|
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute (medicine), Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis. Common causes in include: endometriosis in women, bowel adhesions, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis. The cause may also be a number of poorly understood conditions that may represent abnormal psychoneuromuscular function. The role of the nervous system in the genesis and moderation of pain is explored. The importance of psychological factors is discussed, both as a primary cause of pain and as a factor which affects the pain experience. As with other chronic syndromes, the biopsychosocial model offers a way of integrating physical causes of pain with psychological and social factors. Terminology Pelvic pain is a general term that may have many causes, listed below. The sub-categorical term urologic chronic pelvic pain syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
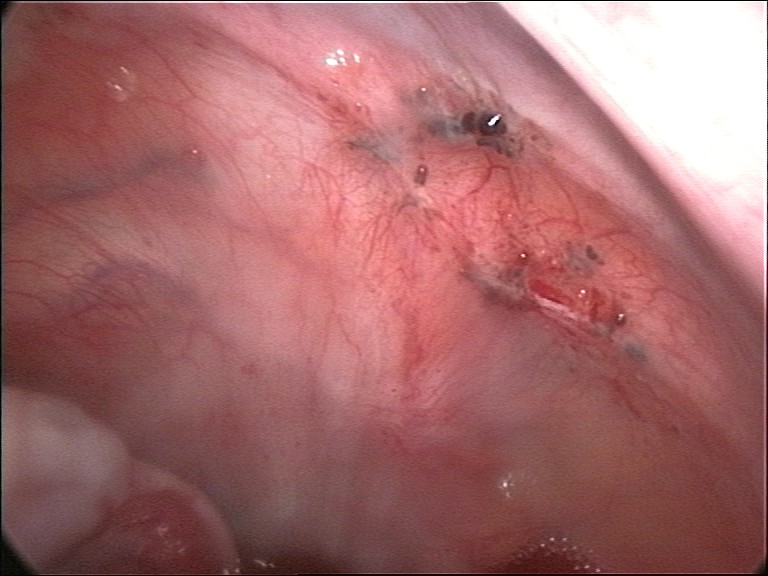
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which Tissue (biology), tissue similar to the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, grows in other places in the body, outside the uterus. It occurs in women and a limited number of other female mammals. Endometrial tissue most often grows on or around reproductive organs such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes, on the outside surface of the uterus, or the tissues surrounding the uterus and the ovaries (peritoneum). It can also grow on other organs in the pelvic region like the Gastrointestinal tract, bowels, stomach, bladder, or the cervix. Rarely, it can also occur in other parts of the body. Symptoms can be very different from person to person, varying in range and intensity. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms, while for some it can be a debilitating disease. Common symptoms include pelvic pain, Heavy menstrual bleeding, heavy and Dysmenorrhea, painful periods, pain with bowel movements, Dysuria, painful urination, Dyspareunia, pain dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asherman's Syndrome
Asherman's syndrome (AS) is an acquired uterine condition that occurs when scar tissue (adhesions) forms inside the uterus and/or the cervix. It is characterized by variable scarring inside the uterine cavity, where in many cases the front and back walls of the uterus stick to one another. AS can be the cause of menstrual disturbances, infertility, and placental abnormalities. Although the first case of intrauterine adhesion was published in 1894 by Heinrich Fritsch, it was only after 54 years that a full description of Asherman syndrome was carried out by Joseph Asherman. Several other terms have been used to describe the condition and related conditions including: uterine/cervical atresia, traumatic uterine atrophy, sclerotic endometrium, and endometrial sclerosis. There is no one cause of AS. Risk factors can include myomectomy, cesarean section, infections, age, genital tuberculosis, and obesity. Genetic predisposition to AS is being investigated. Some studies show that a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
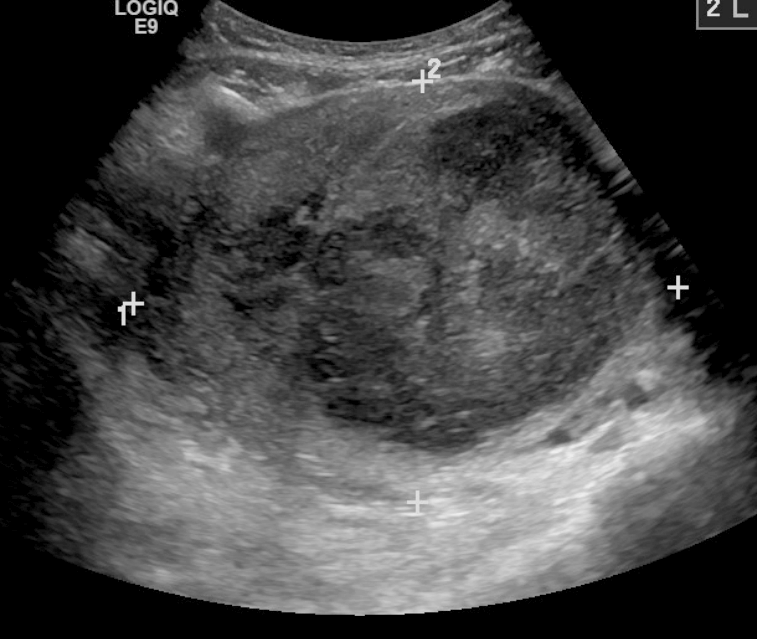
Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. They usually cause no symptoms, but occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either #Cyst rupture, breaks open or causes ovarian torsion, twisting of the ovary, it may cause severe pain. This may result in vomiting or Lightheadedness, feeling faint, and even cause headaches. Most ovarian cysts are related to ovulation, being either follicular cyst of ovary, follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. Other types include Endometrioma, cysts due to endometriosis, dermoid cysts, and cystadenomas. Many small cysts occur in both ovaries in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Pelvic inflammatory disease may also result in cysts. Rarely, cysts may be a form of ovarian cancer. Diagnosis is undertaken by pelvic examination with a pelvic ultrasound or other testing used to gather further details. Often, cysts are simply observed over time. If they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland, thyroid, parathyroid gland, parathyroid, pituitary gland, pituitary, pineal gland, pineal, and adrenal glands, and the (male) testis and (female) ovaries. The hypothalamus, pancreas, and thymus also function as endocrine glands, among other functions. (The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are organs of the Neuroendocrinology#Neuroendocrine system, neuroendocrine system. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamusit is located in the brain adjacent to the pituitary glandis to link the endocrine system to the nervous system via the pituitary gland.) Other organs, such as the kidneys, also have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name originated from the observation of cysts which form on the ovaries of some women with this condition. However, this is not a universal symptom and is not the underlying cause of the disorder. The primary characteristics of PCOS include hyperandrogenism, anovulation, insulin resistance, and neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine disruption. Women may also experience Abnormal uterine bleeding, irregular menstrual periods, Menorrhagia, heavy periods, hirsutism, excess hair, acne, pelvic pain, infertility, difficulty getting pregnant, and patches of acanthosis nigricans, darker skin. Beyond its reproductive implications, PCOS is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial metabolic condition with significant long-term health consequences, including an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. Although usually just a cosmetic ailment, in some cases they cause fatigue, pain, itch, itching, and cramp, nighttime leg cramps. These veins typically develop in the legs, just under the skin. Their complications can include bleeding, ulcer (dermatology), skin ulcers, and superficial thrombophlebitis. Varices in the scrotum are known as varicocele, while those around the Human anus, anus are known as hemorrhoids. The physical, social, and psychological effects of varicose veins can lower their bearers' quality of life. Varicose veins have no specific cause. Risk factors include obesity, lack of exercise, leg trauma, and family history of the condition. They also develop more commonly during pregnancy. Occasionally they result from chronic venous insufficiency. Underlying causes include weak or damaged valves in the veins. They are typically diagnosed by examina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic (medicine)
A chronic condition (also known as chronic disease or chronic illness) is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic as medicine progresses. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic, due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV, which allow these individuals to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
Pelvic congestion syndrome, also known as pelvic vein incompetence, is a long-term condition believed to be due to enlarged veins in the lower abdomen. The condition may cause chronic pain, such as a constant dull ache, which can be worsened by standing or sex. Pain in the legs or lower back may also occur. While the condition is believed to be due to blood flowing back into pelvic veins as a result of faulty valves in the veins, this hypothesis is not certain. The condition may occur or worsen during pregnancy. The presence of estrogen is believed to be involved in the mechanism. Diagnosis may be supported by ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or laparoscopy. Early treatment options include medroxyprogesterone or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Surgery to block the varicose veins may also be done. About 30% of women of reproductive age reporting pelvic pain are affected. It is believed to be the cause of about a third of chronic pelvic pain cases. While pelvic venous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myometrium
The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions. Structure The myometrium is located between the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterine wall) and the serosa or perimetrium (the outer uterine layer). The myometrium can be divided into three layers: * The inner one-third thickness is termed the ''junctional'' or ''sub-endometrial'' layer. In most mammals it is characterized by fibers oriented in a circular way. Humans, having a single uterus form the fusion of two Müllerian ducts, have the fibers forming two cones. Mice have an unfused uterus, so the arrangement is simply circular. * The middle layer occurs in both mice and humans. In mice it is a hard-to-spot mesh-like structure that probably helps coordinate the forces from the inner and outer layers. In humans there is also a mesh-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
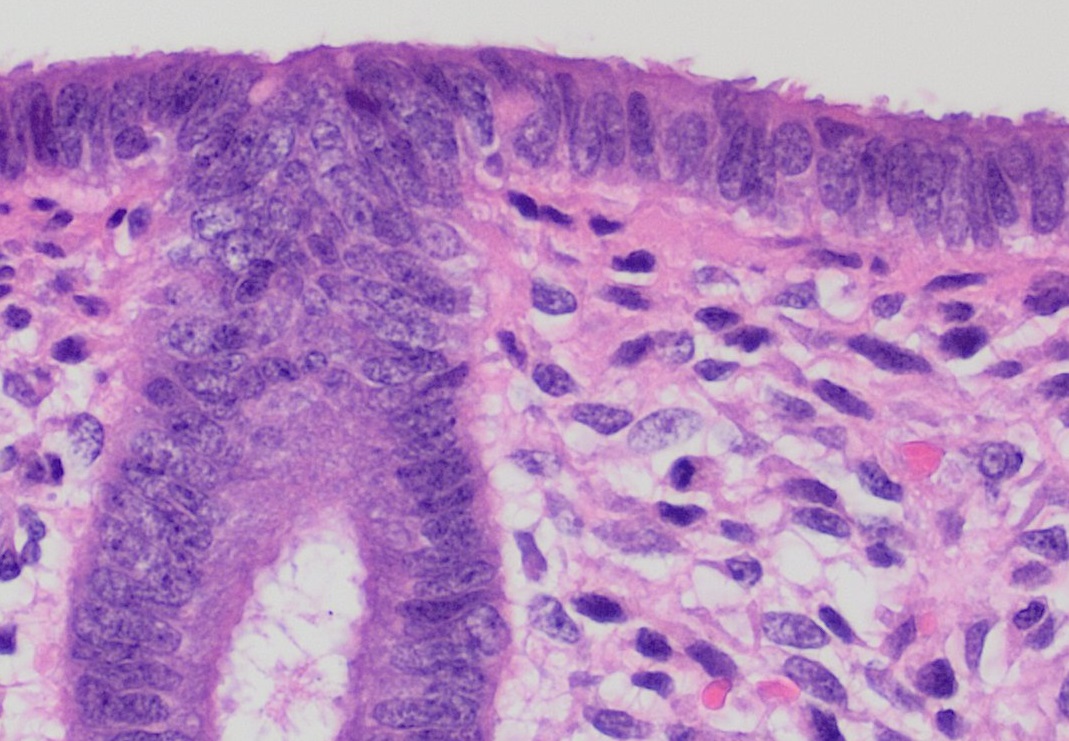
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including other apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |