|
Pendragon (role-playing Game)
''Pendragon'', or ''King Arthur Pendragon'', is a Tabletop role-playing game (RPG) in which players take the role of knights performing chivalric deeds in the tradition of Arthurian legend. It was originally written by Greg Stafford and published by Chaosium, then was acquired by Green Knight Publishing, who in turn passed on the rights to White Wolf Publishing in 2004. White Wolf sold the game to Stewart Wieck in 2009. Wieck formed Nocturnal Media, who updated and reissued the 5th edition originally published by White Wolf. In 2018, it returned to Chaosium. After it was published in 1985, ''Pendragon'' won several industry awards, and reviewers highly recommended it; in following years, it was included in several "Best of" industry lists. Setting Like several other RPGs from Chaosium (most notably '' Call of Cthulhu''), ''Pendragon'' has a literary basis, in this case the fifteenth-century Arthurian romance, ''Le Morte d'Arthur''. It studiously avoids fantasy RPG cliches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jody Lee
Jody A. Lee (born June 18, 1958, in San Francisco, California) is a professional fantasy artist from San Francisco known best for her book cover illustrations. Biography Lee was born June 18, 1958, in San Francisco, California. She graduated from the Academy of Art College in 1980 with a BA in Illustration. She lives in Morro Bay, California with her husband and two children. Career In 1980 Lee relocated to New York to work as a professional artist. ''The Encyclopedia of Science Fiction'' says she has provided book cover art for "many fantasies with carefully designed, brightly coloured, and pleasantly decorous covers". Authors she has worked with include Mercedes Lackey, Mickey Zucker Reichert, Lloyd Alexander, Madeleine L'Engle, and others. She also painted role-playing games' covers such as ''RuneQuest'' (third edition, 1984) and '' Pendragon'' (first edition, 1985). She illustrated the 1991 and 1996 book covers for ''A Wrinkle in Time'', as published by Dell Yearling. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungeon Crawl
A dungeon crawl is a type of scenario in fantasy role-playing games (RPGs) in which heroes navigate a labyrinth environment (a "dungeon"), battling various monsters, avoiding traps, solving puzzles, and looting any treasure they may find. Video games and board games which predominantly feature dungeon crawl elements are considered to be a genre. Board games Dungeon crawling in board games dates to the 1975 release of '' Dungeon!''. Over the years, many games built on that concept. One of the most acclaimed board games of the late 2010s, '' Gloomhaven'', is a dungeon crawler. Video games The first computer-based dungeon crawl was '' pedit5'', developed in 1975 by Rusty Rutherford on the PLATO interactive education system based in Urbana, Illinois. Although this game was quickly deleted from the system, several more like it appeared, including '' dnd'' and '' Moria''. Computer games and series from the 1980s, such as '' Rogue'', '' The Bard's Tale'', '' Cosmic Soldier'', '' D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dice
A die (: dice, sometimes also used as ) is a small, throwable object with marked sides that can rest in multiple positions. Dice are used for generating random values, commonly as part of tabletop games, including dice games, board games, role-playing games, and games of chance. A traditional die is a cube with each of its six faces marked with a different number of dots ( pips) from one to six. When thrown or rolled, the die comes to rest showing a random integer from one to six on its upper surface, with each value being equally likely. Dice may also have other polyhedral or irregular shapes, may have faces marked with numerals or symbols instead of pips and may have their numbers carved out from the material of the dice instead of marked on it. Loaded dice are specifically designed or modified to favor some results over others, for cheating or entertainment purposes. History Dice have been used since before recorded history, and their origin is uncertain. It is hypoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ability Score
In the ''Dungeons & Dragons'' role-playing game, game mechanics and dice rolls determine much of what happens. These mechanics include: * Ability scores, the most basic statistics of a character, which influence all other statistics * Armor class, how well-protected a character is against physical attack * Hit points, how much punishment a character can take before falling unconscious or dying * Saving throws, a character's defenses against nonphysical or area attacks (like poisons, fireballs, and enchantments) * Attack rolls and damage rolls, how effectively a character can score hits against, and inflict damage on, another character * Skills, how competent a character is in various areas of expertise * Feats, what special advantages a character has through natural aptitude or training Ability scores All player characters have six basic statistics: * Strength (STR): Strength is a measure of muscle, endurance and stamina combined; a high strength score indicates superiority in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
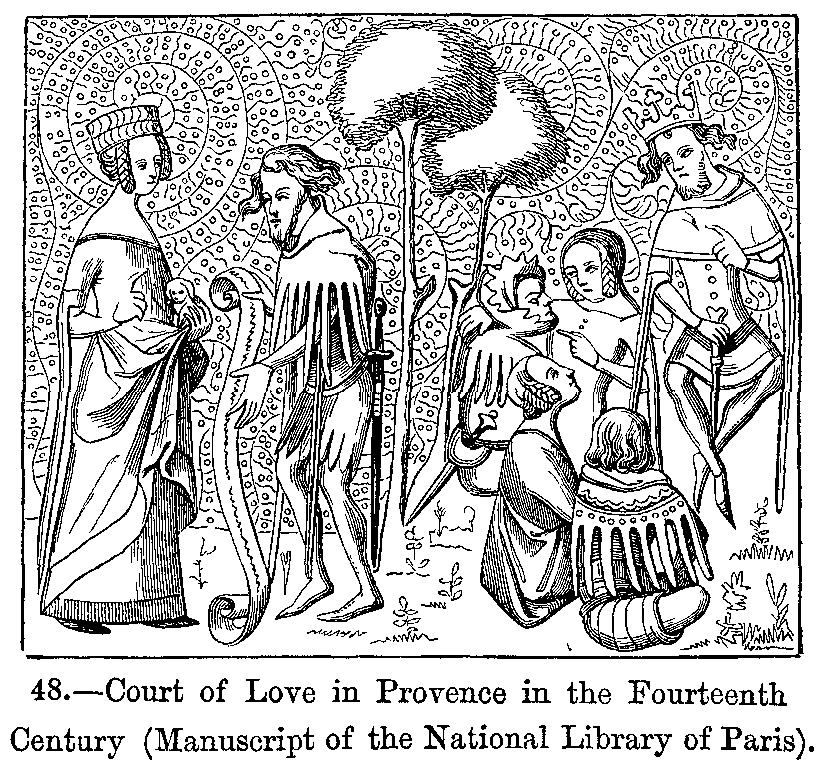
Courtly Love
Courtly love ( ; ) was a medieval European literary conception of love that emphasized nobility and chivalry. Medieval literature is filled with examples of knights setting out on adventures and performing various deeds or services for ladies because of their "courtly love". This kind of love was originally a literary fiction created for the entertainment of the nobility, but as time passed, these ideas about love spread to popular culture and attracted a larger literate audience. In the High Middle Ages, a "game of love" developed around these ideas as a set of social practices. "Loving nobly" was considered to be an enriching and improving practice. Courtly love began in the ducal and princely courts of Aquitaine, Provence, Champagne, ducal Burgundy and the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the end of the eleventh century. In essence, courtly love was an experience between erotic desire and spiritual attainment, "a love at once illicit and morally elevating, passionate and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
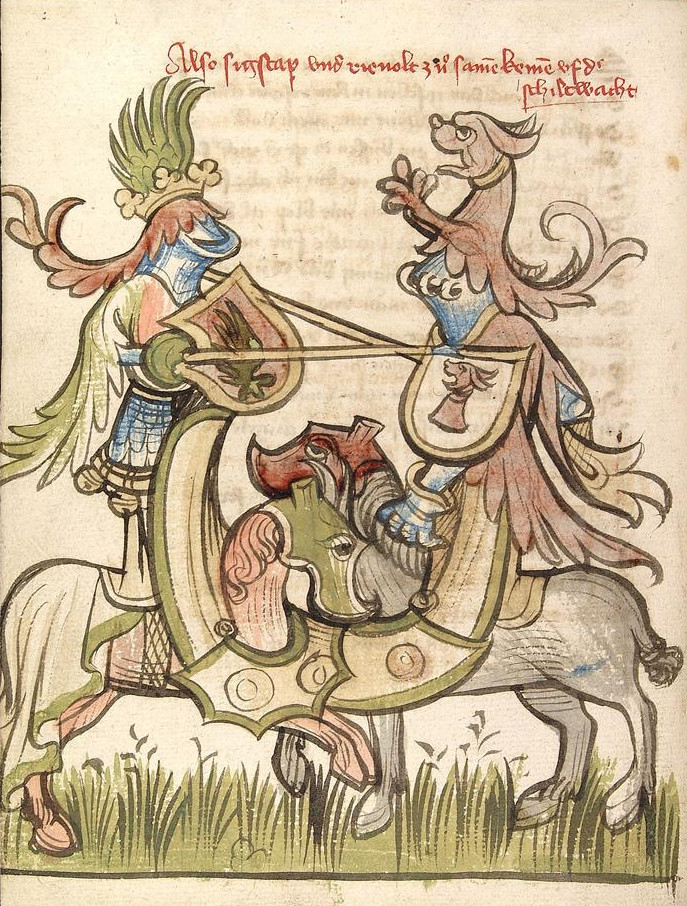
Joust
Jousting is a medieval and renaissance martial game or hastilude between two combatants either on horse or on foot. The joust became an iconic characteristic of the knight in Romantic medievalism. The term is derived from Old French , ultimately from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , ultimately from Latin "to approach, to meet". The word was loaned into Middle English around 1300, when jousting was a very popular sport among the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman knighthood. The synonym tilt (as in tilting at windmills) dates . Jousting on horse is based on the military use of the lance by heavy cavalry. It transformed into a specialized sport during the Late Middle Ages, and remained popular with the nobility in England and Wales, Germany and other parts of Europe throughout the whole of the 16th century (while in France, it was discontinued after the death of King Henry II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. The classic definition, by François Louis Ganshof (1944),François Louis Ganshof (1944). ''Qu'est-ce que la féodalité''. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', with a foreword by F. M. Stenton, 1st ed.: New York and London, 1952; 2nd ed: 1961; 3rd ed.: 1976. describes a set of reciprocal legal and Medieval warfare, military obligations of the warrior nobility and revolved around the key concepts of lords, vassals, and fiefs. A broader definition, as described by Marc Bloch (1939), includes not only the obligations of the warrior nobility but the obligations of all three estates of the realm: the nobility, the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
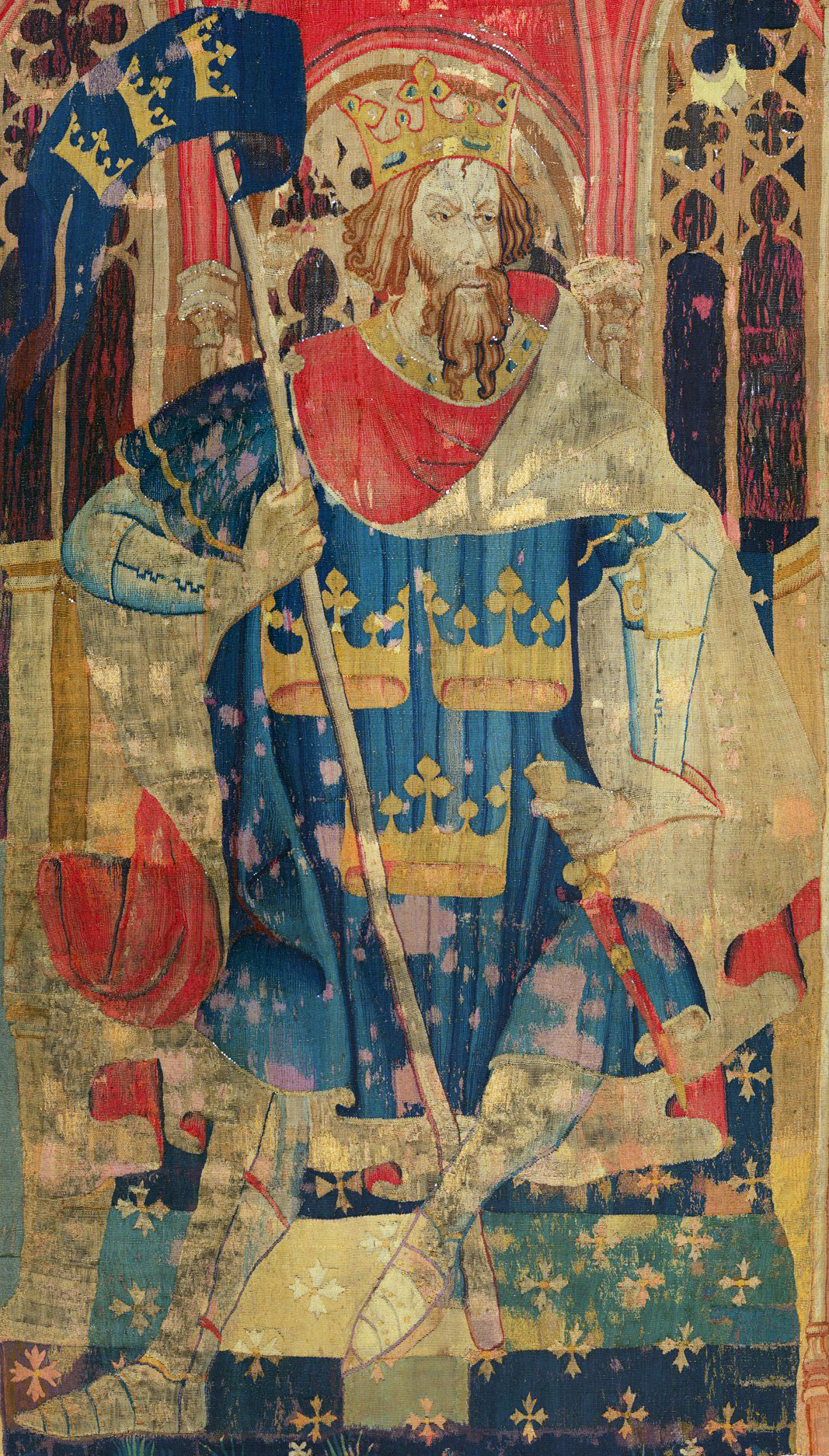
King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain. In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a leader of the Sub-Roman Britain, post-Roman Britons in battles against the Anglo-Saxons in the late-5th and early-6th centuries. He first appears in two early medieval historical sources, the ''Annales Cambriae'' and the ''Historia Brittonum'', but these date to 300 years after he is supposed to have lived, and most historians who study the period Historicity of King Arthur, do not consider him a historical figure.Tom Shippey, "So Much Smoke", ''review'' of , ''London Review of Books'', 40:24:23 (20 December 2018) His name also occurs in early Welsh-language literature, Welsh poetic sources, such as ''Y Gododdin''. The character developed through Welsh mythology, appearing either as a great warrior defending Britain from human and supernatura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain, also called post-Roman Britain or Dark Age Britain, is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the founding of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. The term was originally used to describe archaeological remains found in 5th- and 6th-century AD sites that hinted at the decay of locally made wares from a previous higher standard under the Roman Empire. It is now used to describe the period that began with the recall of Roman troops from Britannia to Gaul by Constantine III in 407 and ended with the Battle of Deorham in 577. This period has attracted a great deal of academic and popular debate, in part because of the lack of written records from the time. Meaning of terms The period of sub-Roman Britain traditionally covers the history of the parts of Britain that had been under Roman rule from the end of Roman imperial rule, traditionally dated to be in 410, to the arrival of Saint Augustine in 597. The date taken for the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastiche
A pastiche () is a work of visual art, literature, theatre, music, or architecture that imitates the style or character of the work of one or more other artists. Unlike parody, pastiche pays homage to the work it imitates, rather than mocking it. The word is the French borrowing of the Italian noun , which is a pâté or pie-filling mixed from diverse ingredients. Its first recorded use in this sense was in 1878. Metaphorically, and describe works that are either composed by several authors, or that incorporate stylistic elements of other artists' work. Pastiche is an example of eclecticism in art. Allusion is not pastiche. A literary allusion may refer to another work, but it does not reiterate it. Allusion requires the audience to share in the author's cultural knowledge. Allusion and pastiche are both mechanisms of intertextuality. By art Literature In literary usage, the term denotes a literary technique employing a generally light-hearted tongue-in-cheek imit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |