|
Perneb
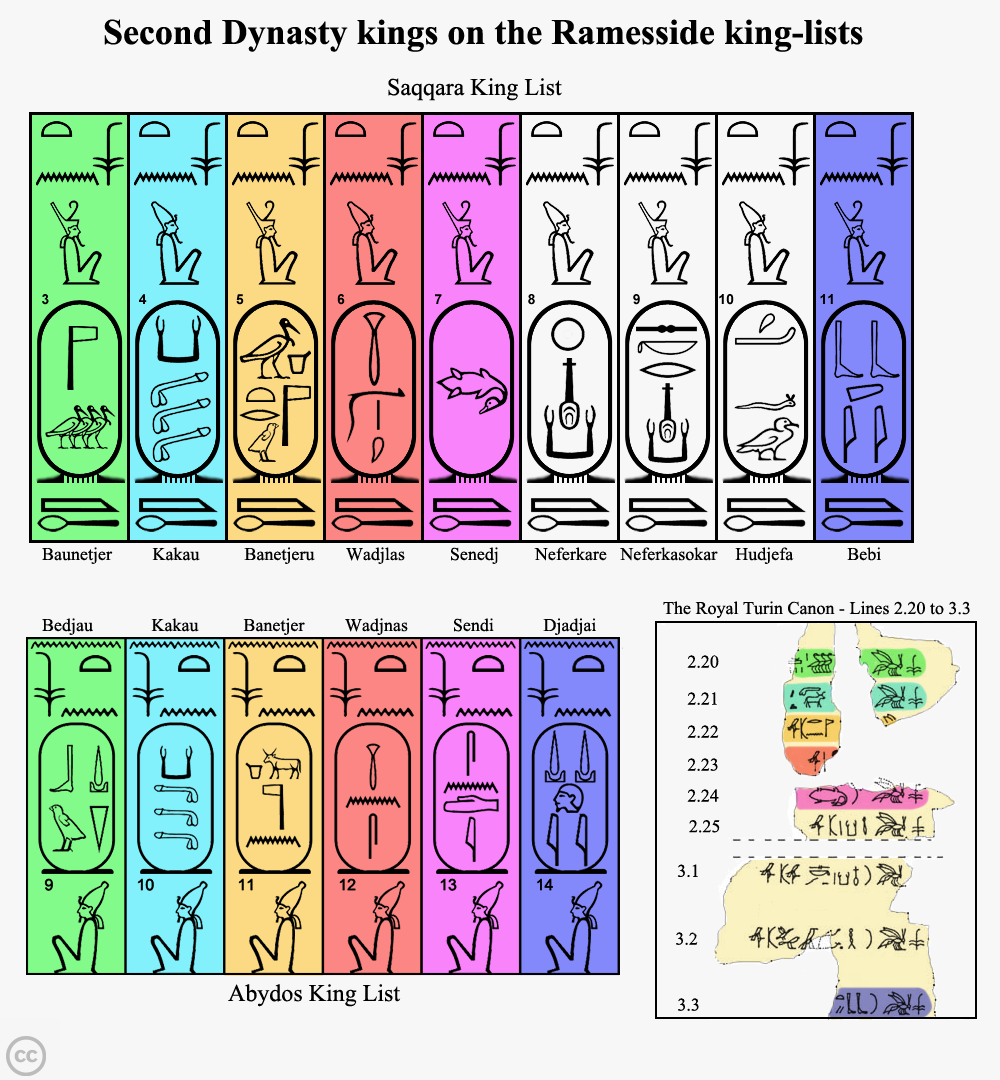
Perneb is the name of an ancient Egyptian prince and priest, who lived at the beginning of the 2nd Dynasty. Identity Perneb's name is preserved on several clay seals found in the gallery tomb A at Saqqara, which is attributed to two kings (pharaohs) at the same time (king Hotepsekhemwy and king Raneb). This circumstance lead to disputes about the family origin of Perneb; it cannot be said for sure whose son he exactly was. Perneb became known for a very rare and unusual title: he was ''priest of Sopdu'', a deity which was rarely named in early Egypt. His cult center was somewhere in the eastern Nile Delta The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ... at a city called ''Iptjw''. The exact geographical position of this town is not known. It is also unknown where Perneb was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotepsekhemwy
Hotepsekhemwy is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who was the founder of the Second Dynasty of Egypt. The exact length of his reign is not known; the Turin canon suggests an improbable 95 yearsAlan H. Gardiner: ''The royal canon of Turin''. Griffith Institute of Oxford, Oxford (UK) 1997, ; page 15 & Table I. while the ancient Egyptian historian Manetho reports that the reign of "Boëthôs" lasted for 38 years.William Gillian Waddell: ''Manetho (The Loeb Classical Library, Volume 350)''. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (Mass.) 2004 (Reprint), , page 37–41. Egyptologists consider both statements to be misinterpretations or exaggerations. They credit Hotepsekhemwy with either a 25- or a 29-year rule. Name sources Hotepsekhemwy's name has been identified by archaeologists at Sakkara, Giza, Badari and Abydos from clay seal impressions, stone vessels and bone cylinders. Several stone vessel inscriptions mention Hotepsekhemwy along with the name of his successor Ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raneb
Nebra or Raneb is the Horus name of the second early Egyptian king of the 2nd Dynasty. The exact length of his reign is unknown since the Turin canon is damaged and the year accounts are lost.Alan H. Gardiner: ''The royal canon of Turin''. Griffith Institute of Oxford, Oxford (UK) 1997, ; page 15 & Table I. Manetho suggests that Nebra's reign lasted 39 years, but Egyptologists question Manetho's view as a misinterpretation or exaggeration of information that was available to him. They credit Nebra with either a 10- or 14-year rule. Attestations Nebra's name appears on several stone vessels, mostly made of schist, alabaster and marble. Most of the bowls were found at Abydos, Giza and Saqqara. The inscriptions contain depictions of cultic buildings such as the ''Ka''-house, depictions of deities such as Bastet, Neith and Seth and also the mentionings of cultic feasts. All found objects present Nebra's name either together with that of his predecessor Hotepsekhemwy or with hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince
A prince is a Monarch, male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary title, hereditary, in some European State (polity), states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English language, English word derives, via the French language, French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble monarch, ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first [place/position]"), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to Roman Empire, empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not Dominate, dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the 'priesthood', a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred texts and keep temple or church rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Dynasty Of Egypt
The Second Dynasty of ancient Egypt (or Dynasty II, c. 2890 – c. 2686 BC) is the latter of the two dynasties of the Egyptian Archaic Period, when the seat of government was centred at Thinis. It is most known for its last ruler, Khasekhemwy, but is otherwise one of the most obscure periods in Egyptian history. Though archaeological evidence of the time is very scant, contrasting data from the First and Third Dynasties indicates important institutional and economic developments during the Second Dynasty. Rulers For the first three pharaohs, sources are fairly close in agreement and the order is supported by an inscription on the statuette of Hetepdief, who served in the mortuary cults of these three kings. But the identity of the next few rulers is unclear. Surviving sources might be giving the Horus name or the Nebty name and the birth names of these rulers. They may also be entirely different individuals, or could be legendary names. This might never be re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopdu
Sopdu (also rendered Septu or Sopedu) was a god of the sky and of eastern border regions in the religion of Ancient Egypt.Wilkinson, Richard H. (2003). ''The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt''. Thames & Hudson. p. 211 He was Khensit's husband. As a sky god, Sopdu was connected with the god Sah, the personification of the constellation Orion, and the goddess Sopdet, representing the star Sirius. According to the Pyramid Texts, Horus-Sopdu, a combination of Sopdu and the greater sky god Horus, is the offspring of Osiris-Sah and Isis-Sopdet. As a god of the east, Sopdu was said to protect Egyptian outposts along the frontiers and to help the pharaoh control those regions' foreign inhabitants. He was referred to as ''Lord of the East'', and had his greatest cult centre at the easternmost nome of Lower Egypt, which was named Per-Sopdu, meaning ''place of Sopdu''. He also had shrines at Egyptian settlements in the Sinai Peninsula, such as the turquoise mines at Serabit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Delta
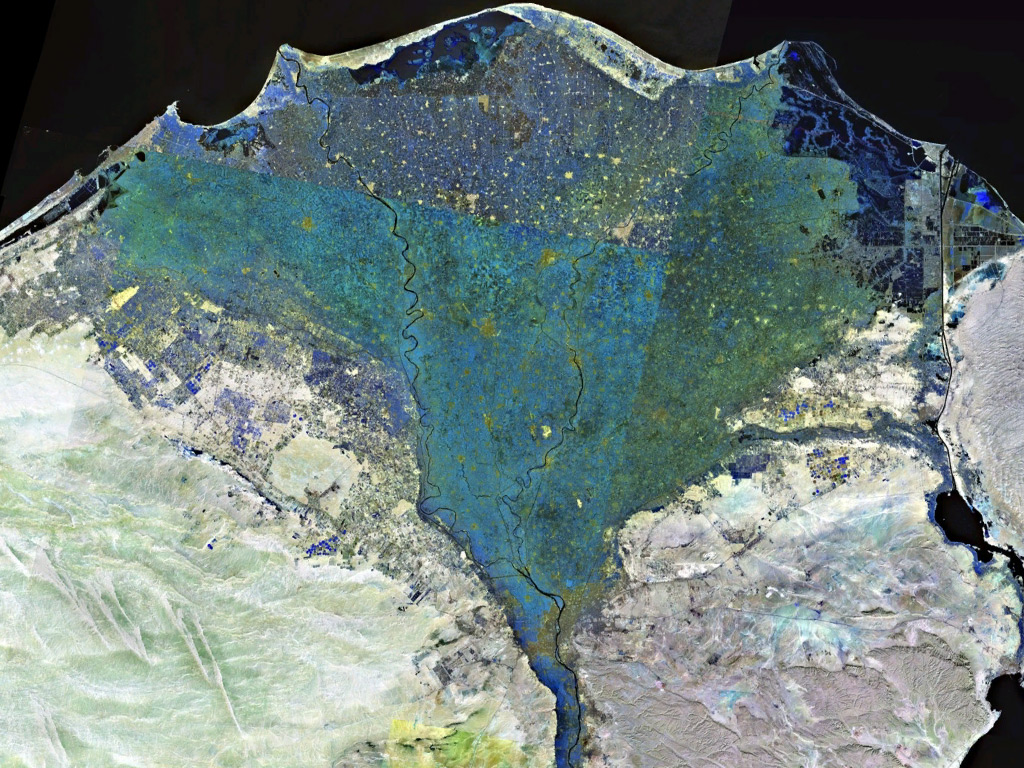
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kaplony
Peter Árpád Kaplony (June 15, 1933 in Budapest – February 11, 2011 in Zurich) was a Hungarian-born Swiss egyptologist. Life Kaplony, son of a Hungarian military officer, emigrated to Switzerland as a child in December 1944. He became a Swiss citizen in 1958. He studied Ancient History, Egyptology, Arabic language and Arabic literature in the University of Zurich and University of Basel. He participated in the excavations of the Sun temple of Userkaf in Abusir from 1954 until 1957 with a joint Swiss and German team of archeologists. In 1959, he was awarded the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Zurich and, in 1964, his Habilitation Habilitation is the highest university degree, or the procedure by which it is achieved, in many European countries. The candidate fulfills a university's set criteria of excellence in research, teaching and further education, usually including .... From 1970 until his retirement in 2000, Kaplony was assistant professor and then professor emer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Princes
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |