securities, known as the secondary market. This is usually in the form of bond (finance), bonds, but it may include notes, bills, and so on for public and private expenditures. The bond market has largely been dominated by the United States, which accounts for about 39% of the market. In 2021, the size of the bond market (total debt outstanding) was estimated to be $119 Trillion (short scale), trillion worldwide and $46 trillion for the US market, according to the Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association (SIFMA). Bonds and bank loans form what is known as the ''credit market''. The global credit market in aggregate is about three times the size of the global equity market. Bank loans are not securities under the U.S. Securities and Exchange Act, but bonds typically are and are therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callable Bond
A callable bond (also called redeemable bond) is a type of bond ( debt security) that allows the issuer of the bond to retain the privilege of redeeming the bond at some point before the bond reaches its date of maturity. In other words, on the call date(s), the issuer has the right, but not the obligation, to buy back the bonds from the bond holders at a defined call price. Technically speaking, the bonds are not really bought and held by the issuer but are instead cancelled immediately. The call price will usually exceed the par or issue price. In certain cases, mainly in the high-yield debt market, there can be a substantial call premium. Thus, the issuer has an option which it pays for by offering a higher coupon rate. If interest rates in the market have gone down by the time of the call date, the issuer will be able to refinance its debt at a cheaper level and so will be incentivized to call the bonds it originally issued. Another way to look at this interplay is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Requirements
A capital requirement (also known as regulatory capital, capital adequacy or capital base) is the amount of capital a bank or other financial institution has to have as required by its financial regulator. This is usually expressed as a capital adequacy ratio of equity as a percentage of risk-weighted assets. These requirements are put into place to ensure that these institutions do not take on excess leverage and risk becoming Insolvency, insolvent. Capital requirements govern the ratio of equity to debt, recorded on the liabilities and equity side of a firm's balance sheet. They should not be confused with reserve requirements, which govern the assets side of a bank's balance sheet—in particular, the proportion of its assets it must hold in cash or highly-liquid assets. Capital is a source of funds, not a use of funds. From the 1880s to the end of the First World War, the capital-to-assets ratios globally declined sharply, before remaining relatively steady during the 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tier 1 Capital
Tier 1 capital is the core measure of a bank's financial strength from a regulator's point of view.By definition of Bank for International Settlements. It is composed of ''core capital'', which consists primarily of common stock and disclosed reserves (or retained earnings), but may also include non-redeemable non-cumulative preferred stock as well as physical gold held in vaults. The Basel Committee also observed that banks have used innovative instruments over the years to generate Tier 1 capital; these are subject to stringent conditions and are limited to a maximum of 15% of total Tier 1 capital. This part of the Tier 1 capital will be phased out during the implementation of Basel III. Capital in this sense is related to, but different from, the accounting concept of shareholders' equity. Both Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital were first defined in the Basel I capital accord and remained substantially the same in the replacement Basel II accord. Tier 2 capital represents " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuiver
The stuiver was a coin used in the Netherlands, worth of a guilder (16 ''penning'' or 8 '' duit'', later 5 cents). It was also minted on the Lower Rhine region and the Dutch colonies. The word can still refer to the 5 euro cent coin, which has almost exactly the same diameter and colour despite being over twice the value of the older coin. Netherlands The ''Stüber'' emerged from the ''vierlander'' ("coin of four provinces"), that Philip III of Burgundy had minted from 1434 as a common denomination for Brabant, Flanders, Holland and the Hainault (''Hennegau'') and which had a value of Rhenish ''gulden''. It corresponded to 3 Brabant ''Plakken'', 2 Flemish '' Groten'', 16 Dutch ''pfennigs'' or 1 Artesian ''schilling''. The name "stuiver" derives from the Dutch ''stuiven'' ("flying sparks"), since on early Flemish ''stuivers'' "spark-producing flints of the Collar of the Golden Fleece" were depicted. Twenty stuivers equalled a ''Dutch Guilder.'' It circulated until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |