|
Penrose Drain
A Penrose drain is a soft, flexible rubber tube used as a surgical drain, to prevent the buildup of fluid in a surgical site. It belongs to the "passive" type of drain, the other broad type being "active". The Penrose drain is named after American gynecologist Charles Bingham Penrose (1862–1925). See photo of a Penrose drain & its packaging in the following external link Common uses A Penrose drain removes fluid from a wound area. Frequently it is put in place by a surgeon after a procedure is complete to prevent the area from accumulating fluid, such as blood, which could serve as a medium for bacteria to grow in. In podiatry, a Penrose drain is often used as a tourniquet during a hallux nail avulsion procedure or ingrown toenail extraction. It can also be used to drain cerebrospinal fluid to treat a hydrocephalus patient. See also *Instruments used in general surgery There are many different Surgery, surgical specialties, some of which require specific kinds of Surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
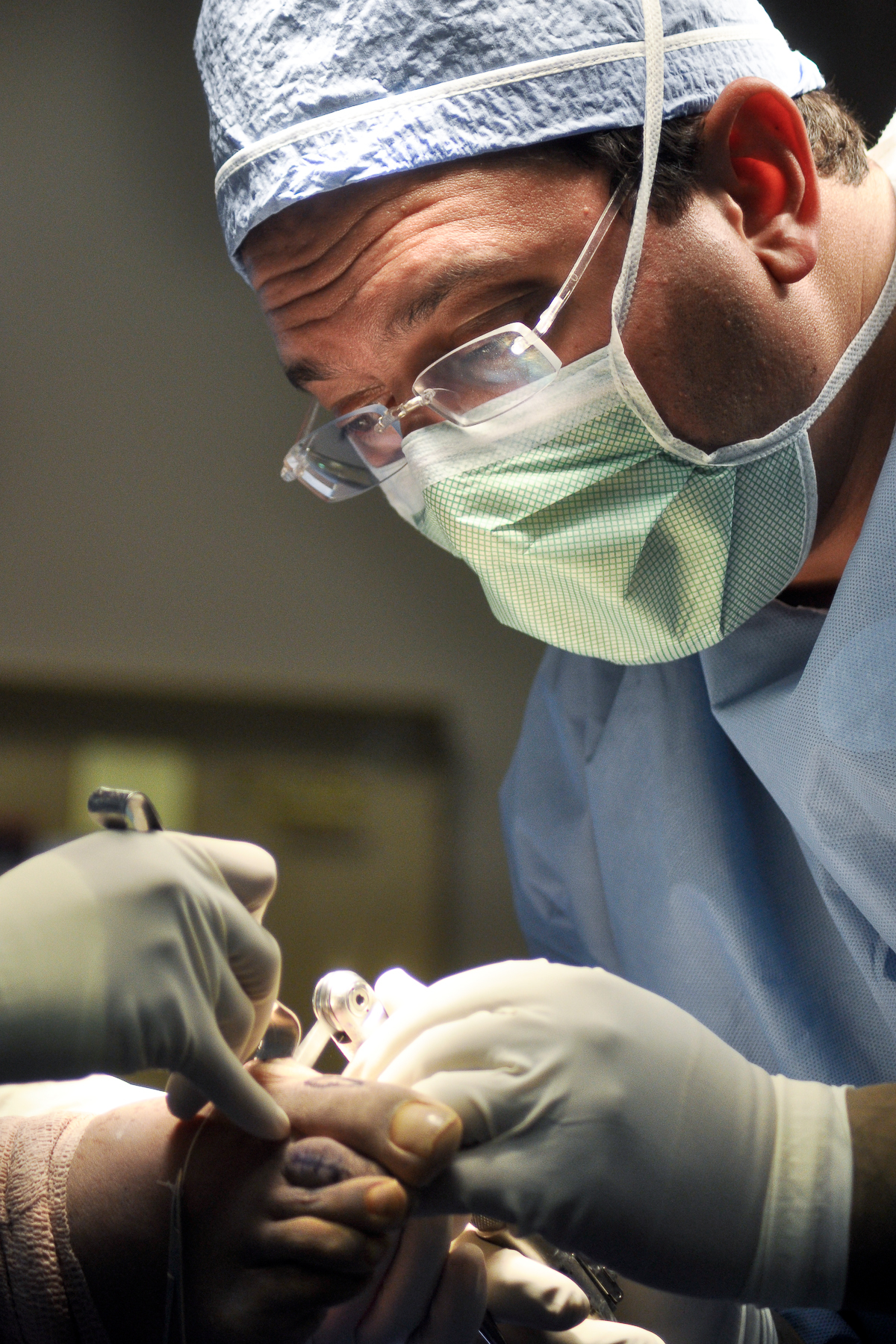
Compartment Syndrome In The Hand Intraoperative Image Of The Dorsal Region Of The Right Hand
Compartment may refer to: Biology * Compartment (anatomy), a space of connective tissue between muscles * Compartment (chemistry), in which different parts of the same protein molecule serve different functions * Compartment (development), fields of cells of distinct cell lineage, cell affinity, and genetic identity * Compartment (pharmacokinetics), a defined and distinct volume of body fluids * Cellular compartment, a closed part within a cell, surrounded by a membrane Other uses * Compartment coach, a railway car divided into separate areas or compartments, with no means of moving between them * Compartment (ship), subdivision of the space within a ship * Compartment (heraldry), the part of a coat of arms design which appears immediately below the shield * Multi-compartment model, a type of mathematical model * "Compartments", a song and album by José Feliciano * Hidden compartment See also * * * Compartmentalization (other) * Apartment An apartment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drain (surgery)
A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound, body cavity, or organ. They are commonly placed by surgeons or interventional radiologists after procedures or some types of injuries, but they can also be used as an intervention for decompression. There are several types of drains, and selection of which to use often depends on the placement site and how long the drain is needed. Use and Management Drains help to remove contents, usually fluids, from inside the body. This is beneficial since fluid accumulation may cause distension and pressure, which can lead to pain. For example, nasogastric (NG) tubes inserted through the nose and into the stomach can help remove stomach contents for patients who have a blockage further along in their gastrointestinal tract. After surgery, drains can be placed to remove blood, lymph, or other fluids that accumulate in the wound bed. This helps to promote wound healing and allows healthcare providers to moni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Bingham Penrose
Charles Bingham Penrose (February 1, 1862February 28, 1925) was an American gynecologist, surgeon, zoologist and conservationist, known for inventing a type of surgical drainage tubing called the Penrose drain. He was a professor at the University of Pennsylvania, wrote several editions of a textbook on medical problems in women, and was named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. A native of Philadelphia, Penrose was the son of a medical school professor, and his brothers included U.S. senator Boies Penrose, mining engineer R. A. F. "Dick" Penrose and geologist Spencer Penrose. The grandson of prominent politician Charles B. Penrose, he married into the wealthy Drexel family of the same city. Penrose held two doctorates, which he earned concurrently: a medical degree from the University of Pennsylvania and a Ph.D. in physics from Harvard College. After completing residency training at Pennsylvania Hospital, Penrose founded Philadelphia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiatry
Podiatry ( ), also know as podiatric medicine and surgery ( ), is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle and lower limb. The healthcare professional is known as a podiatrist. The US podiatric medical school curriculum includes lower extremity anatomy, general human anatomy, physiology, general medicine, physical assessment, biochemistry, neurobiology, pathophysiology, genetics and embryology, microbiology, histology, pharmacology, women's health, physical rehabilitation, sports medicine, research, ethics and jurisprudence, biomechanics, general principles of orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, and foot and ankle surgery. Podiatry is practiced as a Specialty (medicine), specialty in many countries. In Australia, graduates of recognised academic programs can register through the Podiatry Board of Australia as a "podiatrist", and those with additional recognised training may also receive endorsement to prescribe or adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourniquet
A tourniquet is a device that is used to apply pressure to a limb or extremity in order to create ischemia or stopping the flow of blood. It may be used in emergencies, in surgery, or in post-operative rehabilitation. A simple tourniquet can be made from a stick and a rope, but the use of makeshift tourniquets has been reduced over time due to their ineffectiveness compared to a commercial and professional tourniquet. This may stem the flow of blood, but side effects such as soft tissue damage and nerve damage may occur. History During Alexander the Great’s military campaigns in the fourth century BC, tourniquets were used to stanch the bleeding of wounded soldiers. Romans used them to control bleeding, especially during amputations. These tourniquets were narrow straps made of bronze, using only leather for comfort. In 1718, French surgeon Jean Louis Petit developed a screw device for occluding blood flow in surgical sites. Before this invention, the ''tourniquet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallux
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; '' unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe (). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by skin, and present on all five toes is a toenail. The toes are, from medial to lateral: * the first toe, also known as the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) may have poor balance, difficulty controlling urination, or mental impairment. In babies, there may be a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects (primary) or can develop later in life (secondary). Hydrocephalus can be classified via mechanism into communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Diagnosis is made by physical examination and medical imaging, such as a CT scan. Hydrocephalus is typically treated through surgery. One option is the placement of a shunt system. A procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy has gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruments Used In General Surgery
There are many different Surgery, surgical specialties, some of which require specific kinds of Surgical instrument, surgical instruments to perform. General surgery is a specialty focused on the abdomen; the Thyroid, thyroid gland; Disease, diseases involving skin, Breast, breasts, and various Soft tissue, soft tissues; Trauma surgery, trauma; Peripheral artery disease, peripheral vascular disease; Hernia, hernias; and Endoscopy, endoscopic procedures. Instruments can be classified in many ways, but, broadly speaking, there are five kinds of instruments. # Cutting and dissecting instruments # Grasping or holding instruments # Hemostasis, Hemostatic instruments # Retractor (medicine), Retractors # Tissue unifying instruments and materials Instruments used in surgery are: References Medical lists, Surgical instruments Technology-related lists, Surgical instruments Surgical instruments, Surgical instruments {{DEFAULTSORT:Instruments used in Surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |