|
Pavel Traubner
Pavel Traubner (2 May 1941 – 14 November 2024) was a Slovak neurologist. Life and career Traubner was born in Ilava on 2 May 1941, to a Jewish family, which faced persecution by the Hlinka Guard. His father was a dentist. In 1944, a policeman, who was a patient of Traubner's father, warned the family that it is about to be deported to a concentration camp. The family hid in a disused military bunker hidden deep in a forest, leaving all their possessions behind. Traubner studied medicine at the Comenius University. As a medical student, he moonlighted at a morgue to support himself, as his family fell into poverty after a sudden death of his father due to a stroke. Traubner graduated with a medical degree in 1964. In 1985, he defended his candidature. In 1991, he became a professor of neurology at the Comenius University, where he taught until his death. Between 1991 and 2008, Traubner was the head doctor at the neurology department of the university hospital. Between 2000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilava
Ilava (, ) is a town in the Trenčín Region, northwestern Slovakia. Name The name is of uncertain origin. The historic medieval names were ''Lewe'', ''Lewa'' (the same historic name as Levice), ''Lewa de cidca fluviom Vag'', later ''Ilava''. The form ''Illava'' is known from the 19th century and was used after the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. Demographics According to the 2001 census, the town had 5,441 inhabitants. 98.1% of inhabitants were Slovaks, 0.9% Czech people, Czechs and 0.1% Romani people, Roma and Hungarian people, Hungarians. The religious makeup was 87.2% Roman Catholics, 7.9% people with no religious affiliation, and 1.2% Lutherans. Notable people * Ivan Baranka (born 1985), ice hockey player * Mária Bieliková (born 1966), computer scientist * Hana Burzalová (born 2000), racewalker * Radoslav Ďuriš (born 1974), wheelchair curler * Artur Gajdoš (born 2004), association footballer * Katrina Grey (born 1991), actress * Marcel Hossa (born 1981), ice ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Republic (1939–1945)
Slovakia, officially the (First) Slovak Republic, and from 14 March until 21 July 1939 officially known as the Slovak State (, ), was a partially-recognized Clerical fascism, clerical fascist client state of Nazi Germany which existed between 14 March 1939 and 4 April 1945 in Central Europe. The Slovak part of Second Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia declared independence with German support one day before the German occupation of Czechoslovakia, German occupation of Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, Bohemia and Moravia. It controlled most of the territory of present-day Slovakia, without its current southern parts, which were First Vienna Award, ceded by Second Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia to Kingdom of Hungary (1920–46), Hungary in 1938. The state was the first formally independent Slovak state in history. Bratislava was declared the capital city. A one-party state governed by the far-right Slovak People's Party, Hlinka's Slovak People's Party, the Slovak Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, some sources estimate daily number of people moving around the city based on mobile phone SIM cards is more than 570,000. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the Danube and the left bank of the Morava (river), River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital to border two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Jews and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comenius University
Comenius University Bratislava () is the largest university in Slovakia, with most of its faculties located in Bratislava. It was founded in 1919, shortly after the creation of Czechoslovakia. It is named after Jan Amos Comenius, a 17th-century Czech teacher and philosopher. In 2020, Comenius University had more about 23,000 students and 2,500 faculty members. As are most universities in Slovakia, it is funded mostly by the government. History The Comenius University was established in 1919 with assistance from the more established University of Prague. It was meant to replace the former Elisabeth University :sk:Alžbetínska univerzita">''sk'' which had been located in Bratislava since 1912, as the latter had been forcefully disbanded in 1919 by Samuel Zoch, plenipotentiary župan of Slovakia, after Hungarian professors refused to take an oath of allegiance at that time in the First Czechoslovak Republic. This had caused the majority of the university's professors (and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
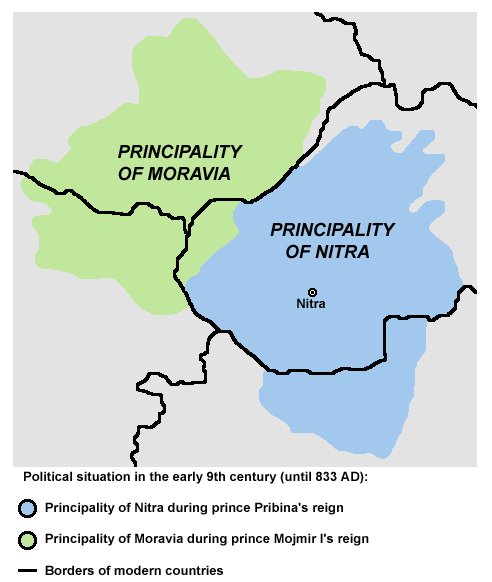
Pribina Cross
Pribina (c. 800861) was a Slavic prince whose adventurous career, recorded in the '' Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians'' (a historical work written in 870), illustrates the political volatility of the Franco–Slavic frontiers of his time. Pribina was the first ruler of Slavic origin to build a Christian church on Slavic territory in Nitra, and also the first to accept baptism. He was attacked and expelled from his homeland by Mojmir I, duke of Moravia. Pribina first fled to Ratpot, one of the border lords in East Francia. Thereafter he was wandering in Central and Southeastern Europe for several years. Finally, in the late 830s, Louis the German, king of East Francia granted Pribina lands near Lake Balaton (now in Hungary) where he set up his own principality under the king's suzerainty. He died fighting against the Moravians. Early life According to a marginal notation to the ''Conversion'' that has by now been incorporated into its main text, Pribina' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hlinka Guard
The Hlinka Guard (; ; abbreviated as HG) was the militia maintained by the Slovak People's Party in the period from 1938 to 1945; it was named after Andrej Hlinka. The Hlinka Guard was preceded by the Rodobrana (Home Defense/Nation's Defense) organization, which existed from 1923 to 1927 when the Czechoslovak authorities ordered its dissolution. During the crisis caused by Hitler's demand for the Sudetenland (in the summer of 1938), the Hlinka Guard emerged spontaneously, and on October 8 of that year, a week after Hitler's demand had been accepted at the Munich conference, the guard was officially set up, with Karol Sidor (1901–1953) as its first commander. The Hlinka Guard was known for its participation in the Holocaust in Slovakia; its members appropriated Jewish property and rounded up Jews for deportation in 1942. In the post-war, under one of the Beneš decrees, No. 16/1945 Coll., membership in the Hlinka Guard was punishable by 5 to 20 years imprisonment. Dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Camp
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploitation or punishment. Prominent examples of historic concentration camps include the British confinement of non-combatants during the Second Boer War, the Internment of Japanese Americans, mass internment of Japanese-Americans by the US during the Second World War, the Nazi concentration camps (which later morphed into extermination camps), and the Soviet labour camps or gulag. History Definition The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War when Spanish forces detained Cuban civilians in camps in order to more easily combat guerrilla forces. Over the following decades the British during the Second Boer War and the Americans during the Philippine–American War also used concentration camps. The term "c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candidate (degree)
Candidate ( or ) is the name of various academic degrees, which are today mainly awarded in Scandinavia. The degree title was phased out in much of Europe through the 1999 Bologna Process, which has re-formatted academic degrees in Europe. The degrees are now, or were once, awarded in the Nordic countries, the Soviet Union, the Netherlands, and Belgium. In Scandinavia and the Nordic countries, a candidate degree is a higher professional-level degree which corresponds to 5–7 years of studies. In the Soviet states, a candidate degree was a research degree roughly equivalent to a Doctor of Philosophy degree. In the Netherlands and Belgium, it was an undergraduate first-cycle degree roughly comparable with the bachelor's degree. Etymology and origins The term is derived from the Latin ''candida'', meaning white. In Ancient Rome, men running for political office would typically wear togas chalked and bleached to be bright white at speeches, debates, conventions, and other public f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B'nai B'rith
B'nai B'rith International ( ; from ) is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit Jewish service organization and was formerly a cultural association for German Jewish immigrants to the United States. B'nai B'rith states that it is committed to the security and continuity of the Jewish people and the State of Israel and combating antisemitism and other forms of bigotry. Although the organization's historic roots stem from a system of fraternal lodges and units in the late 19th century, as fraternal organizations declined throughout the United States, the organization evolved into a dual system of both lodges and units. The membership pattern became more common to other contemporary organizations of members affiliated by contribution in addition to formal dues paying members. B'nai B'rith has members, donors and supporters around the world. History B'nai B'rith was founded in Aaron Sinsheimer's café in New York City's Lower East Side on 13 October 1843, by 12 recent German Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Schuster
Rudolf Schuster (born 4 January 1934) is a Slovak politician, who served as the second president of Slovakia from 1999 to 2004. He was elected on 29 May 1999 and inaugurated on 15 June. In the presidential elections of April 2004, in which he sought re-election, List of presidents who did not win reelection, Schuster was defeated. He received only 7.4% of the vote, with three other candidates (more specifically Ivan Gašparovič, Vladimír Mečiar, and Eduard Kukan) receiving more than that. He was succeeded by Ivan Gašparovič. Life and career Schuster was born in Košice. From 1964 to 1990, he was a member of the Communist Party of Slovakia (1939), Communist Party of Slovakia. Before becoming president, he was Mayor (Slovakian language, Slovak: ''primátor'') of Košice in 1983–1986 and 1994–1999 respectively. He was also the last Communist president of the National Council of the Slovak Republic, Slovak National Council (1989–1990), Ambassador of Czechoslovakia to Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1941 Births
The Correlates of War project estimates this to be the deadliest year in human history in terms of conflict deaths, placing the death toll at 3.49 million. However, the Uppsala Conflict Data Program estimates that the subsequent year, 1942, was the deadliest such year. Death toll estimates for both 1941 and 1942 range from 2.28 to 7.71 million each. Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Euthanasia Centre in Germany, in the first phase of mass killings under the Aktion T4 program here. * January 1 – Thailand's Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram decrees January 1 as the official start of the Thai solar calendar new year (thus the previous year that began April 1 had only 9 months). * January 3 – A decree (''Normalschrifterlass'') promulgated in Germany by Martin Bormann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2024 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |