|
Pazuzu (band)
In ancient Mesopotamian religion, Pazuzu () is a demonic deity who was well known to the Babylonians and Assyrians throughout the first millennium BCE. He is shown with "a rather canine face with abnormally bulging eyes, a scaly body, a snake-headed penis, the talons of a bird and usually wings". He was believed to be the son of the god Hanbi. He was usually regarded as evil, but he could also sometimes be a beneficent entity who protected against winds bearing pestilence and he was thought to be able to force the demoness Lamashtu, his rival, back to the underworld. Amulets bearing his image were positioned in dwellings to protect infants from Lamashtu and pregnant women frequently wore amulets with his head on them as protection from her. As an apotropaic entity, he is considered as both a personification of a destructive and dangerous wind, but also as a repellant to other demons, one who safeguards the home from their influence. In particular he protects pregnant women and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back Silurian, 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The Scorpion sting, venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Exorcist (novel)
''The Exorcist'' is a 1971 horror novel written by American writer William Peter Blatty and published by Harper & Row. The book details the demonic possession of eleven-year-old Regan MacNeil, the daughter of a famous actress, and the two priests who attempt to exorcise the demon. The novel was the basis of a highly successful 1973 film adaptation, whose screenplay was also written and produced by Blatty, for which he won the Academy Award for Best Adapted Screenplay and was nominated for Best Picture. More movies and books were eventually added to ''The Exorcist'' franchise. The novel was inspired by a 1949 case of supposed demonic possession and exorcism that Blatty heard about while he was a student in the class of 1950 at Georgetown University. As a result, the novel takes place in Washington, D.C., near the campus of Georgetown University. In September 2011, the novel was reprinted by HarperCollins to celebrate its 40th anniversary, with slight revisions made by Blat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humbaba
Humbaba (Ḫumbaba; , ''Ḫumbāba'', with an optional determinative ), originally known as Ḫuwawa in Sumerian (, ''Ḫuwāwa''), was a figure in Mesopotamian mythology. The origin and meaning of his name are unknown. He was portrayed as an anthropomorphic figure comparable to an ogre or giant. He is best known from Sumerian and Akkadian narratives focused on the hero Gilgamesh, including short compositions belonging to the curriculum of scribal schools, various versions of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', and several Hurrian and Hittite adaptations. He is invariably portrayed as the inhabitant or guardian of the cedar forest, to which Gilgamesh ventures with his companion Enkidu. The subsequent encounter leads to the death of Humbaba, which provokes the anger of the gods. Humbaba is also attested in other works of Mesopotamian literature. Multiple depictions of him have also been identified, including combat scenes and apotropaic clay heads. It has been suggested that the icono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient Composition (language), literary composition written in Sumerian language, Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims to power of various city-states and kingdoms in southern Mesopotamia during the late third and early second millennium BC. It does so by repetitively listing Sumerian cities, the kings that ruled there, and the lengths of their reigns. Especially in the early part of the list, these reigns often span thousands of years. In the oldest known version, dated to the Third Dynasty of Ur, Ur III period () but probably based on Akkadian Empire, Akkadian source material, the ''SKL'' reflected a more linear transition of power from Kish (Sumer), Kish, the first city to receive kingship, to Akkad (city), Akkad. In later versions from the Old Babylonian Empire, Old Babylonian period, the list consisted of a large number of cities between which kingshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Leilan
Tell Leilan is an archaeological site situated near the Wadi Jarrah in the Khabur River basin in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. The site has been occupied since the 5th millennium BC. During the late third millennium, the site was known as Shekhna. During that time it was under control of the Akkadian Empire and was used as an administrative center. Around 1800 BC, the site was renamed "Šubat-Enlil" by the king Shamshi-Adad I, and it became his residential capital. Shubat-Enlil was abandoned around 1700 BC. Geography The site is located close to some other flourishing cities of the time. Hamoukar is about 50 km away to the southeast. Tell Brak is about 50 km away to the southwest, and also in the Khabur River basin. Tell Mozan (Urkesh) is about 50 km to the west. Leilan, Brak and Urkesh were particularly prominent during the Akkadian period. History The city originated around 5000 BC as a small farming village. Early Bronze Early Dynastic IIIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bazi (king)
Bazi (, '' dBa-z''i) was a legendary king of Mari. He is mentioned in the recension of the ''Sumerian King List'' from Tell Leilan and in a version of the ''Ballad of Early Rulers'' known from Emar. The former of these two texts indicates he was deified. The god Bazi known only from the Old Babylonian ''Song of Bazi'' is presumed to be the same figure. Overview According to the Tell Leilan recension of the ''Sumerian King List'', Bazi was one of the kings of Mari. He is the third of the Mariote kings listed, with Anba as his predecessor and Zizi as his successor, though a variant from Nippur apparently places Zizi before him. The list assigns a 30 years long reign to him and characterizes him as a leatherworker. Bazi is attested as an ordinary given name, presumably of Sumerian origin, and a number of individuals bearing it, including an inhabitant of Mari, have been identified in economic texts from between the Early Dynastic and Ur III periods. However, it is presume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amulet
An amulet, also known as a good luck charm or phylactery, is an object believed to confer protection upon its possessor. The word "amulet" comes from the Latin word , which Pliny's ''Natural History'' describes as "an object that protects a person from trouble". Anything can function as an amulet; items commonly so used include statues, coins, drawings, plant parts, animal parts, and written words. Amulets which are said to derive their extraordinary properties and powers from magic or those which impart luck are typically part of folk religion or paganism, whereas amulets or Sacramental, sacred objects of Organized religion, formalised mainstream religion as in Christianity are believed to have no power of their own without faith in Jesus and being blessing, blessed by a clergyman, and they supposedly will also not provide any preternatural benefit to the bearer who does not have an Disposition#Religion, appropriate disposition. Talisman and amulets have interchangeable meanings. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lulal
Lulal, inscribed dlú.làl in cuneiform(𒀭𒇽𒋭), was a Mesopotamian god associated with Inanna, usually as a servant deity or bodyguard but in a single text as a son. His name has Sumerian origin and can be translated as "syrup man." In the second and first millennium BCE, Lulal evolved into an anthropomorphic god/demon used on protective amulets, figurines and exorcists’ paraphernalia used in apotropaic rituals, such as Šurpu and Maqlu, usually displayed alongside Ugallu, “Big Weather Beast”, the lion-headed demon, or with his Akkadian alter-ego Lātarāk. Function as God As a god, Lulal functioned as the Sumerian counterpart of the Akkadian Latarak. His name likely means "syrup man" or "man sweet like syrup." His precise function is not fully understood. It is theorized that he was a god of animal husbandry, evidenced by one epithet of his ''lugal-eden-na'' "King of the Steppe," and his connection with the cult place of Bad-tibira and the god Šakkan, who se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
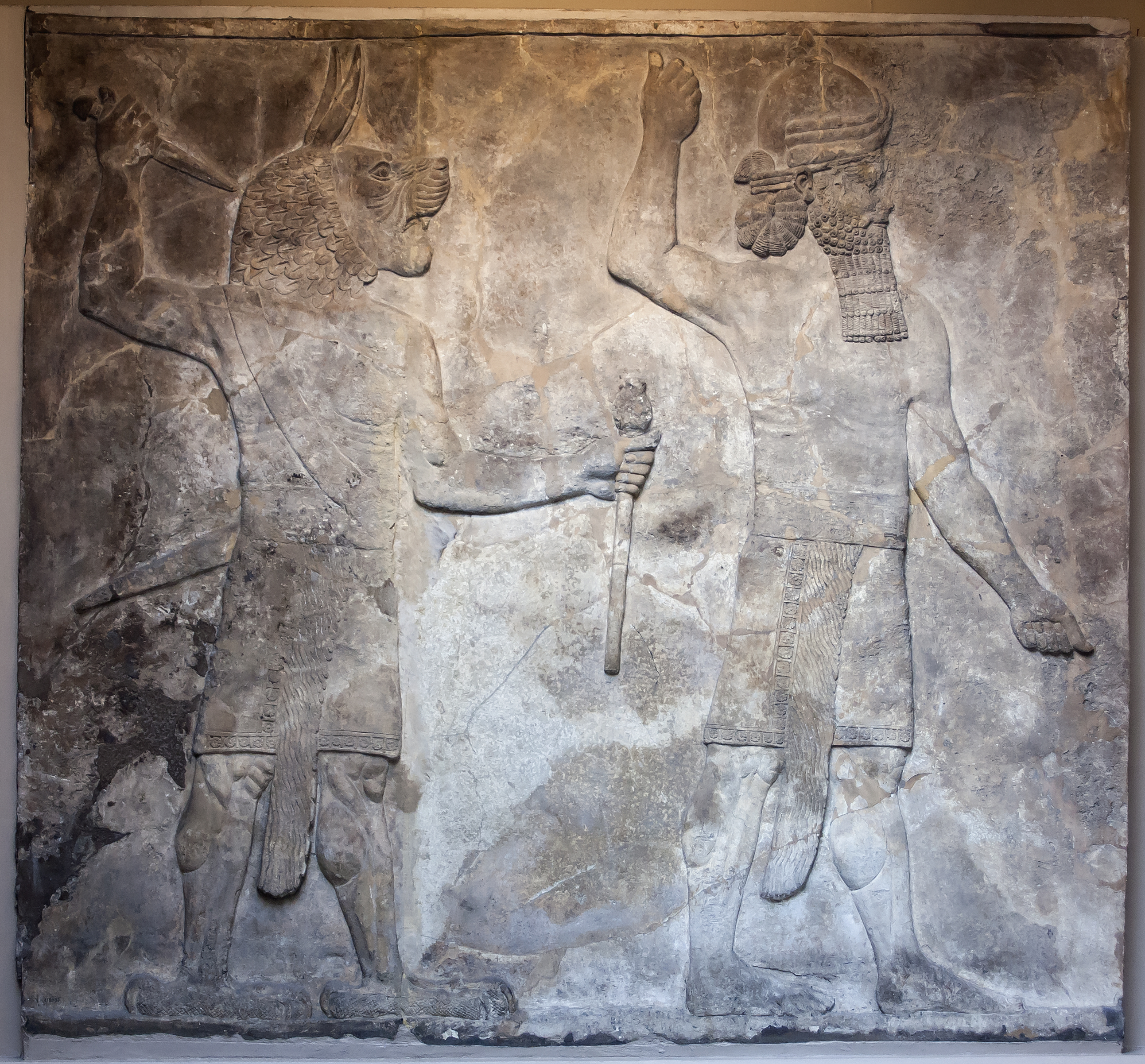
Ugallu
A panel with two divine palace guards, one of which is Ugallu. Ugallu, the "Big Weather-Beast", ( Sumerian inscribed 𒌓𒃲𒆷/UD.GAL.LA, Akkadian: ''ūmu rabû'', meaning "big day"; or, better in this case: "big storm"). It was a lion-headed storm-demon and has the feet of a bird who is featured on protective amulets and apotropaic yellow clay or tamarisk figurines of the first millennium BC but had its origins in the early second millennium. The iconography changed over time, with the human feet morphing into an eagle's talons and dressing him in a short skirt. He was one of the class of ud-demons (day-demons), personifying moments of divine intervention in human life. Function As an ud-demon, Ugallu's function is to intervene in moments of disaster in a person's life, such as saving them from death. His affiliation with the day compares him with other light related deities, Shamash the sun, the star of Sirius, and Nuska, god of the lamp. Many of his rituals as described ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian King
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient literary composition written in Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims to power of various city-states and kingdoms in southern Mesopotamia during the late third and early second millennium BC. It does so by repetitively listing Sumerian cities, the kings that ruled there, and the lengths of their reigns. Especially in the early part of the list, these reigns often span thousands of years. In the oldest known version, dated to the Ur III period () but probably based on Akkadian source material, the ''SKL'' reflected a more linear transition of power from Kish, the first city to receive kingship, to Akkad. In later versions from the Old Babylonian period, the list consisted of a large number of cities between which kingship was transferred, reflecting a more cyclical view of how kingship came to a city, only to be inevitably replaced by the next. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
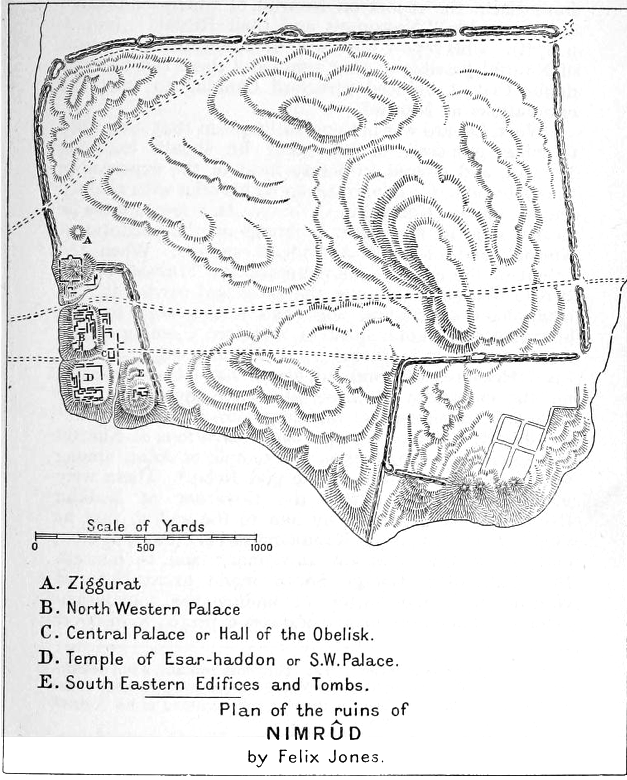
Nimrud
Nimrud (; ) is an ancient Assyrian people, Assyrian city (original Assyrian name Kalḫu, biblical name Calah) located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah (), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day Assyrian people, Assyrian village of Numaniyah, Al-Hamdaniya, Noomanea in Nineveh Governorate, Iraq. The name Nimrud was recorded as the local name by Carsten Niebuhr in the mid-18th century.N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |