|
Peloponnesian
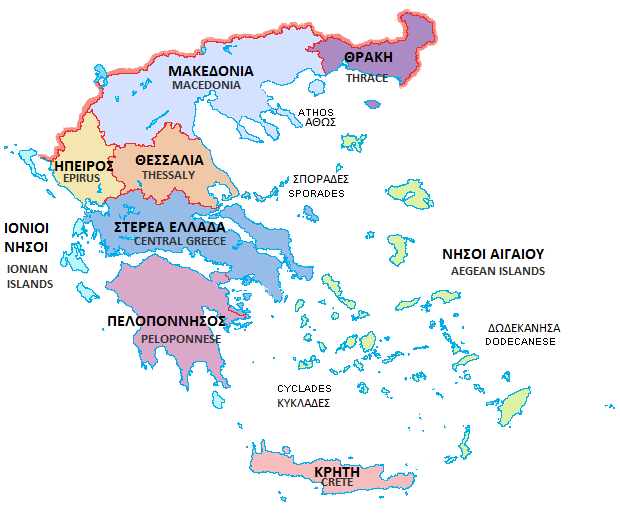
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submersible brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese (region)
The Peloponnese Region (, ) is a region in southern Greece. It borders Western Greece to the north and Attica to the north-east. The region has an area of about . It covers most of the Peloponnese peninsula, except for the northwestern subregions of Achaea and Elis which belong to Western Greece and a small portion of the Argolid peninsula that is part of Attica. Administration The Peloponnese Region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2011 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with the Western Greece and Ionian Islands regions, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian Islands based at Patras. The region is based at Tripoli and is divided into five regional units (pre-Kallikratis prefectures), * Arcadia, * Argolis, * Corinthia, * Laconia and * Messenia, which are further subdivided into 26 municipalities. The largest city of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
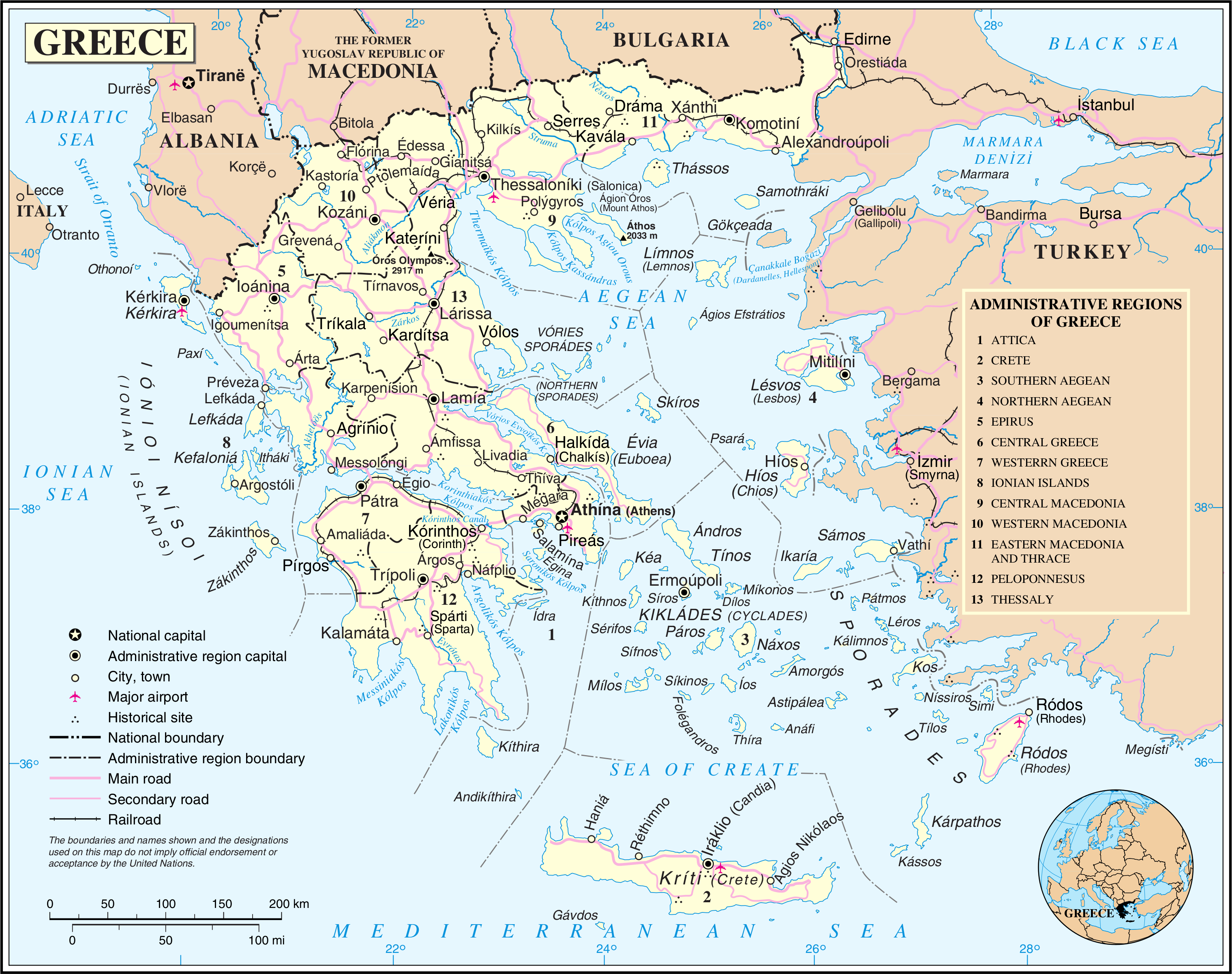
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkadia Idyll Peloponnese
Arcadia ( ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, administrative region of Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese. It is in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological figure Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan (god), Pan. Geography Arcadia is a rural, mountainous regional unit comprising about 18% of the land area of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is the peninsula's largest regional unit. According to the 2021 census, it has 77,592 inhabitants; its capital, Tripoli, has about 30,400 residents in the city proper, and about 44,000 total in the greater metropolitan area. Arcadia consists partly of farmland, and to a larger extent grassland and degenerated Garrigue, shrubland. It also has three mountain ranges, with forestation mainly at altitudes above 1000 meters: Mainalo, a winter ski resort, situated in the central north; Parnon in the central south; and Mount Lyka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demotic Greek
Demotic Greek (, , , ) is the standard spoken language of Greece in modern times and, since the resolution of the Greek language question in 1976, the official language of Greece. "Demotic Greek" (with a capital D) contrasts with the conservative Katharevousa, which was used in formal settings, during the same period. In that context, Demotic Greek describes the specific non-standardized vernacular forms of Greek used by the vast majority of Greeks during the 19th and 20th centuries. As is typical of diglossic situations, Katharevousa and Demotic complemented and influenced each other. Over time, Demotic became standardized. In 1976, it was made the official language of Greece. It continued to evolve and is now called Standard Modern Greek. The term "demotic Greek" (with a minuscule d) also refers to any variety of the Greek language which has evolved naturally from Ancient Greek and is popularly spoken. Basic features Demotic Greek differs in a few ways from Ancient Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Greece
Western Greece Region (, ) is one of the thirteen Modern regions of Greece, administrative regions of Greece. It comprises the western part of Central Greece (geographic region), continental Greece and the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It occupies an area of and its population is, according to the 2011 census, at 679,796 inhabitants. The capital of the Western Greece is Patras, the third-largest-city in the country with a population of about 280,000 inhabitants. The NUTS statistical regions of Greece, NUTS 2 code for the region of Western Greece is EL63. Administration The region of Western Greece was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese and the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands regions, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian Islands based at Patras. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Regions Of Greece
The traditional geographic regions of Greece () are the country's main historical-geographic regions, and were also official administrative subdivisions of Greece, regional subdivisions of Greece until the 1987 administrative reform.Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (''Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of regional development, Government Gazette (Greece), ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987 Despite their replacement as first-level administrative units by only partly identical regions of Greece, administrative regions (), the nine traditional geographic regions—six on the mainland and three island groups—are still widely referred to in unofficial contexts and in daily discourse. , the official administrative divisions of Greece consist of 13 regions ()—nine on the mainland and four island groups—which are furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morea
Morea ( or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used by the Principality of Achaea, the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman Empire for the Morea Eyalet, and later by the Republic of Venice for the short-lived Kingdom of the Morea. Etymology There is some uncertainty over the origin of the medieval name "Morea", which is first recorded in the 10th century in the Byzantine chronicles. Traditionally, scholars thought the name to have originated from the word ''morea'' (μορέα), meaning morus or mulberry, a tree which, though known in the region from the ancient times, gained value after the 6th century, when mulberry-eating silkworms were smuggled from China to Byzantium. The British Byzantinist Steven Runciman suggested that the name comes "from the likeness of its shape to that of a mulberry leaf". History After the conquest of Constantinople by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible Bridge
A submersible bridge is a type of movable bridge that lowers the bridge deck below the water level to permit waterborne traffic to use the waterway. This differs from a lift bridge or table bridge, which operate by raising the roadway. Two submersible bridges exist across the Corinth Canal in Greece, one at each end, in Isthmia and Corinth. They lower the centre span to 8 metres below water level when they give way to vessels crossing the channel. The submersible bridge's primary advantage over the similar lift bridge is that there is no structure above the shipping channel and thus no height limitation on ship traffic. This is particularly important for sailing vessels. Additionally, the lack of an above-deck structure is considered aesthetically pleasing, a similarity shared with the Chicago-style bascule bridge and the table bridge. However, the presence of the submerged bridge structure limits the draft Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to: Watercraft dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |