|
Peneus Patera
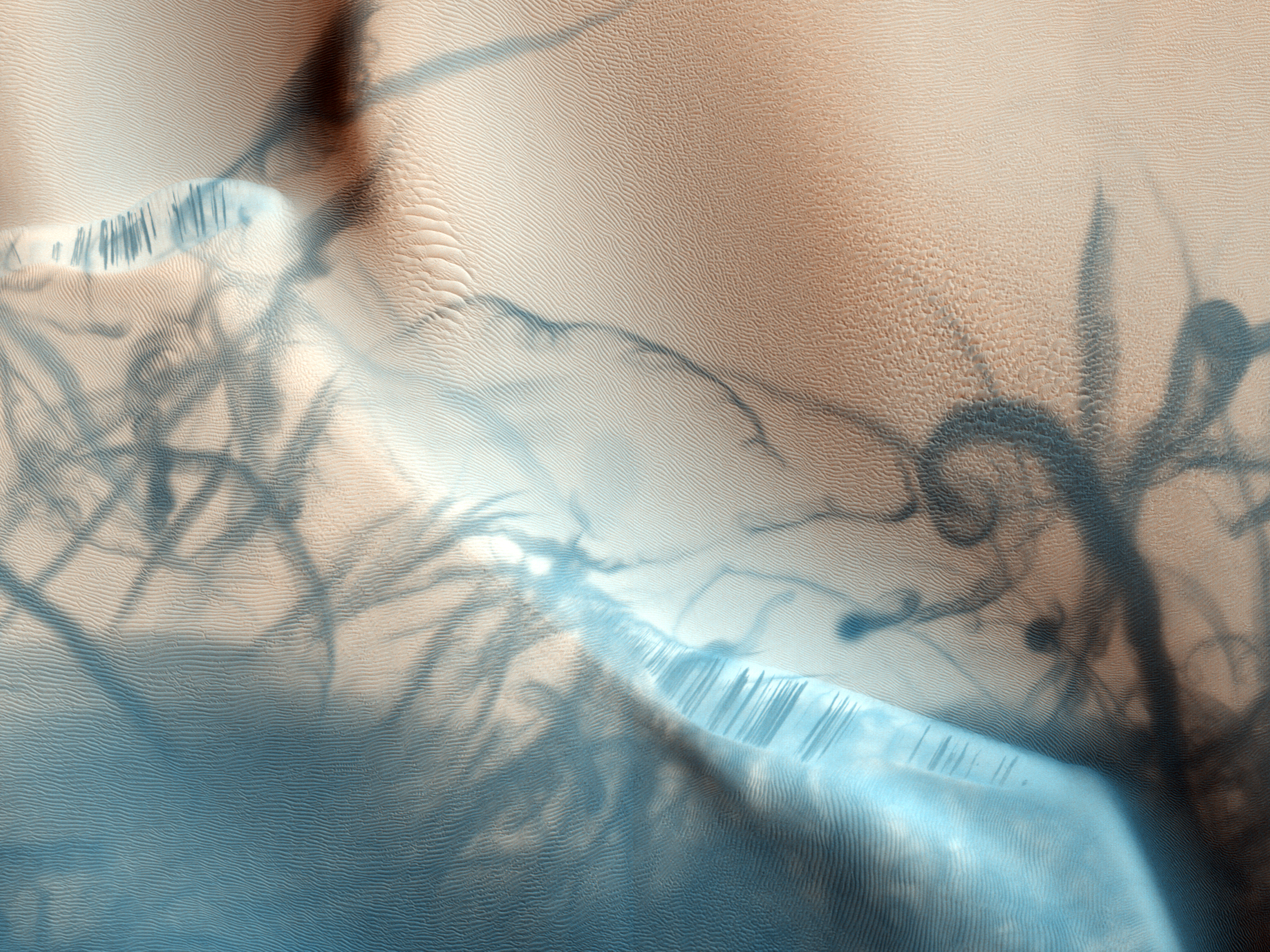
Peneus Patera is a feature in the Noachis quadrangle of Mars. It is located at 58.1 S and 307.5 W. It was named after an albedo feature at 48S, 290W. Scalloped topography Peneus Patera shows scalloped topography - depressions with scalloped edges. Sometimes the depressions seem to coalesce together. These features typically occur at about 55 degrees north and south latitude. They are believed to form from the removal of subsurface material, maybe interstitial ice by sublimation (change from solid to a gas). More gentle slopes face in the direction of the equator, while steep scarps face the pole. This is probably due to differences in solar heating. The process is believed to be ongoing. This topography may be of great importance for future colonization of Mars because it may point to deposits of pure ice. See also * Climate of Mars * HiRISE High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalloped Terrain At Peneus Patera
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve mollusks in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related families within the superfamily Pectinoidea, which also includes the thorny oysters. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family of bivalves found in all of the world's oceans, although never in fresh water. They are one of the very few groups of bivalves to be primarily "free-living", with many species capable of rapidly swimming short distances and even migrating some distance across the ocean floor. A small minority of scallop species live cemented to rocky substrates as adults, while others attach themselves to stationary or rooted objects such as seagrass at some point in their lives by means of a filament they secrete called a byssal thread. The majority of species, however, live recumbent on sandy substrates, and when they sense the presence of a pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachis Quadrangle
The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27 (Mars Chart-27). The Noachis quadrangle covers the area from 300° to 360° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on Mars. It lies between the two giant impact basins on Mars: Argyre and Hellas. The Noachis quadrangle includes Noachis Terra and the western part of Hellas Planitia. Noachis is so densely covered with impact craters that it is considered among the oldest landforms on Mars—hence the term "Noachian" for one of the earliest time periods in martian history. In addition, many previously buried craters are now coming to the surface, where Noachis' extreme age has allowed ancient craters to be filled, and once again newly exposed. Much of the surface in Noachis quadrangle shows a scalloped topography where the disappearance of ground ice has left depressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo Feature
An albedo feature is a large area on the surface of a planet (or other Solar System body) which shows a contrast in brightness or darkness (albedo) with adjacent areas. Historically, albedo features were the first (and usually only) features to be seen and named on Mars and Mercury. Early classical maps (such as those of Schiaparelli and Antoniadi) showed only albedo features, and it was not until the arrival of space probes that other surface features such as craters could be seen. On bodies other than Mars and Mercury, an albedo feature is sometimes called a regio. On bodies with a very thick atmosphere like Venus or Titan, permanent albedo features cannot be seen using ordinary optical telescopes because the surface is not visible, and only clouds and other transient atmospheric phenomena are seen. The ''Cassini–Huygens'' probe observed multiple albedo features on Titan after its arrival in Saturn's orbit in 2004. The first albedo feature ever seen on another planet wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalloped Topography
Scalloped topography is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, between 45° and 60° north and south. It is particularly prominent in the region of Utopia Planitia, in the northern hemisphere, and in the region of Peneus and Amphitrites Paterae in the southern hemisphere. Such topography consists of shallow, rimless depressions with scalloped edges, commonly referred to as "scalloped depressions" or simply "scallops". Scalloped depressions can be isolated or clustered and sometimes seem to coalesce. A typical scalloped depression displays a gentle equator-facing slope and a steeper pole-facing scarp. This topographic asymmetry is probably due to differences in insolation. Scalloped depressions are believed to form from the removal of subsurface material, possibly interstitial ice, by sublimation (direct transition of a material from the solid to the gas phase with no intermediate liquid stage). This process may still be happening at present. This topography may be of great importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublimation (phase Transition)
Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. Sublimation is an endothermic process that occurs at temperatures and pressures below a substance's triple point in its phase diagram, which corresponds to the lowest pressure at which the substance can exist as a liquid. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition or desublimation, in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase. Sublimation has also been used as a generic term to describe a solid-to-gas transition (sublimation) followed by a gas-to-solid transition ( deposition). While vaporization from liquid to gas occurs as evaporation from the surface if it occurs below the boiling point of the liquid, and as boiling with formation of bubbles in the interior of the liquid if it occurs at the boiling point, there is no such distinction for the solid-to-gas transition which always occurs as sublimation from the surface. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escarpment''. Some sources differentiate the two terms, with ''escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory. The university is part of the Association of American Universities and the Universities Research Association. In the former, it is the only member from the state of Arizona. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity". The University of Arizona is one of three universities governed by the Arizona Board of Regents. , the university enrolled 49,471 students in 19 separate colleges/schools, including the University of Arizona College of Medicine in Tucson and Phoenix and the James E. Rogers College of Law, and is affiliated with two academic medical centers ( Banner – University Medical Center Tucson and Banner – University Medical Center Phoenix). In 2021, University of Arizona acquir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water On Mars
Almost all water on Mars today exists as ice, though it also exists in small quantities as vapor in the atmosphere. What was thought to be low-volume liquid brines in shallow Martian soil, also called recurrent slope lineae, may be grains of flowing sand and dust slipping downhill to make dark streaks.Recurring Martian Streaks: Flowing Sand, Not Water? Nasa.org 2017-11-20 The only place where water ice is visible at the surface is at the north polar ice cap. Abundant water ice is also present beneath the permanent |
Climate Of Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope. Although Mars is smaller than the Earth, 11% of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than the Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars' climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars' atmosphere has a scale height of approximately , 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. The climate briefly received more interest in the news due to NASA measurements indicating increased sublim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

