|
Pavel Dolukhanov
Pavel Dolukhanov (January 1, 1937, Leningrad, USSR – December 6, 2009, Newcastle, UK) was a doctor of Geographical Sciences, Professor, Emeritus Professor (2002), Russian and British paleogeographer and archaeologist at the Institute of History of Material Culture (IHMC), RAS (1959–1989) and the University of Newcastle, United Kingdom (1990–2009), a specialist in archaeology and paleoenvironment of Northern Eurasia. He taught and made research at the Leningrad State University, the University of Newcastle (UK), the Institute of Paleontology in Paris and the International Research Center (Kyoto, Japan). Biography Pavel Dolukhanov was born January 1, 1937, in Leningrad. His father was a professor at the Electrical Engineering Institute. In 1959 he graduated from the Geography Department of Leningrad State University with a degree in Geography and Geomorphology and joined the Laboratory of Archaeological Technology at the Leningrad branch of the Institute of Archaeology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad, USSR
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the site of a captured Swedish fortress, and was named after apostle Saint Peter. In Russia, Saint Petersburg is historically and culturally associated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
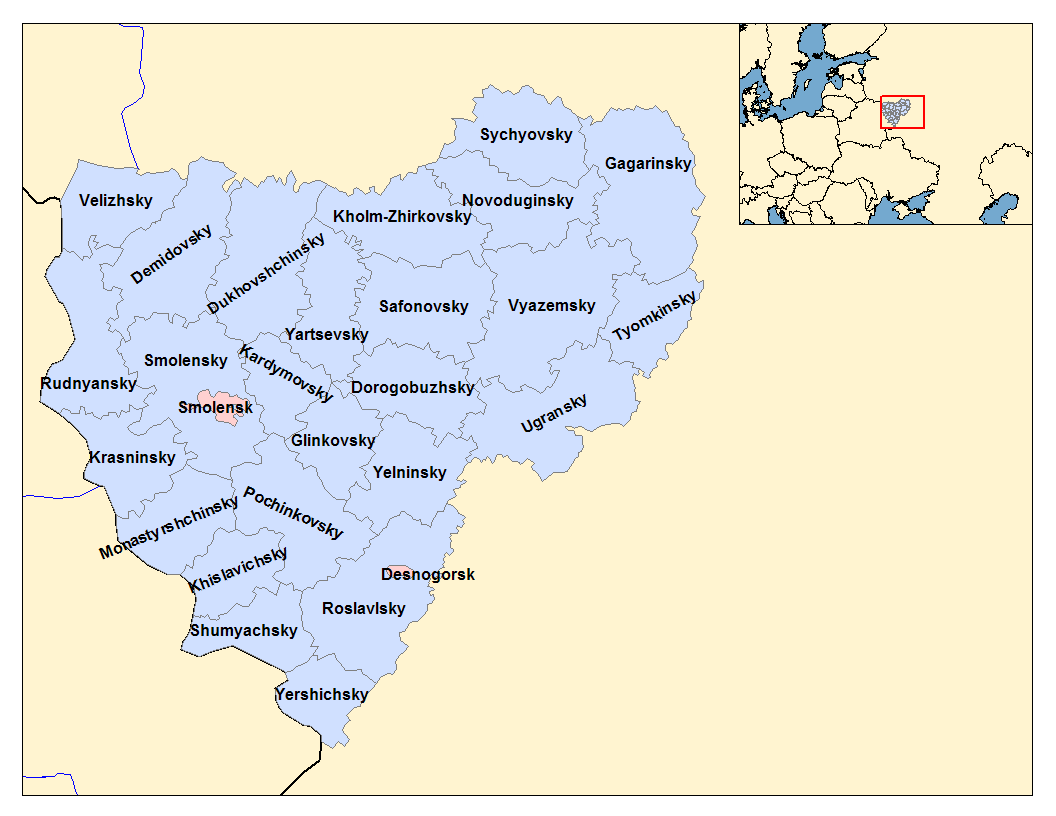
Smolensk Oblast
Smolensk Oblast (russian: Смоле́нская о́бласть, ''Smolenskaya oblast''; informal name — ''Smolenschina'' (russian: Смоле́нщина)) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative centre is the city of Smolensk. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 985,537. Geography The oblast was founded on 27 September 1937.Исполнительный комитет Смоленского областного совета народных депутатов. Государственный архив Смоленской области. "Административно-территориальное устройство Смоленской области. Справочник", изд. "Московский рабочий", Москва 1981. Стр. 8 It borders Pskov Oblast in the north, Tver Oblast in the northeast, Moscow Oblast in the east, Kaluga Oblast in south, Bryansk Oblast in the southwest, and Mogilev and Vitebsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast (russian: Пско́вская о́бласть, ') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the west of the country. Its administrative center is the city of Pskov. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 673,423. Geography Pskov Oblast is the westernmost federal subject of contiguous Russia ( Kaliningrad Oblast, while located further to the west, is an exclave).1september.ru. Д. В. Заяц (D. V. Zayats).Псковская область (''Pskov Oblast''). It borders with Leningrad Oblast in the north, Novgorod Oblast in the east, Tver and Smolensk Oblasts in the southeast, Vitebsk Oblast of Belarus in the south, and with the counties of Latvia ( Alūksne Municipality, Balvi Municipality, and Ludza Municipality) and Estonia ( Võru County) in the west. In the northwest, Pskov Oblast is limited by Lake Peipus, which makes up most of the state border with Estonia. The oblast is located in the Baltic Sea drainage basin, mostly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. The term " Baltic states" refers specifically to one such grouping. Etymology The first to name it the ''Baltic Sea'' ( la, Mare Balticum) was 11th century German chronicler Adam of Bremen. Denotation Depending on the context the ''Baltic Sea Region'' might stand for: * The countries that have shorelines along the Baltic Sea: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. * The group of countries that are members of the inter-governmental '' Baltic Assembly'' and '' Baltic Council of Ministers'', and generally referred to by the shorthand, Baltic states: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. * Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, exclaved from the remainder of Russia.«Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Rudenko
Sergei Ivanovich Rudenko (russian: Серге́й Ива́нович Руде́нко; January 16, 1885, Kharkov - July 16, 1969, Leningrad) was a prominent Soviet anthropologist and archaeologist who discovered and excavated the most celebrated of Scythian burials, Pazyryk in Siberia. Rudenko was a follower of Paul Broca's "French School" of anthropology. He participated in the Russian Geographical Society's (IRGO) Map Commission established in 1910. In that year he participated in an expedition to the Ob River basin in Western Siberia, where he studied the Khanty people. In 1917 he was a founder participant in the Commission for the Study of the Tribal Composition of the Population of the Borderlands of Russia (KIPS), along with several colleagues of the IRGO Map Commission. Rudenko delivered lectures in the Leningrad University from 1921 to 1954. In 1947-1950 and 1954 he was sent by the Soviet Archaeology Institute to explore the kurgans in the Altai Mountains. During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |