|
Peleset
The Peleset () or Pulasati are a people appearing in fragmentary historical and iconographic records in ancient Egyptian from the Eastern Mediterranean in the late 2nd millennium BCE. They are hypothesised to have been one of the several ethnic groups of which the invading Sea Peoples were said to be composed. Today, historians generally identify the Peleset with the Philistines. Records Very few documentary records exist, both for the Peleset and for the other groups hypothesized as Sea Peoples. One group of people recorded as participating in the Battle of the Delta were the ''Peleset''; after this point in time, the "Sea Peoples" as a whole disappear from historical records, the Peleset being no exception. Archaeological evidence supports the existence of a migration of Peleset/Philistines from the Aegean into the southern Levant. The five known sources are below: * : Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III: records a people called the ''P-r-s-t'' (conventionally ''Peleset'') am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia. There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines originated from a Greek immigrant group from the Aegean. The immigrant group settled in Canaan around 1175 BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse. Over time, they intermixed with the indigenous Canaanite societies and assimilated elements from them, while preserving their own unique culture. In 604 BC, the Philistines, who had been under the rule of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–605 BC), were ultimately vanquished by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Much like the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, the Philistines lost their autonomy by the end of the Iron Age, becoming vassals to the Assyrians, Egyptians, and later Babylonians. Historical sources suggest that Nebuchadnezzar II destroyed Ashkelon and Ekron due to the Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologists Emmanuel de Rougé and Gaston Maspero, on the basis of primary sources such as the reliefs on the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III at Medinet Habu (temple), Medinet Habu. Subsequent research developed the hypothesis further, attempting to link these sources to other Late Bronze Age evidence of migration, piracy, and destruction. While initial versions of the hypothesis regarded the Sea Peoples as a primary cause of the Late Bronze Age collapse, more recent versions generally regard them as a symptom of events which were already in motion before their purported attacks. The Sea Peoples included well-attested groups such as the Lukka, as well as others such as the Weshesh whose origins are unknown. Hypotheses regarding the origin of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padiiset's Statue
Padiiset's Statue or Pateese's Statue, also described as the Statue of a vizier usurped by Padiiset, is a basalt statue found in 1894 in an unknown location in the Egyptian delta which includes an inscription referring to trade between Canaan and the Peleset (Philistines) and Ancient Egypt during the Third Intermediate Period.The Statuette of an Egyptian Commissioner in Syria, Georg Steindorff, The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, Vol. 25, No. 1 (Jun., 1939), pp. 30-33 "At the beginning of the year 1894 was found, reputedly in the Delta, a slightly damaged statuette of black basalt..." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
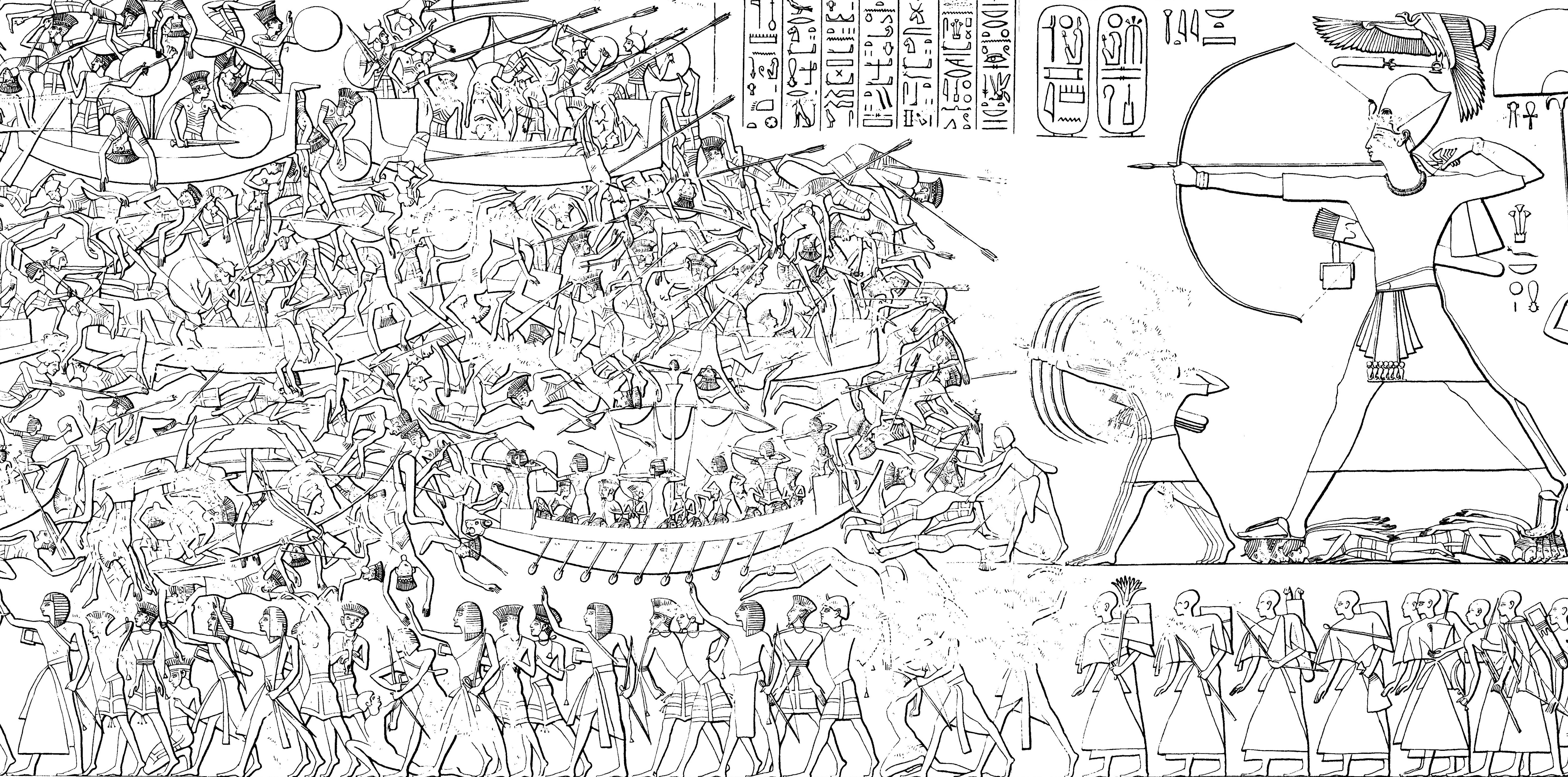
Battle Of The Delta
The Battle of the Delta was a sea battle between Egypt and the Sea Peoples, circa 1175 BC, when the Egyptian pharaoh Ramesses III repulsed a major sea invasion. The conflict occurred on the shores of the eastern Nile Delta and on the border of the Egyptian Empire in Syria, although precise locations of the battles are unknown. This major conflict is recorded on the temple walls of the mortuary temple of pharaoh Ramesses III at Medinet Habu. Historical background In the 12th century BC, the Sea Peoples (which consisted of several groups, such as Tjekker, Peleset, and Sherden) invaded the Middle East from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. They attacked Syria and the Southern Levant, where many cities were burned and ruined. (Carchemish was one of the cities which survived the Sea People's attacks.) Cyprus had also been overwhelmed and its capital sacked. Since the Medinet Habu inscriptions depict women and children loaded in ox carts, the attackers are believed to have been migrants l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. Some scholars date his reign from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC, and he is considered the last pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom to have wielded substantial power. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. This coincided with a decline in the cultural sphere of Ancient Egypt. However, his successful defense was able to slow down the decline, although it still meant that his successors would have a weaker military. He has also been described as a "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when Late Bronze Age c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shekelesh
The Shekelesh (Egyptian language: ''šꜣkrwšꜣꜣ'' or ''šꜣꜣkrwšꜣꜣ'') were one of the several ethnic groups the Sea Peoples were said to be composed of, appearing in fragmentary historical and iconographic records in ancient Egyptian from the Eastern Mediterranean in the late 2nd millennium BC. Earliest records The Shekelesh first appears in Egyptian records during accounts of the pharaoh Merneptah's military campaigns in modern Libya in the closing years of the 13th century BC, as recounted on the Great Karnak Inscription. In the text, the Shekelesh, alongside other clans of the Sea Peoples, are described as auxiliary troops of the Libyan ruler Meryey, and Merneptah recounts he killed between 200 and 222 of them. Nearly thirty years later, the Shekelesh are mentioned within the exploits of Ramesses III, where they, along with the Peleset, Tjeker, Denyen, and Weshesh, are described as forming a foothold in the Amurru kingdom during the 8th year of his reign. Ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjeker
The Tjeker or Tjekker (Egyptian: ''ṯꜣkꜣr'' or ''ṯꜣkkꜣr'') were one of the Sea Peoples. Known mainly from the "Story of Wenamun", the Tjeker are also documented earlier, at Medinet Habu, as raiders defeated by Pharaoh Ramesses III of Egypt in years 5, 8, and 12 of his reign. They are thought to be the people who developed the port of Dor in Canaan during the 12th century BCE from a small Bronze Age town to a large city. References Origin As with other Sea Peoples, the origins of the Tjeker are uncertain. Their name is an Egyptian exonym, usually romanized as ''tkr'', and expanded as ''Tjekru'' or ''Djekker''. As such there is no consensus on the original form or etymology of the name, or the origin of the people. They have sometimes been identified with the Sicels of Sicily, who are also linked to '' Shekelesh'': another exonym attributed to a different group amongst the Sea Peoples. Another theory, put forward by Flinders Petrie, links the ethnonym to Zakros, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Islands In The Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea basin is supposed to host more than 10,000 islands, with 2,217 islands larger than 0.01 km2. The two main island countries in the region are Malta and Cyprus, while other countries with islands in the Mediterranean Sea include Albania, Algeria, Croatia, Egypt, France, Greece, Israel, Italy, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Montenegro, Palestine, Spain, Syria, Tunisia and Turkey. By area By population (above 200,000) By country Albania * Sazan * Kunë * Ksamil Islands * Franz Joseph Island * Zvërnec Islands * Tongo Island * Stil Island Croatia France * Corsica ** Lavezzi Islands ** Cavallo Island * Frioul archipelago * Lérins Islands * Îles d'Hyères Greece * Crete * Euboea * Gavdos Cyclades Dodecanese Islands Ionian Islands North Aegean islands Saronic Islands Sporades Islands Italy Notable Italian islands include: * Calabria ** Coreca Reefs ** Isola di Dino ** San Nicola Arcella * Campanian Archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekwesh
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively. The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwesh which appear in texts from the Late Bronze Age and are believed to refer to the Mycenaean civilization or some part of it. In the historical period, the term fell into disuse as a general term for Greek people, and was generally reserved for inhabitants of the region of Achaea, a region in the north-central part of the Peloponnese. The city-states of this region later formed a confederation known as the Achaean League, which was influential during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. Etymology According to Margalit Finkelberg the name Ἀχαιοί ( earlier Ἀχαιϝοί) is possibly derived, via an intermediate form *Ἀχαϝyοί, from a hypothetical older Greek form reflected in the Hittite form ''Aḫḫiyawā''; the latter is atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
02010 Sea People, Medinet Habu Ramses III
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |