|
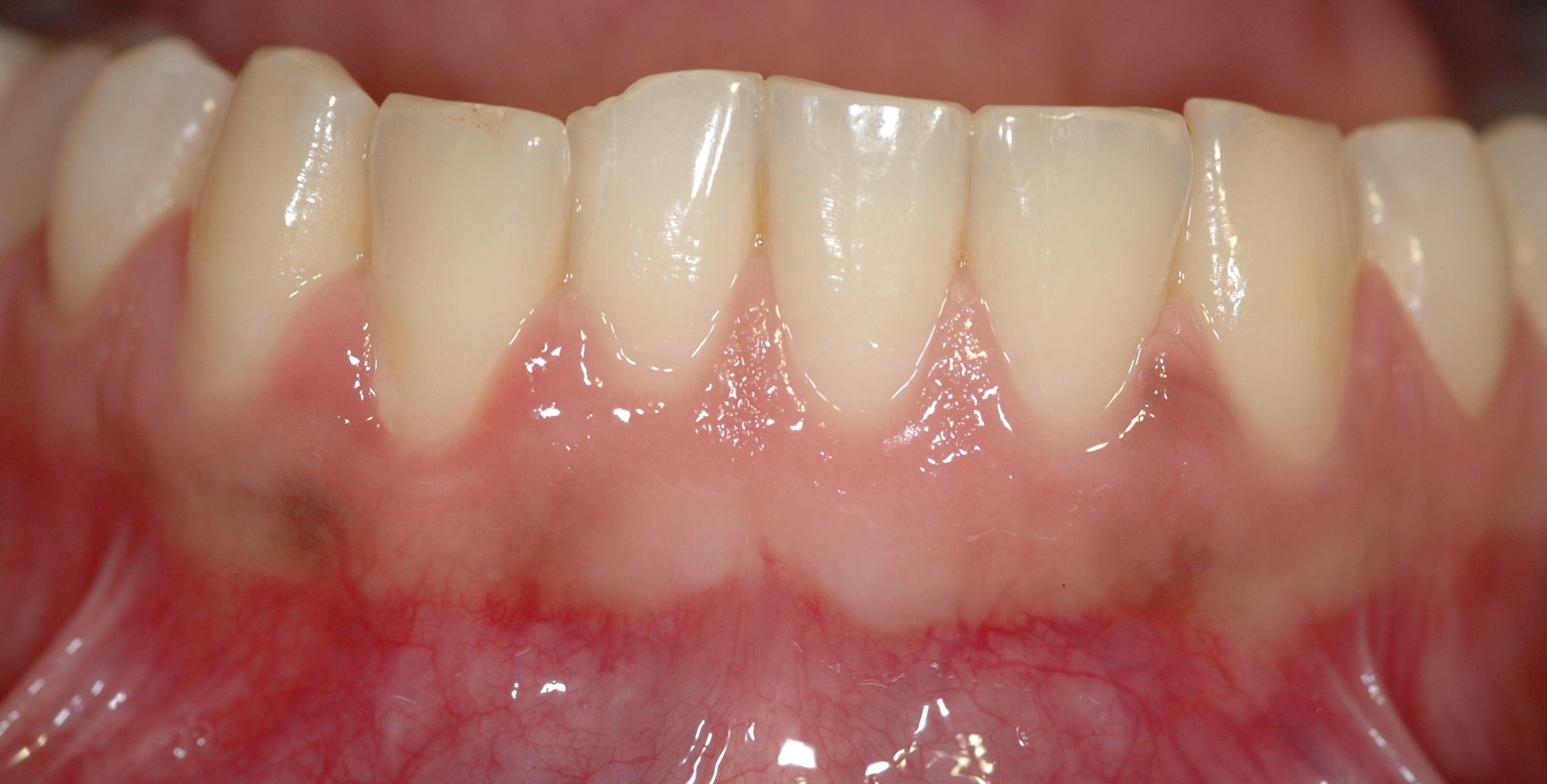
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Halitosis (bad breath) may also occur. Periodontal disease typically arises from the development of plaque biofilm, which harbors harmful bacteria such as ''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' and ''Treponema denticola''. These bacteria infect the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, leading to inflammation and, if left untreated, progressive damage to the teeth and gum tissue. Recent meta-analysis have shown that the composition of the oral microbiota and its response to periodontal disease differ between men and women. These differences are particularly notable in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontology
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the Specialty (dentistry), specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of Tooth, teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), Alveolar process, alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
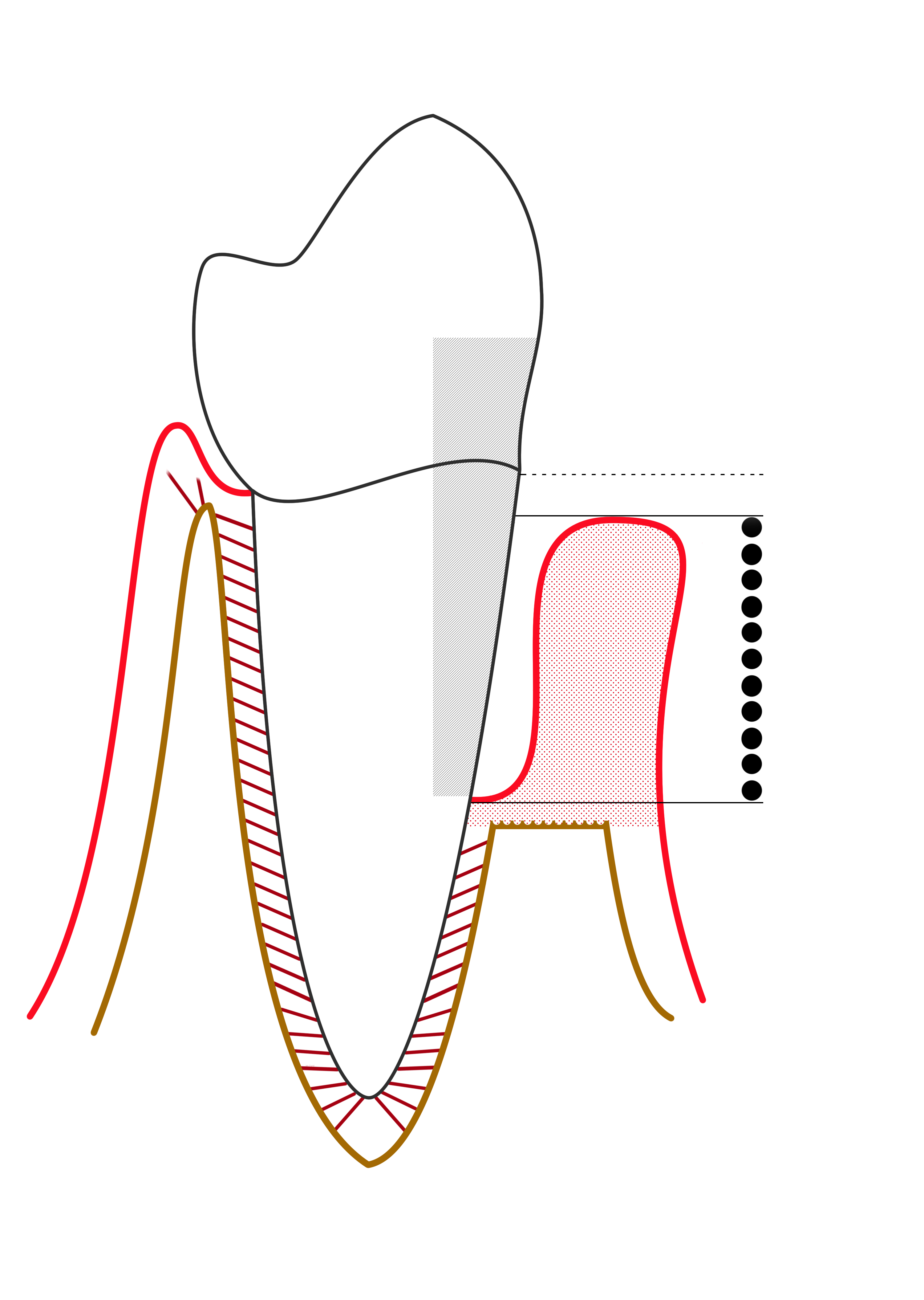
Periodontal Terms Diagram Gingival Recession
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone are known as the gingiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms (mostly bacteria, but also fungi) that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms Calculus (dental), tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gums, gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease. It has been observed that differences in the composition of dental plaque microbiota exist between men and women, particularly in the presence of periodontal disease, periodontitis. Progression and build-up of dental plaque can give rise to tooth decay – the localised destruction of the tissues of the tooth by acid produced from the bacterial degrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
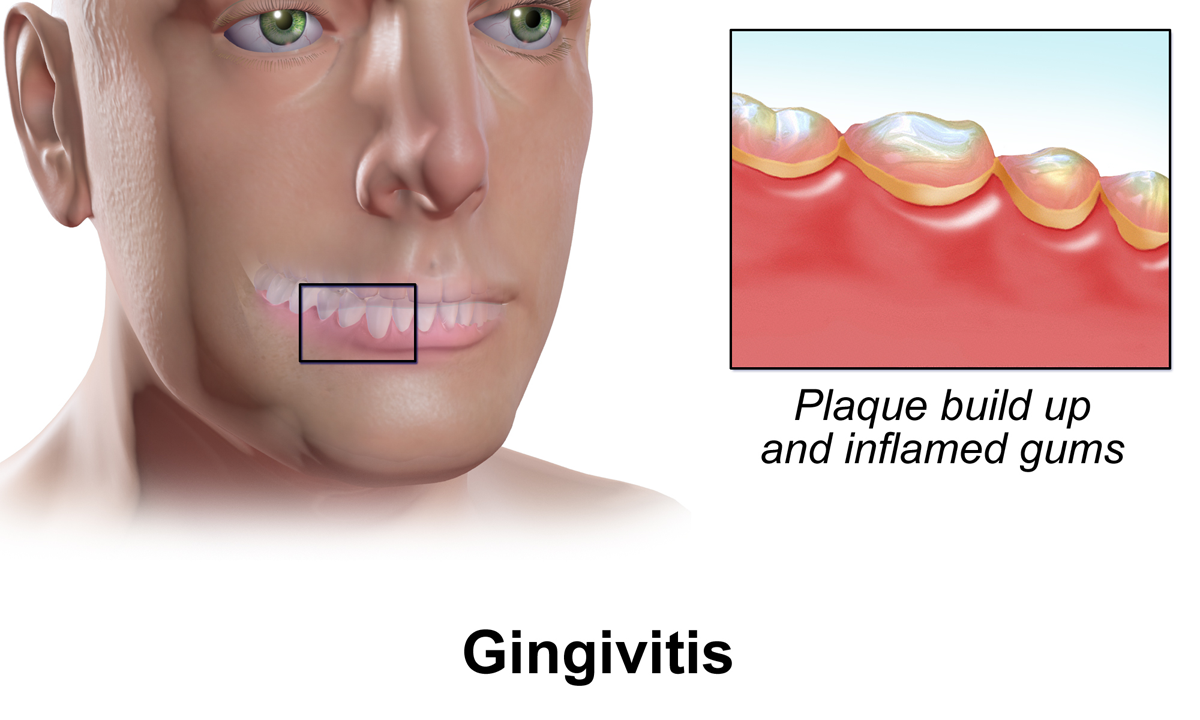
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums; ulitis is an alternative term. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that are attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced. While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation: *Swollen gums *Bright red gums *Gums that are tender or painful to the touch *B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay (''cavities'', ''dental caries'') and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis. General guidelines for adults suggest brushing at least twice a day with a fluoridated toothpaste: brushing before going to sleep at night and after breakfast in the morning. Cleaning between the teeth is called interdental cleaning and is as important as tooth brushing. This is because a toothbrush cannot reach between the teeth and therefore only removes about 50% of plaque from the surface of the teeth. There are many tools available for interdental cleaning which include Dental floss, floss, tape and interden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Brushing
Tooth brushing is the act of scrubbing teeth with a toothbrush equipped with toothpaste. Interdental cleaning (with floss or an interdental brush) can be useful with tooth brushing, and together these two activities are the primary means of cleaning teeth, one of the main aspects of oral hygiene. The recommended amount of time for tooth brushing is two minutes each time for two times a day. History Teeth-cleaning twigs have long been used throughout human history. As long ago as 3000 B.C., the ancient Egyptians constructed crude toothbrushes from twigs and leaves to clean their teeth. Similarly, other cultures such as the Greeks, Romans, Arabs and Indians also cleaned their teeth with twigs. Some would fray one end of the twig so that it could penetrate between the teeth more effectively. In the Islamic prophetic tradition, Muhammad taught his disciples to brush their teeth using miswak five times per day, and this remains prevalent amongst many Muslims world wide since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Microbiology
Oral microbiology is the study of the microorganisms (microbiota) of the oral cavity and their interactions between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment present in the human mouth is suited to the growth of characteristic microorganisms found there. It provides a source of water and nutrients, as well as a moderate temperature. Resident microbes of the mouth adhere to the teeth and gums to resist mechanical flushing from the mouth to stomach where acid-sensitive microbes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid. Anaerobic bacteria in the oral cavity include: ''Actinomyces'', ''Arachnia (bacterium), Arachnia'' (''Propionibacterium propionicus''), ''Bacteroides'', ''Bifidobacterium'', ''Eubacterium'', ''Fusobacterium'', ''Lactobacillus'', ''Leptotrichia buccalis, Leptotrichia'', ''Peptococcus'', ''Peptostreptococcus'', ''Propionibacterium'', ''Selenomonas'', ''Treponema'', and ''Veillonella''. The most commonly found protists are ''Entamoeba gingivalis'' and ''Trichomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have been rolled with a small rectangle of paper into an elongated cylinder called a cigarette. Other forms of smoking include the use of a smoking pipe or a bong. Smoking is primarily practised as a route of administration for psychoactive chemicals because the active substances within the burnt dried plant leaves vaporize and can be airborne-delivered into the respiratory tract, where they are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream of the lungs and then reach the central nervous system. In the case of tobacco smoking, these active substances are a mixture of aerosol particles that includes the pharmacologically active alkaloid nicotine, which stimulates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain. Other notable active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Probe
In dentistry, a periodontal probe is a dental instrument which is usually long, thin, and blunted at the end. Its main function is to evaluate the depth of the pockets surrounding a tooth in order to determine the periodontium's overall health. For accuracy and readability, the instrument's head has markings written on it. Use Proper use of the periodontal probe is necessary to maintain accuracy. The tip of the instrument is placed with light pressure of 10-20 gramsWilkins, 1999 into the gingival sulcus, which is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding tissue. It is important to keep the periodontal probe parallel to the contours of the root of the tooth and to insert the probe down to the base of the pocket. This results in obscuring a section of the periodontal probe's tip. The first marking visible above the pocket indicates the measurement of the pocket depth. It has been found that the average, healthy pocket depth is around 3 mm with no b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
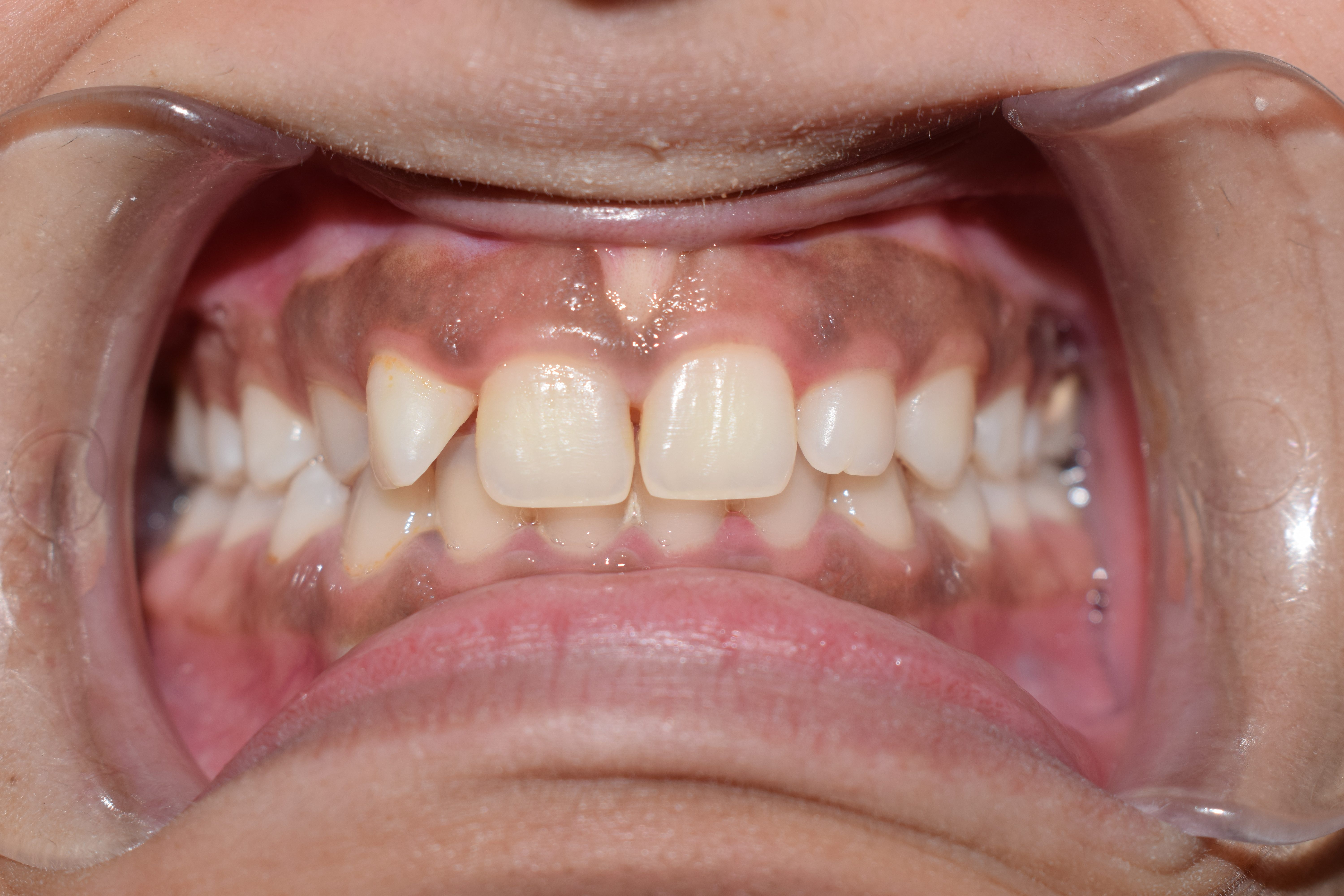
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have been rolled with a small rectangle of paper into an elongated cylinder called a cigarette. Other forms of smoking include the use of a smoking pipe or a bong. Smoking is primarily practised as a route of administration for psychoactive chemicals because the active substances within the burnt dried plant leaves vaporize and can be airborne-delivered into the respiratory tract, where they are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream of the lungs and then reach the central nervous system. In the case of tobacco smoking, these active substances are a mixture of aerosol particles that includes the pharmacologically active alkaloid nicotine, which stimulates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain. Other notable active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Breath
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder. The concerns of bad breath may be divided into genuine and non-genuine cases. Of those who have genuine bad breath, about 85% of cases come from inside the mouth. The remaining cases are believed to be due to disorders in the nose, sinuses, throat, lungs, esophagus, or stomach. Rarely, bad breath can be due to an underlying medical condition such as liver failure or ketoacidosis. Non-genuine cases occur when someone complains of having bad breath but other people cannot detect it. This is estimated to make up between 5% and 72% of cases. The treatment depends on the underlying cause. Initial efforts may include tongue cleaning, mouthwash, and flossing. Tentative evidence supports the use of mouthwash containing chlorhexidine or cetylpyridi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |