|
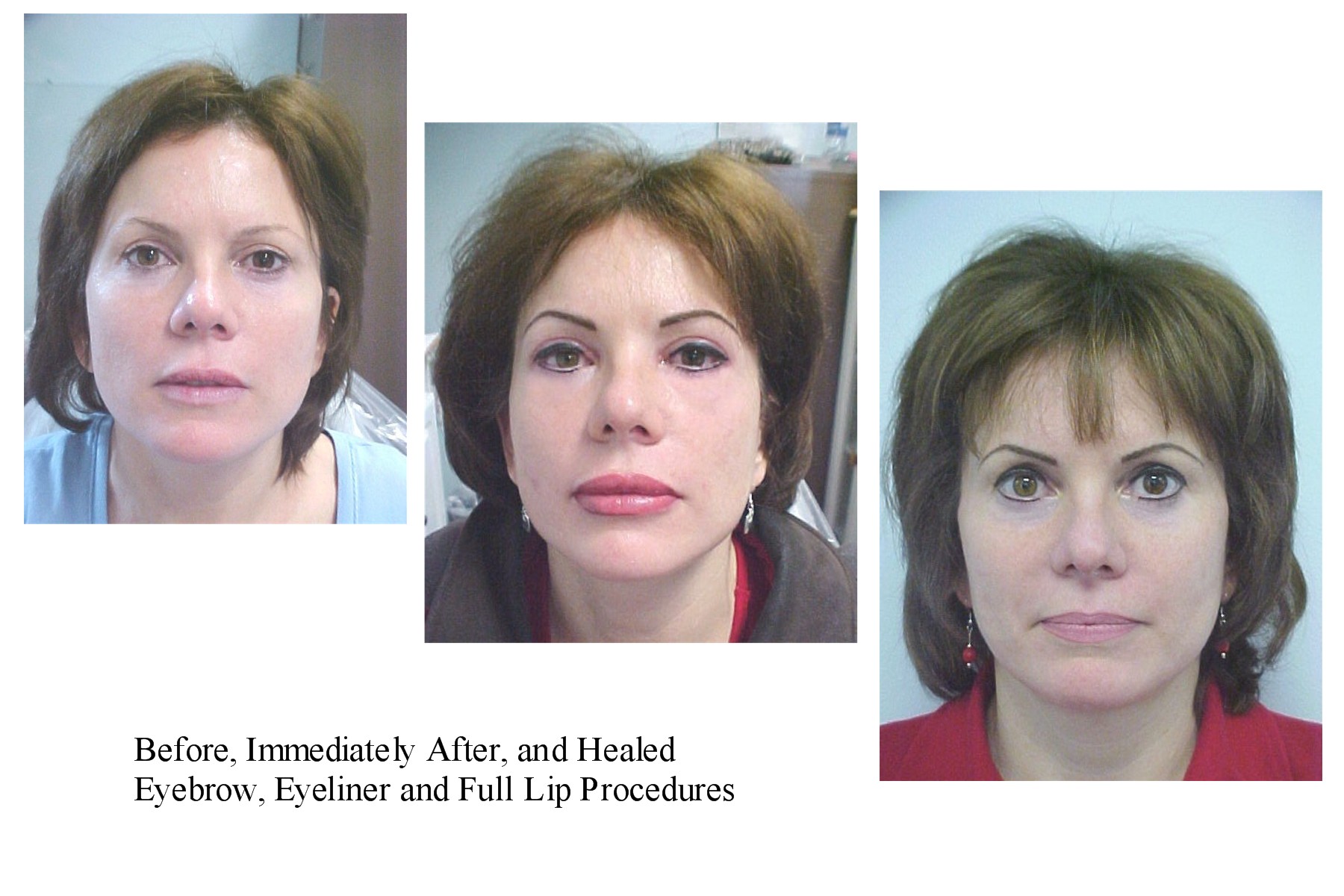
Permanent Makeup
Permanent makeup, also known as permanent cosmetics, derma-pigmentation, micro-pigmentation, semi-permanent makeup and cosmetic tattooing, is a cosmetic technique which employs tattooing techniques to replicate the appearance of traditional makeup, such as for eye liner, eyebrows, and lip color. Permanent makeup is done for both aesthetic and medical purposes, as it is sometimes used after reconstructive surgery. Permanent makeup has evolved from a tattooing practice to a more widely accepted, sophisticated procedure. It has become very popular, not only because of its cosmetic advantages but also for its convenience and enhancing quality of life. However, it does come with risks. Complications include allergic reactions, migration of pigment, or even infections, which underscore the importance of high-quality materials and skilled technicians. As permanent makeup gradually gained popularity, its safety concerns, regulatory challenges, and options for removal also attracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Permanent Makeup
Composite or compositing may refer to: Materials * Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances ** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts ** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials ** Dental composite, a substance used to fill cavities in teeth ** Composite armor, a type of tank armor * Alloy, a mixture of a metal and another element * Mixture, the combination of several different substances without chemical reaction Mathematics * Composite number, a positive integer that has at least one factor other than one or itself Science * Composite particle, a particle which is made up of smaller particles * ''Compositae'' or "composite family" of flowering plants * Composite volcano, a layered conical volcano * Compositing, another name for superposed epoch analysis, a statistical method used to analyze time series involving multiple events Technology * Compositing, combining of visual elements from separate sources int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itches leads to a scratch reflex. Unmyelinated nerve fibers for itches and pain both originate in the skin. Information for them is conveyed centrally in two distinct systems that both use the same nerve bundle and spinothalamic tract. Classification Most commonly, an itch is felt in one place. If it is felt all over the body, then it is called ''generalized itch'' or ''generalized pruritus''. Generalized itch is infrequently a symptom of a serious underlying condition, such as cholestatic liver disease. If the sensation of itching persists for six weeks or longer, then it is called ''chronic itch'' or ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microblading
Microblading is a tattooing technique which uses a small handheld tool made of several tiny needles to add semi-permanent pigment to the skin. Microblading differs from standard eyebrow tattooing, a form of permanent makeup, as each hair stroke is created by hand with a blade that creates fine slices in the skin, whereas eyebrow tattoos are done with a tattoo machine. Microblading is used on eyebrows to create, enhance, or alter their appearance in shape and color. It deposits pigment into the upper region of the dermis, so it fades more rapidly than traditional tattooing techniques. Microblading is often referred to as eyebrow embroidery, eyebrow feathering, microstroking, 3D eyebrows, nanoblading or hair-like strokes. History The technique of implanting pigment following fine incisions in the skin may date back thousands of years, but the trend of using the technique for eyebrows is thought to have emerged in Asia, becoming popular in Singapore and Korea as early as 2005, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exfoliation (cosmetology)
In cosmetology, exfoliation is the removal of the surface skin cells and built-up dirt from the skin's surface. The term comes from the Latin word ('to strip off leaves'). This is a regular practice within the cosmetic industry, both for its outcome of promoting skin regeneration as well as providing a deep cleanse of the skin barrier. Being used in facials, this process can be achieved by mechanical or chemical means, such as microdermabrasion or chemical peels. Exfoliants are advertised as treatments that enhance beauty and promote a youthful and healthy appearance. History Exfoliation was first practiced among the ancient Egyptians. This was also used in Asia, specifically in China, during the Qing Dynasty (1644–1944). Mechanical exfoliation Mechanical exfoliation methods involve physically scrubbing the skin with an abrasive material. These types of exfoliants include microfiber cloths, adhesive exfoliation sheets, microbead facial scrubs, crêpe paper, crushed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a type of surgical skin planing, generally with the goal of removing acne, scarring and other skin or tissue irregularities, typically performed in a professional medical setting by a dermatologist or plastic surgeon trained specifically in this procedure. Dermabrasion has been practiced for many years (before the advent of lasers) and involves the controlled deeper abrasion (wearing away) of the upper to mid layers of the skin with any variety of strong abrasive devices including a wire brush, diamond wheel or fraise, sterilized sandpaper, salt crystals or other mechanical means. Dermabrasion procedures are surgical, invasive procedures that typically require a local anaesthetic. Often, they are performed in surgical suites or in professional medical centers. Since the procedure can typically remove the top to deeper layers of the epidermis and extend into the reticular dermis, there is always minor skin bleeding. The procedure carries risks of scarring, skin d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattoo Removal
Tattoo removal is a procedure to eliminate or significantly lighten a tattoo from the skin. People pursue removal for many reasons, including changes in personal taste, social or professional considerations, or a desire to relocate a tattoo. Modern techniques include laser removal, dermabrasion, surgical excision, and other methods. The process of tattooing generally creates permanent markings in the skin, but people have attempted many methods to try to hide or destroy tattoos. The standard modern method is the non-invasive removal of tattoo pigment using Q-switched lasers. Different types of Q-switched lasers are used to target different colors of tattoo ink; depending on the specific light absorption spectra of the tattoo pigments. Typically, black and other darker-colored inks can be removed completely using Q-switched lasers, while lighter colors, such as yellows and greens, are very difficult to remove. Success depends on a wide variety of factors including skin color, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetism is the property of materials that are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The Permeability (electromagnetism), magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the Vacuum_permeability, permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductivity, superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it entirely expels any magnetic field from its inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite, vomiting, fatigue (medicine), tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is ''acute (medicine), acute'' if it resolves within six months, and ''chronic condition, chronic'' if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can self-limiting (biology), resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer. Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus ''hepatovirus A'', ''hepatitis B virus, B'', ''hepatitis C virus, C'', ''hepatitis D virus, D'', and ''hepatitis E virus, E''. Other Viral hepatitis, viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type III) at the site of a healed skin injury, which is then slowly replaced by collagen type I. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect the movement of the skin. In the United States, keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |