|
Peptide Vaccine
Peptide-based synthetic vaccines (epitope vaccines) are subunit vaccines made from peptides. The peptides mimic the epitopes of the antigen that triggers direct or potent immune responses. Peptide vaccines can not only induce protection against infectious pathogens and non-infectious diseases but also be utilized as therapeutic cancer vaccines, where peptides from tumor-associated antigens are used to induce an effective anti-tumor T-cell response. History The traditional vaccines are the whole live or fixed pathogens. The second generation of vaccines is mainly the protein purified from the pathogen. The third generation of vaccines is the DNA or plasmid that can express the proteins of the pathogen. Peptide vaccines are the latest step in the evolution of vaccines. Advantages and disadvantages Compared with the traditional vaccines such as the whole fixed pathogens or protein molecules, the peptide vaccines have several advantages and disadvantages. Advantages: * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subunit Vaccine
A subunit vaccine is a vaccine that contains purified parts of the pathogen that are antigenic, or necessary to elicit a protective immune response. Subunit vaccine can be made from dissembled viral particles in cell culture or recombinant DNA expression, in which case it is a recombinant subunit vaccine. A "subunit" vaccine doesn't contain the whole pathogen, unlike attenuated vaccine, live attenuated or inactivated vaccine, but contains only the antigenic parts such as protein subunit, proteins, polysaccharides or peptides. Because the vaccine doesn't contain "live" components of the pathogen, there is no risk of introducing the disease, and is safer and more stable than vaccines containing whole pathogens. Other advantages include being well-established technology and being suitable for immunodeficiency, immunocompromised individuals. Disadvantages include being relatively complex to manufacture compared to some vaccines, possibly requiring immunologic adjuvant, adjuvants and boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
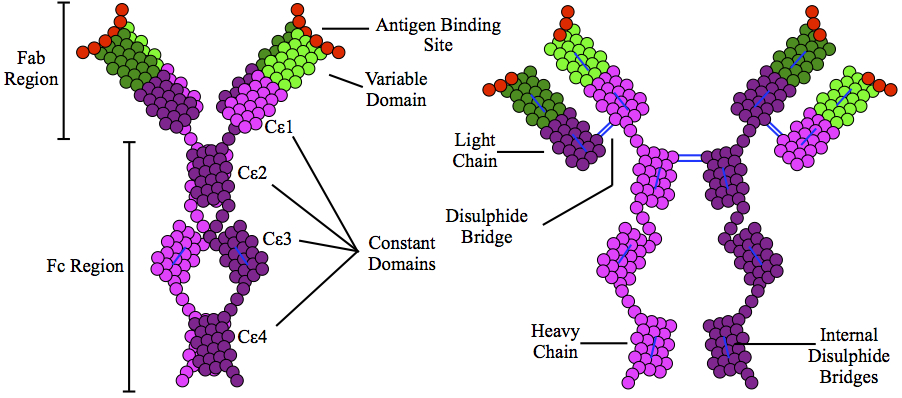
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including '' Schistosoma mansoni'', ''Trichinella spiralis'', and ''Fasciola hepatica''. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as ''Plasmodium falciparum''. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms. IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity, which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, and specific types of chronic urticaria and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Factor Receptor
A growth factor receptor is a receptor that binds to a growth factor. Growth factor receptors are the first stop in cells where the signaling cascade for cell differentiation and proliferation begins. Growth factors, which are ligands that bind to the receptor are the initial step to activating the growth factor receptors and tells the cell to grow and/or divide. These receptors may use the JAK/STAT, MAP kinase, and PI3 kinase pathways. A majority of growth factor receptors consists of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). There are 3 dominant receptor types that are exclusive to research : the epidermal growth factor receptor, the neurotrophin receptor, and the insulin receptors. All growth factor receptors are membrane bound and composed of 3 general protein domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic. The extracellular domain region is where a ligand may bind, usually with very high specificity. In RTKs, the binding of a ligand to the extracellular ligand binding si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rindopepimut
Rindopepimut (CDX-110) is an injectable peptide cancer vaccine which targets a mutant protein called EGFRvIII present in about 25% to 30% of glioblastoma cases. The vaccine consists of the EGFRv3-specific peptide (a 13-amino acid mutant vIII epitope) conjugated to the non-specific immunomodulator keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH). The US FDA granted it Breakthrough Therapy designation for glioblastoma in Feb 2015 meaning that it might be able to get approval sooner if it is effective. __TOC__ Clinical trials Glioblastoma The phase II ACT III study reported encouraging results in June 2015. The ReACT clinical trial for glioblastoma reported encouraging results in 2015. In March 2016 the phase III ACT IV trial was terminated because it did not increase overall survival Survival rate is a part of survival analysis. It is the proportion of people in a study or treatment group still alive at a given period of time after diagnosis. It is a method of describing prognosis in certain d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare cases melanoma can also happen in the lung which is known as primary pulmonary melanoma and only happens in 0.01% of primary lung tumors. In women, melanomas most commonly occur on the legs; while in men, on the back. Melanoma is frequently referred to as malignant melanoma. However, the medical community stresses that there is no such thing as a 'benign melanoma' and recommends that the term 'malignant melanoma' should be avoided as redundant. About 25% of melanomas develop from nevus, moles. Changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include increaseespecially rapid increasein size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or nevus#Classification, skin breakdown. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunologic Adjuvant
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word , meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens." In the early days of vaccine manufacture, significant variations in the efficacy of different batches of the same vaccine were correctly assumed to be caused by contamination of the reaction vessels. However, it was soon found that more scrupulous cleaning actually seemed to ''reduce'' the effectiveness of the vaccines, and some contaminants actually enhanced the immune response. There are many known adjuvants in widespread use, including potassium alum, various plant and animal derived oils and virosomes. Overview Adjuvants in immunology are often used to modify or augment the effects of a vaccine by stimulating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone amino, N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl, C=O group of the amino acid that is four residue (biochemistry), residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gcn4
Gcn4 is a transcription factor and a “master regulator” for gene expression which regulates close to one tenth of the yeast genome. In a study by Razaghi et al, amino acid starvation activated the transcription factor Gcn4p, resulting in transcriptional induction of almost all genes involved in amino acid biosynthesis, including ''HIS4''. Thus involvement of Gcn4 in regulation of both histidinol dehydrogenase ''HIS4'' and interferon gamma ''hIFNγ'' was hypothesised as a scenario explaining the increased level of ''hIFNγ'' under amino acid starvation. Overexpression of Gcn4 leads to the reduction in protein synthesis capacity which contributes to Gcn4-mediated increase of yeast lifespan. In budding yeast, deletion of Gcn4 prevents ''HIS4'' from targeting to the nuclear periphery upon transcriptional activation, indicating that Gcn4 is necessary for regulation of gene positioning and transcription. See also * DNA-binding protein * Transcription factor References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. In addition, B cells Antigen presentation, present antigens (they are also classified as professional Antigen-presenting cell, antigen-presenting cells, APCs) and secrete cytokines. In mammals B cells Cellular differentiation, mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the ''B'' stands for ''bursa'' and not ''bone marrow'', as commonly believed. B cells, unl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |