|
Peire Rogier
Peire Rogier (born c. 1145) was a twelfth-century Auvergnat troubadour (floruit, fl. 1160 – 1180) and cathedral canon from Clermont-Ferrand, Clermont. He left his cathedral to become a travelling minstrel before settling down for a time in Narbonne at the court of Ermengard of Narbonne, Viscountess Ermengard. His life and career are known because his late thirteenth-century ''Vida (Occitan literary form), vida'' survives, as well as some of his works. The reliability of his ''vida'', upon which all the details of his goings and comings are known, however, is not complete. According to it, he left the religious life to become a jongleur. He fell in love with his hostess and patron and wrote many songs in her honour, giving Ermengard the nickname ''Tort-n'avetz'' ("You are wrong"), but for what reasons is unknown.Cheyette, 8. Eventually the people of the Narbonnaise believed that he was in a sexual relationship with the viscountess and so she asked him to leave. He moved on to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfonso II Of Aragon
Alfonso II (1–25 March 1157Benito Vicente de Cuéllar (1995)«Los "condes-reyes" de Barcelona y la "adquisición" del reino de Aragón por la dinastía bellónida» p. 630-631; in ''Hidalguía''. XLIII (252) pp. 619–632."Alfonso II el Casto, hijo de Petronila y Ramón Berenguer IV, nació en Huesca en 1157;". ''Cfr''. Josefina Mateu Ibars, María Dolores Mateu Ibars (1980)''Colectánea paleográfica de la Corona de Aragon: Siglo IX-XVIII'' Universitat Barcelona, p. 546. , .Antonio Ubieto Arteta (1987)''Historia de Aragón. Creación y desarrollo de la Corona de Aragón'' Zaragoza: Anúbarpp. 177–184§ "El nacimiento y nombre de Alfonso II de Aragón". . – 25 April 1196), called the Chaste or the Troubadour, was the King of Aragon and, as Alfons I, the Count of Barcelona from 1164 until his death. The eldest son of Count Ramon Berenguer IV of Barcelona and Queen Petronilla of Aragon, he was the first King of Aragon who was also Count of Barcelona. He was also Count of Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1140s Births
114 may refer to: *114 (number) 114 (one hundred [and] fourteen) is the natural number following 113 (number), 113 and preceding 115 (number), 115. In mathematics *114 is an abundant number, a sphenic number and a Harshad number. It is the sum of the first four hyperfactorials, ... *AD 114 *114 BC *114 (1st London) Army Engineer Regiment, Royal Engineers, an English military unit *114 (Antrim Artillery) Field Squadron, Royal Engineers, a Northern Irish military unit *114 (MBTA bus) *114 (New Jersey bus) *114 Kassandra, a main-belt asteroid See also *11/4 (other) *Flerovium, synthetic chemical element with atomic number 114 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musicians From Clermont-Ferrand
A musician is someone who composes, conducts, or performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general term used to designate a person who follows music as a profession. Musicians include songwriters, who write both music and lyrics for songs; conductors, who direct a musical performance; and performers, who perform for an audience. A music performer is generally either a singer (also known as a vocalist), who provides vocals, or an instrumentalist, who plays a musical instrument. Musicians may perform on their own or as part of a group, band or orchestra. Musicians can specialize in a musical genre, though many play a variety of different styles and blend or cross said genres, a musician's musical output depending on a variety of technical and other background influences including their culture, skillset, life experience, education, and creative preferences. A musician who records and releases music is often referred to as a recordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century French Troubadours
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculum (journal)
''Speculum: A Journal of Medieval Studies'' is a quarterly academic journal published by University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Medieval Academy of America. Established in 1926 by Edward Kennard Rand, it is widely regarded as the most prestigious journal in medieval studies. The journal's primary focus is on the time period from 500 to 1500 in Western Europe, but also on related subjects such as Byzantine, Hebrew, Arabic, Armenian and Slavic studies. , the editor is Katherine L. Jansen. The organization and its journal were first proposed in 1921 at a meeting of the Modern Language Association, and the journal's focus was interdisciplinary from its beginning, with one reviewer noting a specific interest in Medieval Latin Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiraut De Bornelh
Giraut de Bornelh (; c. 1138 – 1215), whose first name is also spelled Guiraut and whose toponym is de Borneil or de Borneyll, was a troubadour connected to the castle of the viscount of Limoges. He is credited with the formalisation, if not the invention, of the "light" style, or '' trobar leu''. Giraut was born to a lower-class family in the Limousin, probably in Bourney, near Excideuil in modern-day France. Giraut's poems were first published in various collections, including Millot's ''Histoire litteraire des troubadours'' (Paris, 1774) and Raynouard's ''Choix des poésies originales des troubadours'' (Paris, 1816). Several of his poems were publosher in Alan R. Press' ''Anthology of Troubadour Lyric Poetry'' (1971). An English edition by Ruth V. Sharma has been published in 1989. One of the most popular troubadours of his day, Giraut's reputation endured throughout the 13th century, when he was known as the Master of the Troubadours. Dante placed him in Paradise as a '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman De Flamenca
''Flamenca'' () is a 13th-century anonymous romance, written in the Occitan language in Occitania. Most literary allusions in the text are from Old French sources. Authorship A certain Sir Bernardet may have been the author, however the Bernardet mentioned may simply be the fictional narrator. Nothing is known for certain about the author; however, a number of things may be inferred from the circumstances of the text itself. The author was probably not a minstrel, but rather a cleric, most likely in the service of the House of Roquefeuil-Blanquefort, Roquefeuil family at the court of Alga, and may have written the romance at the Benedictine monastery at Nant, Aveyron, Nant, Aveyron, and was erudite and may have even studied at the University of Paris. The author was probably a native of Rouergue, based on linguistic similarities in the language used in the romance and that of the region. Plot synopsis The beginning and the end of the manuscript are missing (in addition t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
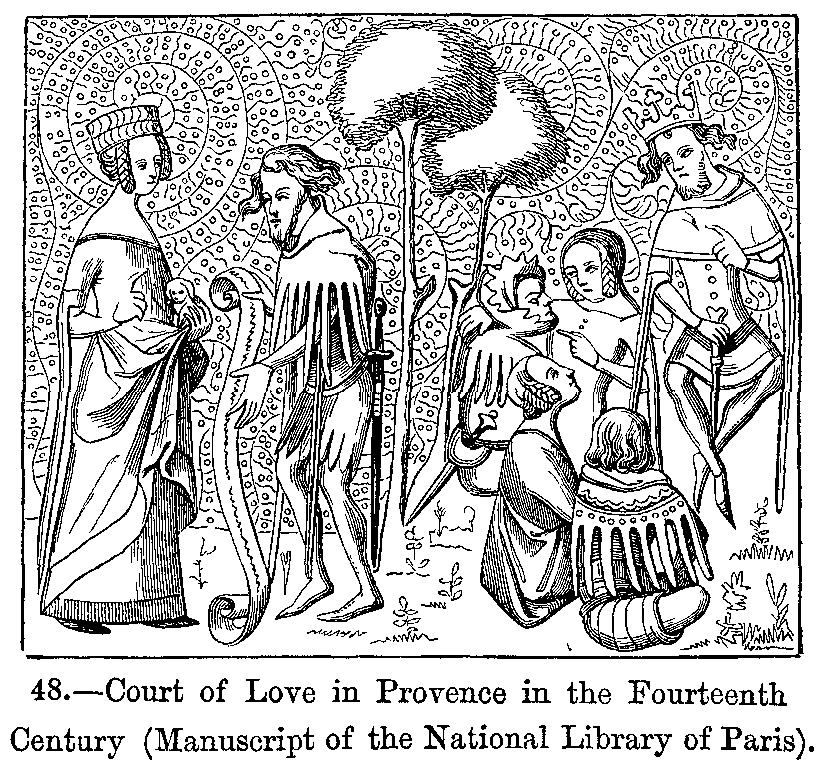
Courtly Love
Courtly love ( ; ) was a medieval European literary conception of love that emphasized nobility and chivalry. Medieval literature is filled with examples of knights setting out on adventures and performing various deeds or services for ladies because of their "courtly love". This kind of love was originally a literary fiction created for the entertainment of the nobility, but as time passed, these ideas about love spread to popular culture and attracted a larger literate audience. In the High Middle Ages, a "game of love" developed around these ideas as a set of social practices. "Loving nobly" was considered to be an enriching and improving practice. Courtly love began in the ducal and princely courts of Aquitaine, Provence, Champagne, ducal Burgundy and the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the end of the eleventh century. In essence, courtly love was an experience between erotic desire and spiritual attainment, "a love at once illicit and morally elevating, passionate and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Grandmont
Grandmontines were the monks of the Order of Grandmont, a religious order founded by Saint Stephen of Thiers, towards the end of the 11th century. The order was named after its motherhouse, Grandmont Abbey in the eponymous village, now part of the commune of Saint-Sylvestre, Haute-Vienne, Saint-Sylvestre, in the department of Haute-Vienne, in Limousin (province), Limousin, France. They were also known as the ''Boni Homines'' or ''Bonshommes''. Founding The exact date of the foundation of the order is very uncertain. The traditional story involves serious chronological difficulties, and is based on a bull of Pope Gregory VII, Gregory VII, now known to be a forgery. The founder, St. Stephen of Muret (Étienne in French; also called 'of Thiers') was so impressed by the lives of the hermits whom he saw in Calabria that he desired to introduce the same manner of life into his native country. Stephen, being ordained, in 1073 obtained the Pope's permission to establish an order. He is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peire D'Alvernhe
Peire d'Alvernhe or d'Alvernha (''Pèire'' in modern Occitan; b. c. 1130) was an Auvergnat troubadour (active 1149–1170) with twenty-oneGaunt and Kay, 287. or twenty-fourEgan, 72.Aubrey, ''The Music of the Troubadours'', 8. surviving works. He composed in an "esoteric" and "formally complex" style known as the '' trobar clus''. He stands out as the earliest troubadour mentioned by name in Dante's ''Divine Comedy'' and ''De vulgari eloquentia''. Life According to his '' vida'', Peire was a burgher's son from the Diocese of Clermont.Egan, 71. As testified to by his ''vida'', his popularity was great within his lifetime and afterwards. Said to be handsome, charming, wise, and learned, he was "the first good inventor of poetry to go beyond the mountains" (i.e. the Pyrenees) and travel in Spain. He passed his time in Spain at the court of Alfonso VII of Castile and that of his son Sancho III in 1157–1158. It is possible that he was present at a meeting between Sancho of Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond V Of Toulouse
Raymond V (; c. 1134 – c. 1194) was Count of Toulouse from 1148 until his death in 1194. He was the son of Alphonse I of Toulouse and Faydida of Provence. Alphonse took his son with him on the Second Crusade in 1147. When Alphonse died in Caesarea in 1148, the county of Toulouse passed to his son Raymond, then aged 14. Raymond co-ruled with his brother Alfonso II. The young count was honoured by Rorgo Fretellus, archdeacon of Nazareth, who dedicated a new edition of his ''Description of the Holy Places'' to him. As count, Raymond permitted the first assembly of townsmen in Toulouse, the origin of the later capitouls. In 1165, in the town of Lombers, the bishop of Albi, attended by both clerics and members of the nobility, including Constance, the wife of Raymond V, interrogated and debated with members of an alleged heretical sect. Calling themselves "Good Men", this group held beliefs similar to those of Henry of Lausanne and Peter of Bruys as well as indicating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |