|
Pedro De Garmendia
Pedro de Garmendia (1794-1865) was briefly Governor of Tucumán Province in Argentina from December 1840 to January 1841 during a civil war between Unitarian and Federalist factions. Background Pedro de Garmendia was a wealthy resident of San Miguel de Tucumán, born in 1794 to José Ignacio de Garmendia y Aguirre and Elena Alurralde. His house was on what today is the corner of 24 de Septiembre and Laprida, across from the cathedral. He was a member of the Tucumán House of Representatives that declared against the rule of Juan Manuel de Rosas, and was a minister of Governor Bernabé Piedrabuena. Governor of Tucumán On 1 December 1840 the House of Representatives accepted Piedrabuena's resignation and appointed Pedro de Garmendia as his replacement. The election was controversial, since the House was divided. On assuming office, Garmendia confirmed Dr. Marco Manuel de Avellaneda as his chief minister, a post he had held under Piedrabuena. Avellaneda was the driving force in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignacio Baz
Ignacio Baz (1826–1887) was an Argentine painter who painted many portraits of notable people in the region during his lifetime. Life Ignacio Baz was born in San Miguel de Tucumán in 1826 and died in 1887. He was a disciple, alongside Fernando García del Molino and Eustaquio Carrandi, of the renowned painter Carlos Morel. Work Baz portrayed great personalities in Tucumán, Córdoba, Buenos Aires, Santiago, Chile and Lima, Peru. He also made portraits of '' caudillos'' such as Juan Manuel de Rosas, Juan Felipe Ibarra, Facundo Quiroga and Ángel Vicente Peñaloza. When his niece offered a collection of his work for sale to state in 1904, the Senator for Tucumán Province, Alberto Soldati, spoke in favor of the purchase, saying Ignacio Baz was one of the greatest of national portrait artists. His portraits, painted over a period of forty years, were striking resemblances of the most distinguished members of the leading families in the provinces of North and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marco Manuel De Avellaneda
Marco Manuel Avellaneda (18 June 1813 – 3 October 1841) was the governor of Tucumán Province in Argentina, and father of the Argentine President Nicolás Avellaneda. He was executed after an unsuccessful revolt against the Federal government, and his head was displayed on a pike. Early years Manuel Marco Avellaneda was born in San Fernando del Valle de Catamarca on 18 June 1813, son of Nicolás Avellaneda y Tula, the first governor of Catamarca Province. He learned his first letters in the Franciscan school of Father Ramon de la Quintana, who taught Latin and rhetoric. In 1823, his parents moved to San Miguel de Tucumán. Marco Avellaneda won an official scholarship to study at the College of Moral Sciences in Buenos Aires. There he made friends with Juan Bautista Alberdi, Vicente Fidel López, Marcos Paz, Carlos Tejedor and Juan María Gutiérrez. In 1834 he earned his doctorate in Jurisprudence. Even then he stood out as speaker, and his companions called him "Marco Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1794 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The Stibo Group is founded by Niels Lund as a printing company in Aarhus (Denmark). * January 13 – The U.S. Congress enacts a law providing for, effective May 1, 1795, a United States flag of 15 stars and 15 stripes, in recognition of the recent admission of Vermont and Kentucky as the 14th and 15th states. A subsequent act restores the number of stripes to 13, but provides for additional stars upon the admission of each additional state. * January 21 – King George III of Great Britain delivers the speech opening Parliament and recommends a continuation of Britain's war with France. * February 4 – French Revolution: The National Convention of the French First Republic abolishes slavery. * February 8 – Wreck of the Ten Sail on Grand Cayman. * February 11 – The first session of the United States Senate is open to the public. * March 4 – The Eleventh Amendment to the United States Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobernador Garmendia
Gobernador Garmendia is a small town in Burruyacú Department in the Tucumán Province of Argentina. It is located on Provincial Road 336, and is from the border with Santiago del Estero Province. It is named in honor of Pedro de Garmendia Pedro de Garmendia (1794-1865) was briefly Governor of Tucumán Province in Argentina from December 1840 to January 1841 during a civil war between Unitarian and Federalist factions. Background Pedro de Garmendia was a wealthy resident of San Mi ..., appointed governor of Tucumán in 1840. The town lies in an area where soybeans are grown. There is high unemployment and limited state jobs or private commercial activity. References Populated places in Tucumán Province {{Tucumán-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoza Province
Mendoza, officially Province of Mendoza, is a province of Argentina, in the western central part of the country in the Cuyo region. It borders San Juan to the north, La Pampa and Neuquén to the south, San Luis to the east, and the republic of Chile to the west; the international limit is marked by the Andes mountain range. Its capital city is the homonymous city of Mendoza. Covering an area of 148,827 km2, it is the seventh biggest province of Argentina with 5.35% of the country's total area. The population for 2010 is 1,741,610 inhabitants, which makes it the fourth most populated province of the country, or 4.35% of the total national population. History Pre-Columbian times Archeological studies have determined that the first inhabitants in the area date from the Holocene, but there are few remains of those people to know their habits. The earliest sites of human occupation in Mendoza Province, Agua de la Cueva and Gruta del Indio, are 12,000–13,000 years old. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rodeo Del Medio
The Battle of Rodeo del Medio, fought in Mendoza Province, Argentina on 24 September 1841, was a battle between the Federalist army of Ángel Pacheco and the Unitarian army of Gregorio Aráoz de Lamadrid during the Argentine Civil Wars. The consequences of the Federalist victory would last for a decade. Background In 1840 the Northern Coalition had formed an alliance of almost all the northern provinces against the governor of Buenos Aires Province, Juan Manuel de Rosas, and his allies. General Juan Lavalle had spent more than a year fighting Rosas in Entre Ríos and Corrientes, when he had invaded Buenos Aires Province. But he failed in the invasion, retreating to Córdoba Province, where he was defeated at the Battle of Quebracho Herrado. Lavalle joined forces with Gregorio Aráoz de Lamadrid, and together they retreated to Tucumán Province. From there, Lamadrid marched towards the Cuyo provinces to open a new war front, thinking José Félix Aldao only had 800-1000 troo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Famaillá
The Battle of Famaillá (Famaillá, Tucumán Province, Argentina, September 19, 1841), was a Federal Party victory, under the command of former Uruguayan president Manuel Oribe, over the army of the Unitarian Party under general Juan Lavalle, during the Argentine Civil War. Prelude to the battle After the failure of Lavalle's army to occupy Buenos Aires and its defeat at the Battle of Quebracho Herrado, his army and the one under the command of Gregorio Aráoz de Lamadrid had to abandon Córdoba Province, marching to the northern Argentine provinces. There they formed an alliance known as Coalition of the North, of Unitarian inspiration, which assembled powerful forces in the fight against Juan Manuel de Rosas and his allies. While Lamadrid formed a new army in Tucumán Province, Lavalle spent several months in a campaign in La Rioja Province, to delay Oribe and to give his ally time to prepare. In order to open new fronts, he sent two divisions, one to Santiago del Estero, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
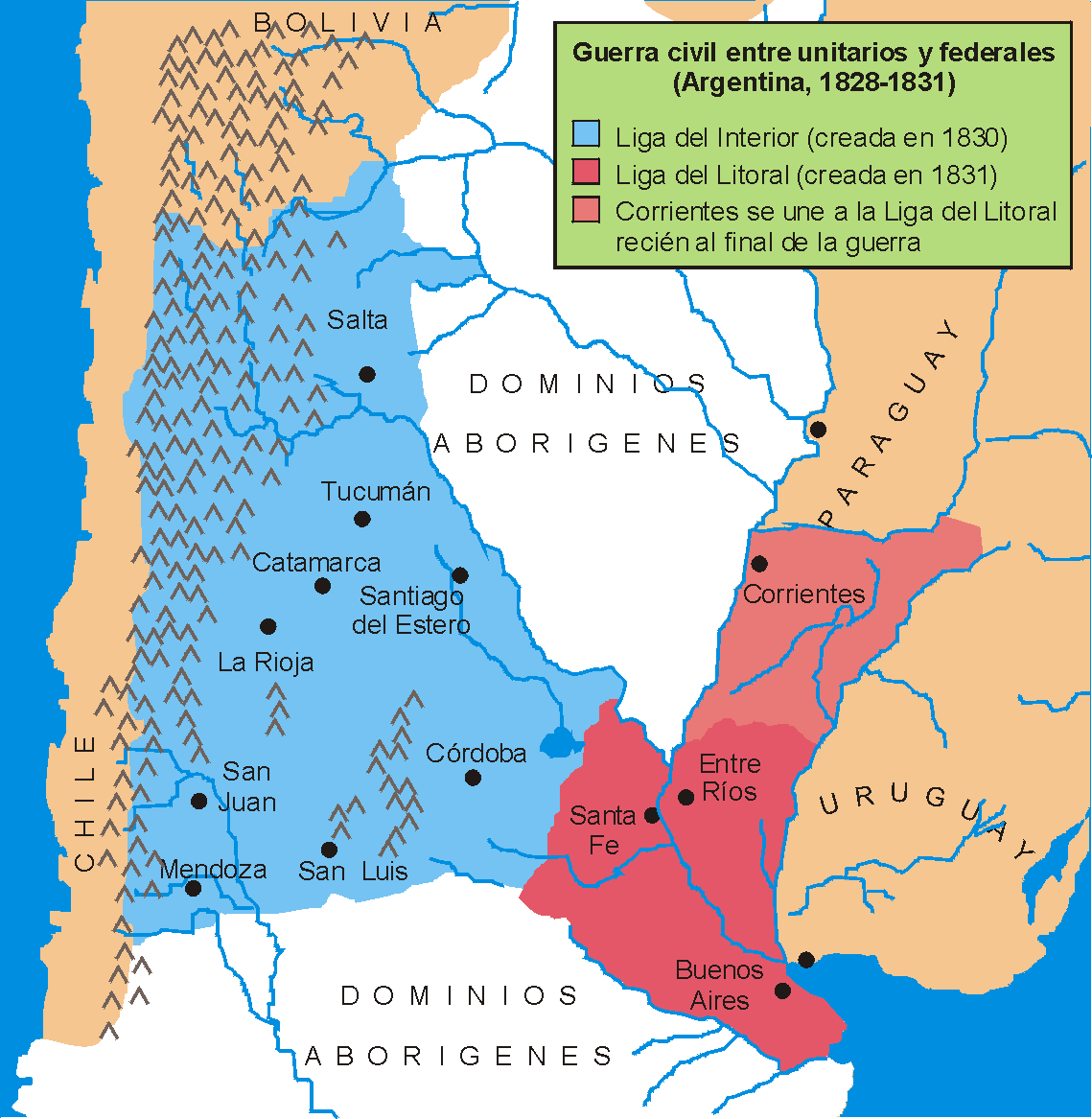
Unitarian League
The Unitarian League ( es, Liga Unitaria) also referred to as the League of the Interior () was a league of provinces of Argentina led by José María Paz, established in 1830, aiming to unite the country under unitarian principles. It comprised the provinces of San Luis, La Rioja, Catamarca, Mendoza, San Juan, Tucumán, Córdoba, Salta and Santiago del Estero. It was opposed and ultimately defeated by the provinces of the Federal Pact. Formation After the Argentine-Brazilian war, which brought the independence of the Banda Oriental del Uruguay, the political situation in the provinces was greatly effected by the disappearance of Rivadavia's Unitarian national government. Due to this the provinces proclaimed their autonomy and gave the governor of Buenos Aires, Manuel Dorrego, the responsibility to manage Argentina's foreign relations. Many attempts were made to reorganize the national government under the ideals of the Federalist Party, but they all failed, as a result, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Manuel De Rosas
Juan Manuel José Domingo Ortiz de Rosas (30 March 1793 – 14 March 1877), nicknamed "Restorer of the Laws", was an Argentine politician and army officer who ruled Buenos Aires Province and briefly the Argentine Confederation. Although born into a wealthy family, Rosas independently amassed a personal fortune, acquiring large tracts of land in the process. Rosas enlisted his workers in a private militia, as was common for rural proprietors, and took part in the disputes that led to numerous civil wars in his country. Victorious in warfare, personally influential, and with vast landholdings and a loyal private army, Rosas became a caudillo, as provincial warlords in the region were known. He eventually reached the rank of brigadier general, the highest in the Argentine Army, and became the undisputed leader of the Federalist Party. In December 1829, Rosas became governor of the province of Buenos Aires and established a dictatorship backed by state terrorism. In 1831, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors Of Tucumán Province
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federales (Argentina)
The Federalist Party was the nineteenth century Argentine political party that supported federalism. It opposed the Unitarian Party that claimed a centralised government of Buenos Aires Province, with no participation of the other provinces of the custom taxes benefits of the Buenos Aires port. The ''federales'' supported the autonomy of the provincial governments and the distribution of external commerce taxes among the provinces. The federalists advocated a form of political organization that would ensure coexistence between autonomous provinces and a central government with limited powers. They took as a model the federalism of the United States. The view on its historical leader is controversial. Juan Manuel de Rosas is considered by his detractors as a "dictator". Among the various possible ways of characterizing him, his supporters call him a "man of order."http://biblioteca.clacso.edu.ar/clacso/otros/20130610085809/ANSALDI.pdf Ideology and principles They promoted econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
