|
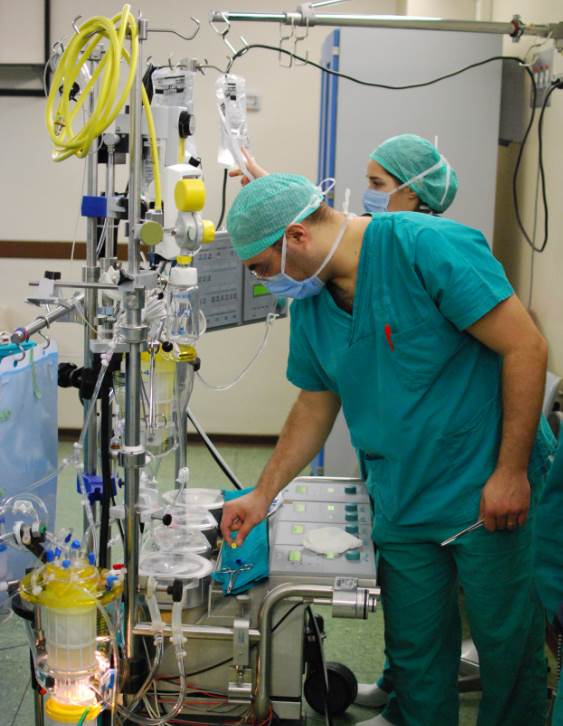
Perfusionist
A cardiovascular perfusionist, clinical perfusionist or perfusiologist, and occasionally a cardiopulmonary bypass doctor or clinical perfusion scientist, is a healthcare professional who operates the cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart–lung machine) during cardiac surgery and other surgeries that require cardiopulmonary bypass to manage the patient's physiological status. As a member of the cardiovascular surgical team, the perfusionist helps maintain blood flow to the body's tissues as well as regulate levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, using a heart–lung machine. Duties Perfusionists form part of the wider cardiovascular surgical team which includes cardiac surgeons, anesthesiologists, and Medical resident, residents. Their role is to conduct extracorporeal circulation as well as ensure the management of physiologic functions by monitoring the necessary variables. The perfusionist provides consultation to the physician in selecting appropriate equipment an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) or heart-lung machine, also called the pump or CPB pump, is a machine that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery by maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen throughout the body. As such it is an Extracorporeal, extracorporeal device. CPB is operated by a perfusionist. The machine mechanically circulates and oxygenates blood throughout the patient's body while bypassing the heart and lungs allowing the surgeon to work in a bloodless surgical field. Uses CPB is commonly used in operations or surgical procedures involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate safely on the heart. In many operations, such as Coronary artery bypass surgery, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), the heart is Cardioplegia, arrested, due to the degree of the difficulty of operating on a beating heart. Operations requiring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery Image 657C-PH , part of a mammalian eye.
{{Set index article ...
Coronary () may, as shorthand in English, be used to mean: * Coronary circulation, the system of arteries and veins in mammals ** Coronary artery disease ** Coronary occlusion ** A myocardial infarction, a heart attack As adjective * Referring to the work of a Coroner, a person entitled to investigate deaths * Referring to a stellar corona, the outermost atmosphere of a star * Mistakenly to a Cornea The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe hypothermia, there may be hallucinations and paradoxical undressing, in which a person removes their clothing, as well as an increased risk of the heart stopping. Hypothermia has two main types of causes. It classically occurs from exposure to cold weather and cold water immersion. It may also occur from any condition that decreases heat production or increases heat loss. Commonly, this includes alcohol intoxication but may also include low blood sugar, anorexia and advanced age. Body temperature is usually maintained near a constant level of through thermoregulation. Efforts to increase body temperature involve shivering, increased voluntary activity, and putting on warmer clothing. Hypothermia may be diagnosed based on either a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS) is a congenital heart defect in which the structures on the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, are underdeveloped. This defect causes inadequate blood flow to the lungs, and thus a Blue baby syndrome, cyanotic infant. Symptoms and signs Common symptoms include a grayish-blue (cyanosis) coloration to the skin, lips, fingernails and other parts of the body. Other pronounced symptoms can be Hyperventilation, rapid or difficult breathing, poor feeding due to lack of energy, cold hands or feet, or being inactive and drowsy. Notably, patent ductus arteriosus and patent foramen ovale, normally dangerous defects, are necessary for a newborn with HRHS to survive. If either formation does close, the child will go into shock, signs of which can include cool or clammy skin, a weak or rapid pulse, and dilated pupils. Causes It is mostly unknown what causes hypoplastic right heart syndrome in a given individual. It is thought tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped and incapable of supporting the systemic circulation. It is estimated to account for 2-3% of all congenital heart disease. Early signs and symptoms include poor feeding, cyanosis, and diminished pulse in the extremities. The etiology is believed to be multifactorial resulting from a combination of genetic mutations and defects resulting in altered blood flow in the heart. Several structures can be affected including the left ventricle, aorta, aortic valve, or mitral valve all resulting in decreased systemic blood flow. Diagnosis can occur prenatally via ultrasound or shortly after birth via echocardiography. Initial management is geared to maintaining patency of the ductus arteriosus - a connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta that closes shortly after birth. Thereafter, a patient subsequently undergoes a three-stage palliative repair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrupted Aortic Arch
Interrupted aortic arch is a very rare heart defect (affecting 3 per million live births) in which the aorta is not completely developed. There is a gap between the ascending and descending thoracic aorta. In a sense it is the complete form of a coarctation of the aorta. Almost all patients also have other cardiac anomalies, including a ventricular septal defect (VSD), aorto-pulmonary window, and truncus arteriosus. There are three types of interrupted aortic arch, with type B being the most common. Interrupted aortic arch (especially Type B) is often associated with DiGeorge syndrome. Signs and symptoms Patients with an interrupted aortic arch usually have symptoms from birth, with nearly all presenting symptoms within two weeks (when the ductus arteriosus is usually closed). Causes It is thought that an interrupted aortic arch occurs through excessive apoptosis in the developing, embryonic aorta. Around 50% of patients have DiGeorge syndrome. Diagnosis It can be diagnosed with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coarctation Of The Aorta
Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a congenital condition whereby the aorta is narrow, usually in the area where the ductus arteriosus ( ligamentum arteriosum after regression) inserts. The word ''coarctation'' means "pressing or drawing together; narrowing". Coarctations are most common in the aortic arch. The arch may be small in babies with coarctations. Other heart defects may also occur when coarctation is present, typically occurring on the left side of the heart. When a patient has a coarctation, the left ventricle has to work harder. Since the aorta is narrowed, the left ventricle must generate a much higher pressure than normal in order to force enough blood through the aorta to deliver blood to the lower part of the body. If the narrowing is severe enough, the left ventricle may not be strong enough to push blood through the coarctation, thus resulting in a lack of blood to the lower half of the body. Physiologically its complete form is manifested as interrupted ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Transplant
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one Lobes of the lung, lung lobe. With some lung diseases, a recipient may only need to receive a single lung. With other lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, it is imperative that a recipient receive two lungs. While lung transplants carry certain associated risks, they can also extend life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for those with end stage pulmonary disease. Qualifying conditions Lung transplantation is the therapeutic measure of last resort for patients with end-stage lung disease who have exhausted all other available treatments without improvement. A variety of conditions may make such surgery necessary. The most common indications for a lung transplant are pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cysti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart from a recently deceased organ donor (brain death is the most common) and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart ( orthotopic procedure) or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart (heterotopic, or "piggyback", transplant procedure). Approximately 5,000 heart transplants are performed each year worldwide, more than half of which are in the US. Post-operative survival periods average 15 years. Heart transplantation is not considered to be a cure for heart disease; rather it is a life-saving treatment intended to improve the quality and duration of life for a recipient. History American medical researcher Simon Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition Of The Great Vessels
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates. Types Transposed vessels can present with atriovenous, ventriculoarterial and/or arteriovenous discordance. The effects may range from a slight change in blood pressure to an interruption in circulation depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement, and on which specific vessels are involved. Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncus Arteriosus
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Structure The truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis are divided by the aorticopulmonary septum. The truncus arteriosus gives rise to the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The caudal end of the bulbus cordis gives rise to the smooth parts (outflow tract) of the left and right ventricles (aortic vestibule & conus arteriosus respectively). The cranial end of the bulbus cordis (also known as the conus cordis) gives rise to the aorta and pulmonary trunk with the truncus arteriosus. This makes its appearance in three portions. # Two distal ridge-like thickenings project into the lumen of the tube: the truncal and bulbar ridges. These increase in size, and ultimately meet and fuse to form a septum ( aorticopulmonary septum), which takes a spiral course toward th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |