|
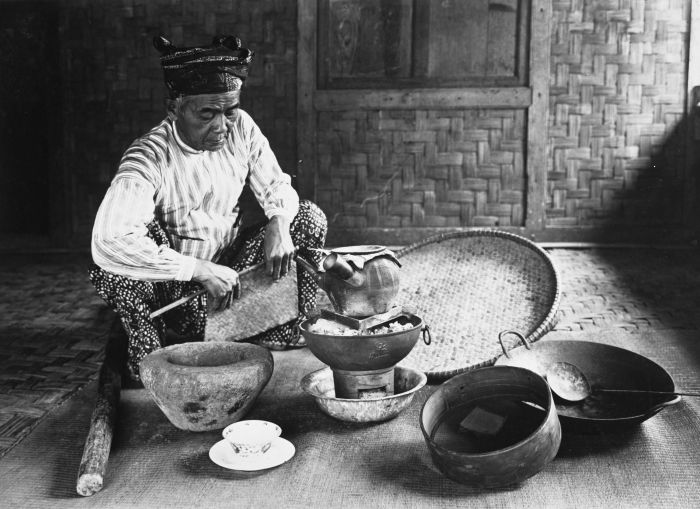
Pawang
A pawang is a type of Shamanism, shaman from Indonesia and Malaysia. The pawang deals with magic involving weather, wild animals and spirits, but they may also be employed for cases of sorcery. Pawang are usually associated with mountains and sky in contrast to the traditional healers (dukun or bomoh) who are most often linked to rivers. Particular variations of pawang exist. Some specialise in Weather modification, controlling weather such as the ''pawang hujan'' (rain pawang). Others Animal taming, prevent attacks from animals (especially a dangerous ones) such as the ''pawang harimau'' (tiger pawang) and the ''pawang buaya'' (crocodile pawang). Some of them are able to do particular rituals and chants for ensuring good luck, such as bountiful hunt, having a safe trip, or success in mining or construction. A pawang is said to control elements and entities by chanting and usually by having spirit servants to do his bidding. Practitioners believe the spirits can perform healings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomoh
A ''bomoh'' ( Jawi: توء بوموه) is a Malay shaman and traditional medicine practitioner. The term is used mainly in Malaysia and parts of Sumatra, whereas most Indonesians use the word ''dukun''. It is often mistranslated into English as medicine man or witch doctor. In colloquial usage, the term ''bomoh'' is often interchangeable with another type of shaman or dukun, the pawang, but they generally serve different functions. The ''bomoh'' is primarily a healer, herbalist, geomancer, and sorcerer. The ''pawang'' on the other hand usually specialises in rituals involving weather, nature, animals, and a good harvest. Their roles do overlap, however, and both claim to act as intermediaries for the spirits and gods. Etymology The word ''bomoh'' (at times spelled ''bomo'' or ''bomor'') has been in common usage since at least classical times. It is a loan of the Thai term ''maw'' or ''mohr'' (; , "doctor"). This word can mean either doctor or sorcerer, as in terms like ''mawpii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dukun
Dukun is an Indonesian language, Indonesian term for shaman. Their societal role is that of a traditional healer, spirit medium, custom and tradition experts and on occasion Magician (paranormal), sorcerers and masters of black magic. In common usage the dukun is often confused with another type of shaman, the pawang. It is often mistranslated into English as "witch doctor" or "medicine man". Many self-styled dukun in Indonesia are simply scammers and criminals, preying on people who were raised to believe in the supernatural. The dukun is the very epitome of the kejawen or kebatinan belief system indigenous to Java. Very strong and ancient beliefs of animism, ancestor worship and shamanism are held by the people of the Malay world, Nusantara. While medical doctors and revivalist Islam and Christianity have caused a decrease in the prominence of dukun, they remain highly respected and somewhat feared figures in Indonesian-Malay society, even in the most orthodox Muslim-dominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animism In Malaysia
Malaysian folk religion refers to the animistic and polytheistic beliefs and practices that are still held by many in the Islamic-majority country of Malaysia. Folk religion in Malaysia is practised either openly or covertly depending on the type of rituals performed. Some forms of belief are not recognised by the government as a religion for statistical purposes although such practices are not outlawed. There is a deep interaction between the Chinese folk religion of the large Malaysian Chinese population, and the indigenous Malaysian folk religion. Overview There are different types of Malaysian folk religions practised throughout the country. Shamanic performances are held by people known as ''bomohs'', also known as ''pawang'' or ''dukun''. Most Orang Asli (indigenous people) are animists and believe in spirits residing in certain objects. However, some have recently converted to mainstream religions due to state-sponsored Muslim dawah or evangelism by Christian missiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost In Malay Culture
There are many Malay ghost myths ( Malay: ''cerita hantu Melayu''; Jawi: چريتا هنتو ملايو), remnants of old animist beliefs that have been shaped by Hindu-Buddhist cosmology and later Muslim influences, in the modern states of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore and among the Malay diaspora in neighbouring Southeast Asian countries. The general word for ghost is hantu, of which there exist a wide variety. Some ghost concepts such as the female vampires pontianak and penanggal are shared throughout the region. While traditional belief does not consider all ghosts as necessarily evil, Malaysian popular culture tends to categorise them all as types of evil djinn. History Traditional ghost beliefs are rooted in prehistoric animist beliefs. However, the region has long had extensive contact with other cultures, and these have affected the form of some of the legends. Trade links with southern India and China were established several centuries BCE, in large par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
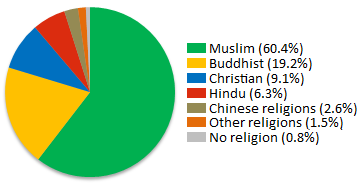
Religion In Malaysia
Islam is the state religion of Malaysia, as per Article 3 of the Constitution. Meanwhile, other religions can be practised by non-Malay citizens of the country. In addition, per Article 160, one must be Muslim to be considered Malay. As of the 2020 Population and Housing Census, 63.5 percent of the population practices Islam; 18.7 percent Buddhism; 9.1 percent Christianity; 6.1 percent Hinduism; and 2.7 percent other religion or gave no information. The remainder is accounted for by other faiths, including Animism, Folk religion, Sikhism, Baháʼí Faith and other belief systems. The states of Sarawak and Penang and the federal territory of Kuala Lumpur have non-Muslim majorities. Numbers of self-described atheists in Malaysia are few as renouncing Islam is prohibited for Muslims in Malaysia. As such, the actual number of atheists or converts in the country is hard to ascertain out of fear from being ostracised or prosecution. The state has come under criticism from human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Shamanism
Asian may refer to: * Items from or related to the continent of Asia: ** Asian people, people in or Asian diaspora, descending from Asia ** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia ** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asia ** Asian (cat), a cat breed similar to the Burmese but in a range of different coat colors and patterns * Asii (also Asiani), a historic Central Asian ethnic group mentioned in Roman-era writings * Asian option, a type of option contract in finance * Asyan, a village in Iran See also * * * East Asia * South Asia * Southeast Asia * Asiatic (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowsing
Dowsing is a type of divination employed in attempts to locate ground water, buried metals or ores, gemstones, Petroleum, oil, claimed radiations (radiesthesia),As translated from one preface of the Kassel experiments, "roughly 10,000 active dowsers in Germany ''alone'' can generate a conservatively-estimated annual revenue of more than 100 million DM (US$50 million)"''GWUP-Psi-Tests 2004: Keine Million Dollar für PSI-Fähigkeiten'' (in German) an. Grave (burial), gravesites, malign "earth vibrations" and many other objects and materials without the use of a Scientific instrument, scientific apparatus. It is also known as divining (especially in water divining), doodlebugging (particularly in the United States, in searching for petroleum or treasure) or water finding, or water witching (in the United States). A Y-shaped twig or rod, or two L-shaped ones, called dowsing rods or divining rods are normally used, and the motion of these are said to reveal the location of the target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curse
A curse (also called an imprecation, malediction, execration, malison, anathema, or commination) is any expressed wish that some form of adversity or misfortune will befall or attach to one or more persons, a place, or an object. In particular, "curse" may refer to such a wish or pronouncement made effective by a supernatural or spirituality, spiritual power, such as a god or gods, a spirit, or a Natural phenomenon, natural force, or else as a kind of spell (paranormal), spell by magic (paranormal), magic (usually black magic) or witchcraft; in the latter sense, a curse can also be called a hex or a jinx. In many belief systems, the curse itself (or accompanying ritual) is considered to have some causative force in the result. To reverse or eliminate a curse is sometimes called "removal" or "breaking", as the Incantation, spell has to be dispelled, and often requires elaborate rituals or prayers. Types The study of the forms of curses comprises a significant proportion of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |