|
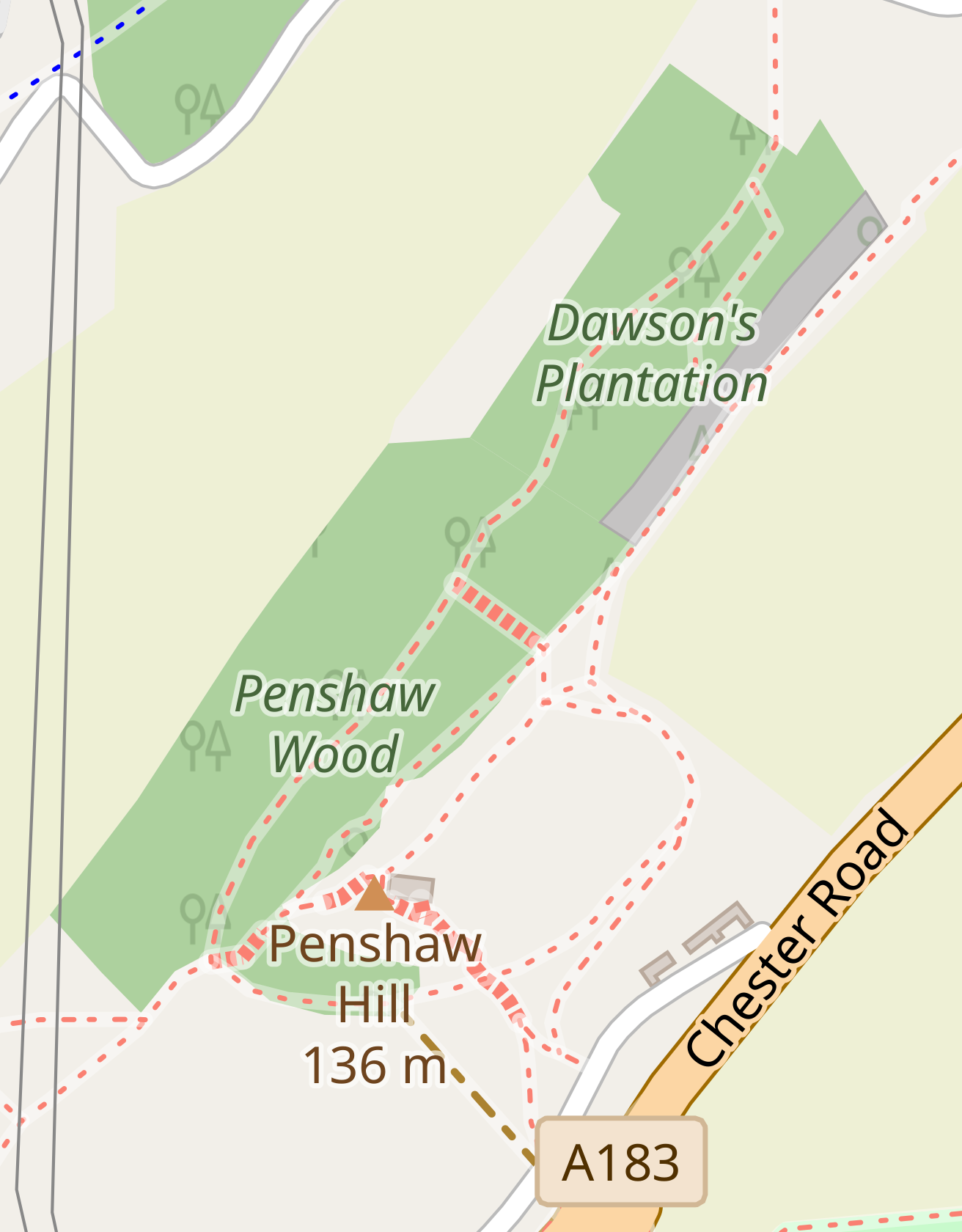
Penshaw
Penshaw , formerly known as ''Painshaw'' or ''Pensher'' is a village in the metropolitan district of Sunderland, in Tyne and Wear, England. Historically, Penshaw was located in County Durham. Name and etymology The name ''Penshaw'' was recorded in the 1190s as ''Pencher'' and is of Cumbric origin. The first element is ''pen'', meaning 'hill' or 'summit' and the second ''*cerr/*carr'' - 'stone, hard surface'. History Penshaw was formerly a township and chapelry in the parish of Houghton-le-Spring, in 1866 Penshaw became a separate civil parish, on 1 April 1937 the parish was abolished and merged with Houghton le Spring and Offerton. In 1931 the parish had a population of 7183. Features Penshaw is well known locally for Penshaw Monument, a prominent landmark built in 1844 atop Penshaw Hill, which is a half-scale replica of the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens. Owing to its proximity to Durham City, the area was allocated a Durham postcode, DH4, which forms part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
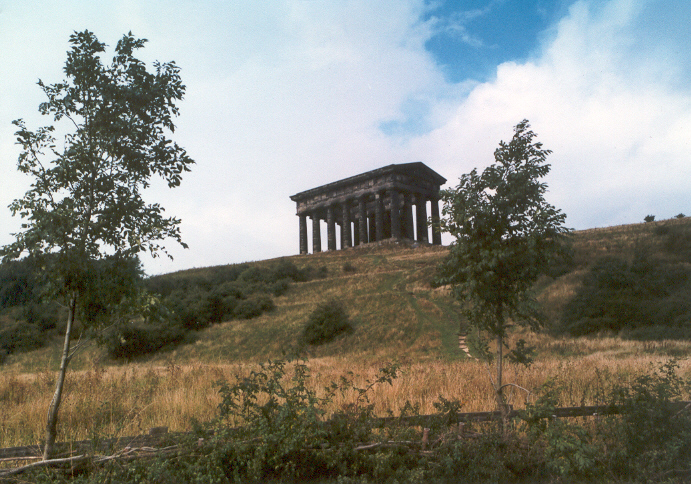
Penshaw Monument
The Penshaw Monument (officially the Earl of Durham's Monument) is a memorial in the style of an ancient Greek temple on Penshaw Hill in the metropolitan borough of the City of Sunderland, North East England. It is located near the village of Penshaw, between the towns of Washington and Houghton-le-Spring in historic County Durham. The monument was built between 1844 and 1845 to commemorate John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham (1792–1840), Governor-General of British North America and author of the Durham Report on the future governance of the American territories. Owned by the National Trust since 1939, it is a Grade I listed structure. The monument was designed by John and Benjamin Green and built by Thomas Pratt of Bishopwearmouth using local gritstone at a cost of around £6000; the money was raised by subscription. On 28 August 1844, while it was partially complete, its foundation stone was laid by Thomas Dundas, 2nd Earl of Zetland in a Masonic ceremony which drew t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penshaw Monument On Hill
Penshaw , formerly known as ''Painshaw'' or ''Pensher'' is a village in the metropolitan district of Sunderland, in Tyne and Wear, England. Historically, Penshaw was located in County Durham. Name and etymology The name ''Penshaw'' was recorded in the 1190s as ''Pencher'' and is of Cumbric origin. The first element is ''pen'', meaning 'hill' or 'summit' and the second ''*cerr/*carr'' - 'stone, hard surface'. History Penshaw was formerly a township and chapelry in the parish of Houghton-le-Spring, in 1866 Penshaw became a separate civil parish, on 1 April 1937 the parish was abolished and merged with Houghton le Spring and Offerton. In 1931 the parish had a population of 7183. Features Penshaw is well known locally for Penshaw Monument, a prominent landmark built in 1844 atop Penshaw Hill, which is a half-scale replica of the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens. Owing to its proximity to Durham City, the area was allocated a Durham postcode, DH4, which forms part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Sunderland
Sunderland () is a port city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is a port at the mouth of the River Wear on the North Sea, approximately south-east of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is the most populous settlement in the Wearside conurbation and the second most populous settlement in North East England after Newcastle. Sunderland was once known as 'the largest shipbuilding town in the world' and once made a quarter of all of the world's ships from its famous yards, which date back to 1346 on the River Wear. The centre of the modern city is an amalgamation of three settlements founded in the Anglo-Saxon era: Monkwearmouth, on the north bank of the Wear, and Sunderland and Bishopwearmouth on the south bank. Monkwearmouth contains St Peter's Church, which was founded in 674 and formed part of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey, a significant centre of learning in the seventh and eighth centuries. Sunderland was a fishing settlement and later a port, being granted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Hephaestus
The Temple of Hephaestus or Hephaisteion (also "Hephesteum" or "Hephaesteum"; , , and formerly called in error the Theseion or "Theseum"; , ), is a well-preserved Greek temple dedicated to Hephaestus; it remains standing largely intact today. It is a Doric peripteral temple, and is located at the north-west side of the Agora of Athens, on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill. From the 7th century until 1834, it served as the Greek Orthodox church of Saint George Akamates. The building's condition has been maintained due to its history of varied use. Name Hephaestus is the patron god of metal working, craftsmanship, and fire. There were numerous potters' workshops and metal-working shops in the vicinity of the temple, as befits the temple's honoree. Archaeological evidence suggests that there was no earlier building on the site except for a small sanctuary that was burned during the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BCE. The name ''Theseion'' or Temple of Theseus was attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyne And Wear
Tyne and Wear () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North East England. It borders Northumberland to the north and County Durham to the south, and the largest settlement is the city of Newcastle upon Tyne. The county is largely urbanised, with a population of 1.14 million in 2021. After Newcastle, the largest settlements are the city of Sunderland, Gateshead, and South Shields. Nearly all of the county's settlements belong to the Tyneside or Wearside conurbations, the latter of which extends into County Durham. For local government purposes Tyne and Wear comprises five metropolitan boroughs: Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead, Gateshead, Newcastle upon Tyne, City of Sunderland, Sunderland, North Tyneside and South Tyneside. The borough councils collaborate through the North East Combined Authority, which also includes Durham County Council and Northumberland County Council. The county was created in 1974 from south-east Northumberland and north-east County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "fellow countrymen"). The Welsh and the Cumbric-speaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DH Postcode Area
The DH postcode area, also known as the Durham postcode area,Royal Mail, ''Address Management Guide'', (2004) is a group of nine postcode districts in north-east England, within five post towns. These cover northern County Durham (including Durham, England, Durham, Chester-le-Street, Consett and Stanley, County Durham, Stanley), parts of southern Tyne and Wear (including Houghton-le-Spring) and a small part of southern Northumberland. __TOC__ Coverage The approximate coverage of the postcode districts: , - ! DH1 , DURHAM , Durham, England, Durham , County Durham (district), County Durham , - ! DH2 , CHESTER LE STREET , Chester-le-Street (west of East Coast Main Line), Ouston, Pelton, Birtley (west of East Coast Main Line) , County Durham, Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead, Gateshead , - ! DH3 , CHESTER LE STREET , Chester-le-Street (east of East Coast Main Line), Great Lumley, Birtley, Tyne and Wear, Birtley (east of East Coast Main Line) , County Durham, Gateshead , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houghton-le-Spring
Houghton-le-Spring ( ) is a town in the Sunderland district, in Tyne and Wear, England which has its recorded origins in Norman times. Historically in County Durham, it is now administered as part of the Tyne and Wear county. It lies between Durham, southwest and Sunderland, northeast. Seaham is also directly east. The villages and towns of Newbottle, Fencehouses and Hetton-le-Hole lie nearby. It had a population of 36,746. Other villages within the Houghton-le-Spring postal district include: Philadelphia, Penshaw, Shiney Row, Chilton Moor and Woodstone Village. History The earliest mention of the town's name is in the Boldon Book in 1183 as 'Hoctona'. An English transcription states: :''In Houghton are thirteen cottagers, whose tenures, works and payments are like those of Newbotill; and three other half cottagers, who also work like the three half cottagers of Newbotill. Henry the greeve, holds two oxgangs of for his service. The smith – for his servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
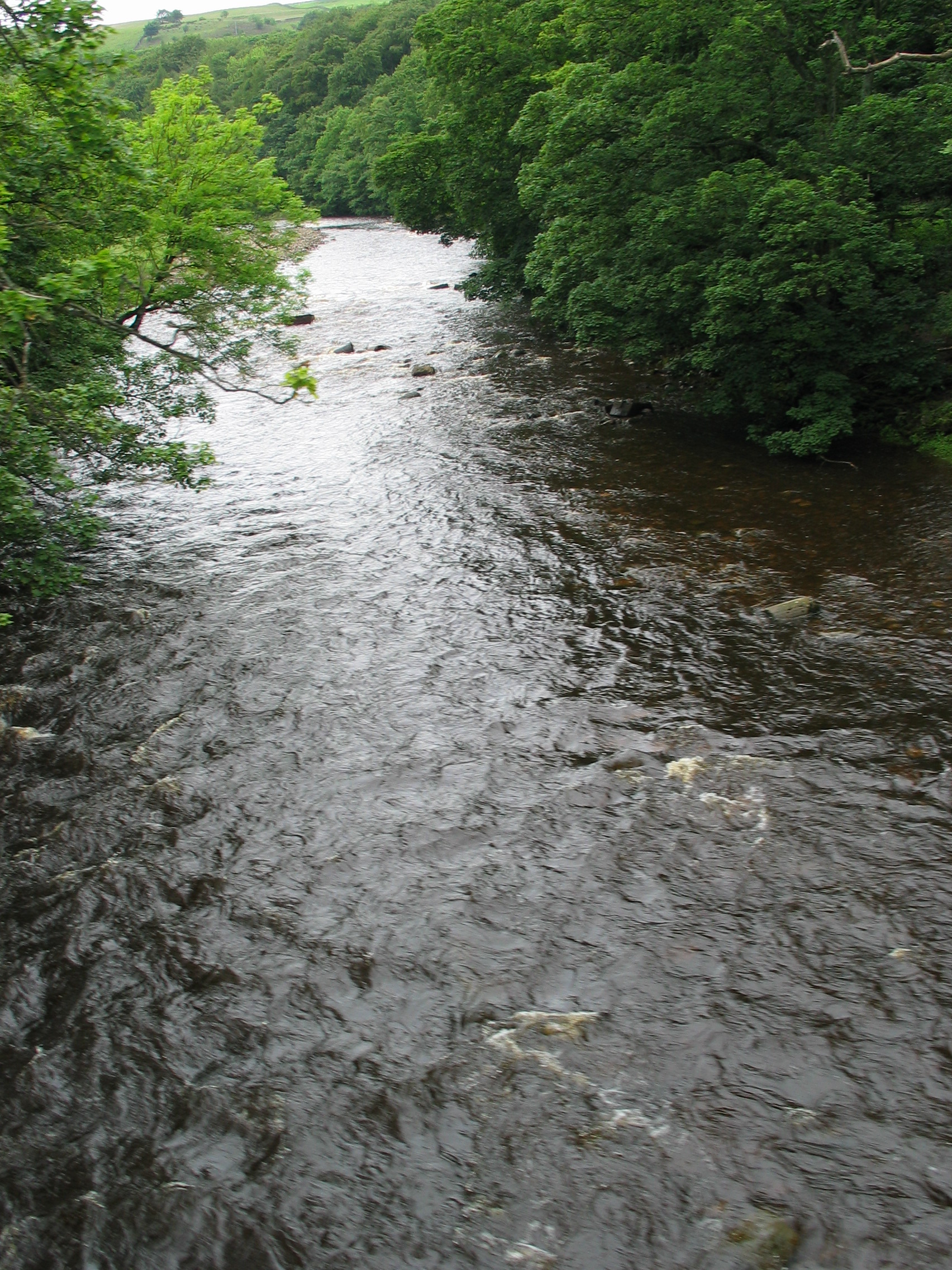
River Wear
The River Wear (, ) in Northern England rises in the Pennines and flows eastwards, mostly through County Durham, to the North Sea in the City of Sunderland. At long, it is one of the region's longest rivers. The Wear wends in a steep valley through the cathedral city of Durham and gives its name to Weardale in its upper reach and Wearside by its mouth. Etymology The origin behind the hydronym ''Wear'' is uncertain but is generally understood to be Celtic. The ''River Vedra'' on the Roman Map of Britain may very well be the River Wear. The name may be derived from Brittonic ''*wejr'' (<''*wẹ:drā''), which meant "a bend" (cf. Welsh ''-gwair-''). An alternative but very problematic etymology might involve ''*wẹ:d-r-'', from a lengthened form of the |
Cheviot Hills
The Cheviot Hills (), or sometimes The Cheviots, are a range of uplands straddling the Anglo-Scottish border between Northumberland and the Scottish Borders. The English section is within the Northumberland National Park. The range includes The Cheviot (the highest hill), plus Hedgehope Hill to the east, Windy Gyle to the west, and Cushat Law and Bloodybush Edge to the south. The hills are sometimes considered a part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland as they adjoin the uplands to the north. Since the Pennine Way runs through the region, the hills are also considered a part of the northern Pennines although they are separated from the Cheviot Hills by the Tyne Gap, part of which lies within the southern extent of the Northumberland National Park. The Cheviot Hills are primarily associated with geological activity from approximately 480 to 360 million years ago, when the continents of Avalonia and Laurentia collided, resulting in extensive volcanic activity (the Caledonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaburn
Seaburn is a seaside resort and northeastern suburb of Sunderland, North East England. The village of Whitburn borders the area to the north. To the west and south-west is Fulwell and to the south the coastal resort of Roker. Virtually all of Seaburn consists of low-density private housing interspersed with open parkland, laid out in the middle of the 20th century. Much of the housing is amongst the most expensive in Sunderland, with many large mansion houses situated along the coast, and on adjoining streets. The seafront is home to a sandy blue flag beach, seaside promenades, two amusement arcades, children's playgrounds, fish and chip shops, small guest houses and two 4 star hotels, The Grand Hotel and the Seaburn Inn. The main shopping street is Sea Road, which runs from the seafront up through Fulwell to the Seaburn Metro station. The area around Queens Parade hosts a 'strip' of restaurants, with three Italian, two Indian and two Chinese restaurants in operation as o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roker
Roker ( ) is a seaside resort in Sunderland, city of Sunderland district, Tyne and Wear. England. It is located north of the River Wear and Monkwearmouth, east of the southern part of Fulwell with the coastal resort of Seaburn to its north. It lies within historic County Durham. The majority of the houses in Roker are terraced or semi-detached. Further west, to the part bordering Fulwell, are cul-de-sacs with semi-detached bungalows; these are owned mainly by members of Roker's sizeable elderly population. On the seafront, located on Roker Terrace, are apartments, guest houses and the Roker Hotel. In addition to Seaburn seafront, the coast at Roker seafront played host to Sunderland International Airshow, the biggest free air show in Europe; this took place annually, usually over the last weekend in July. However, it was cancelled indefinitely as Sunderland City Council claimed it did not align with their vision to make the city carbon neutral. The popular event, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |