|
Perovskite Nanocrystal
Perovskite nanocrystals are a class of semiconductor nanocrystals, which exhibit unique characteristics that separate them from traditional quantum dots. Perovskite nanocrystals have an ABX3 composition where A = cesium, methylammonium (MA), or formamidinium (FA); B = lead or tin; and X = chloride, bromide, or iodide. Their unique qualities largely involve their unusual band-structure which renders these materials effectively defect tolerant or able to emit brightly without surface passivation. This is in contrast to other quantum dots such as CdSe which must be passivated with an epitaxially matched shell to be bright emitters. In addition to this, lead-halide perovskite nanocrystals remain bright emitters when the size of the nanocrystal imposes only weak quantum confinement. This enables the production of nanocrystals that exhibit narrow emission linewidths regardless of their polydispersity. The combination of these attributes and their easy-to-perform synthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminescent Cesium Lead Halide Nanocrystals
Luminescence is spontaneous emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; or "cold light". It is thus a form of cold-body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a substance as a result of heating. Historically, radioactivity was thought of as a form of "radio-luminescence", although it is today considered to be separate since it involves more than electromagnetic radiation. The dials, hands, scales, and signs of aviation and navigational instruments and markings are often coated with luminescent materials in a process known as "luminising". Types The following are types of luminescence: *Chemiluminescence, the emission of light as a result of a chemical reaction **Bioluminescence, a result of biochemical reactions in a living organism ** Electrochemiluminescence, a result of an electrochemical reaction ** Lyolumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoluminescence
Photoluminescence (abbreviated as PL) is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). It is one of many forms of luminescence (light emission) and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photons that excite electrons to a higher energy level in an atom), hence the prefix ''photo-''. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductorsHayes, G.R.; Deveaud, B. (2002). "Is Luminescence from Quantum Wells Due to Excitons?". ''Physica Status Solidi A'' 190 (3): 637–640doi:10.1002/1521-396X(200204)190:33.0.CO;2-7/ref> up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours. Observation of photoluminescence at a certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Mass (solid-state Physics)
In solid state physics, a particle's effective mass (often denoted m^*) is the mass that it ''seems'' to have when responding to forces, or the mass that it seems to have when interacting with other identical particles in a thermal distribution. One of the results from the band theory of solids is that the movement of particles in a periodic potential, over long distances larger than the lattice spacing, can be very different from their motion in a vacuum. The effective mass is a quantity that is used to simplify band structures by modeling the behavior of a free particle with that mass. For some purposes and some materials, the effective mass can be considered to be a simple constant of a material. In general, however, the value of effective mass depends on the purpose for which it is used, and can vary depending on a number of factors. For electrons or electron holes in a solid, the effective mass is usually stated as a factor multiplying the rest mass of an electron, ''m'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Lifetime
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda) is a positive rate called the exponential decay constant, disintegration constant, rate constant, or transformation constant: :\frac = -\lambda N. The solution to this equation (see derivation below) is: :N(t) = N_0 e^, where is the quantity at time , is the initial quantity, that is, the quantity at time . Measuring rates of decay Mean lifetime If the decaying quantity, ''N''(''t''), is the number of discrete elements in a certain set, it is possible to compute the average length of time that an element remains in the set. This is called the mean lifetime (or simply the lifetime), where the exponential time constant, \tau, relates to the decay rate constant, λ, in the following way: :\tau = \frac. The mean lifetime can be looked at as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric field. There is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility. The term carrier mobility refers in general to both electron and hole mobility. Electron and hole mobility are special cases of electrical mobility of charged particles in a fluid under an applied electric field. When an electric field ''E'' is applied across a piece of material, the electrons respond by moving with an average velocity called the drift velocity, v_d. Then the electron mobility ''μ'' is defined as v_d = \mu E. Electron mobility is almost always specified in units of cm2/( V⋅ s). This is different from the SI unit of mobility, m2/( V⋅ s). They are related by 1 m2/(V⋅s) = 104 cm2/(V⋅s). Conductivity is proportional to the product of mobility and carrier concentration. For example, the same conductivity could come from a small numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Yield
The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system. Applications Fluorescence spectroscopy The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.Lakowicz, Joseph R. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers 1999) p.10. Fluorescence quantum yield is measured on a scale from 0 to 1.0, but is often represented as a percentage. A quantum yield of 1.0 (100%) describes a process where each photon absorbed results in a photon emitted. Substances with the largest quantum yields, such as rhodamines, display the brightest emissions; however, compounds with quantum yields of 0.10 are still considered quite fluorescent. Quantum yield is defined by the fraction of excited state fluorophores that decay through fluorescence: where \Phi_ is the fluorescence quantum yield, k_ is the rate constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
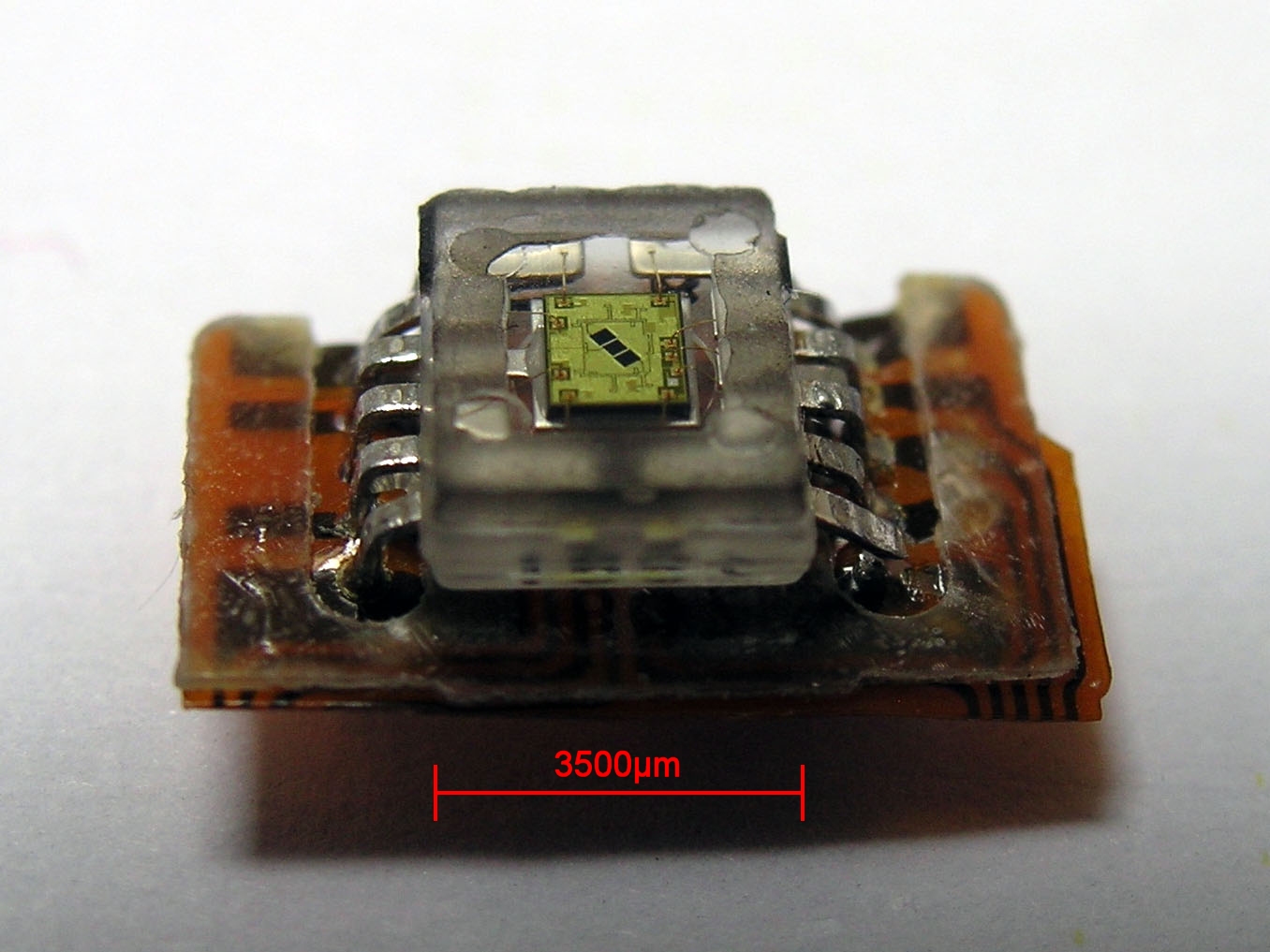
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lower bands, inducing ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanocrystal Solar Cell
Nanocrystal solar cells are solar cells based on a substrate with a coating of nanocrystals. The nanocrystals are typically based on silicon, CdTe or CIGS and the substrates are generally silicon or various organic conductors. Quantum dot solar cells are a variant of this approach, but take advantage of quantum mechanical effects to extract further performance. Dye-sensitized solar cells are another related approach, but in this case the nano-structuring is part of the substrate. Previous fabrication methods relied on expensive molecular beam epitaxy processes, but colloidal synthesis allows for cheaper manufacture. A thin film of nanocrystals is obtained by a process known as " spin-coating". This involves placing an amount of the quantum dot solution onto a flat substrate, which is then rotated very quickly. The solution spreads out uniformly, and the substrate is spun until the required thickness is achieved. Quantum dot based photovoltaic cells based on dye-sensitized collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Wireless Communications
Optical wireless communications (OWC) is a form of optical communication in which unguided visible, infrared (IR), or ultraviolet (UV) light is used to carry a signal. It is generally used in short-range communication. OWC systems operating in the visible band (390–750 nm) are commonly referred to as visible light communication (VLC). VLC systems take advantage of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) which can be pulsed at very high speeds without noticeable effect on the lighting output and human eye. VLC can be possibly used in a wide range of applications including wireless local area networks, wireless personal area networks and vehicular networks, among others. On the other hand, terrestrial point-to-point OWC systems, also known as the free space optical (FSO) systems, operate at the near IR frequencies (750–1600 nm). These systems typically use laser transmitters and offer a cost-effective protocol-transparent link with high data rates, i.e., 10 Gbit/s per wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)