|
Paulus Hector Mair
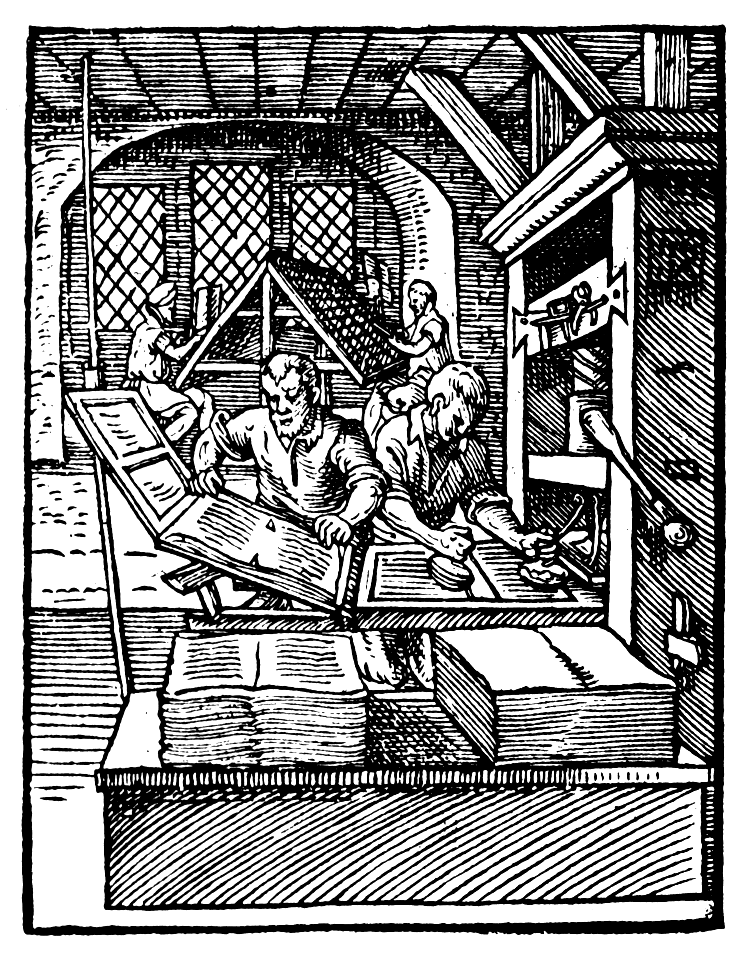
Paulus Hector Mair (1517–1579) was a German civil servant Historical European Martial Arts, fencing master from Augsburg. He collected Fechtbuch, Fechtbücher and undertook to compile all knowledge of the art of fencing in a compendium surpassing all earlier books. For this, he engaged the painter Jörg Breu the Younger, as well as two experienced fencers, whom he charged with perfecting the techniques before they were painted. The project was very costly, taking a full four years, and according to Mair, consumed most of his family's income and property. Three versions of his compilation, and one later, less extensive manuscript, have been preserved. Not only did Mair spend huge sums on his collections and on his projects, he also had a very expensive lifestyle, frequently hosting receptions for the more important Bourgeoisie#Middle Ages, burghers of Augsburg. His own income was not sufficient for this, and during many years, he misappropriated funds from the city treasury, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German School Of Fencing
The German school of fencing (') is a system of combat taught in the Holy Roman Empire during the Late Medieval, German Renaissance, and early modern periods. It is described in the contemporary Fechtbücher ("fencing books") written at the time. The geographical center of this tradition was in what is now Southern Germany including Augsburg, Frankfurt, and Nuremberg. During the period in which it was taught, it was known as the ', or the ''"Art of Fighting"''. The German school of fencing focuses primarily on the use of the two-handed longsword; it also describes the use of many other weapons, including polearms, medieval daggers, messers (with or without a buckler), and the staff, as well as describing mounted combat and unarmed grappling (''ringen''). Most authors of writings on the system are, or claim to be, in the tradition of the 14th-century master Johannes Liechtenauer. The earliest surviving treatise on Liechtenauer's system is a manuscript dated to possibly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well preserved Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg is an Urban districts of Germany, urban district and home to the institutions of the Augsburg (district), Landkreis Augsburg. It is the List of cities in Bavaria by population, third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg), with a population of 304,000 and 885,000 in its metropolitan area. After Neuss, Trier, Worms, Germany, Worms, Cologne and Xanten, Augsburg is one of Germany's oldest cities, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augsburg#Early history, Augusta Vindelicorum and named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
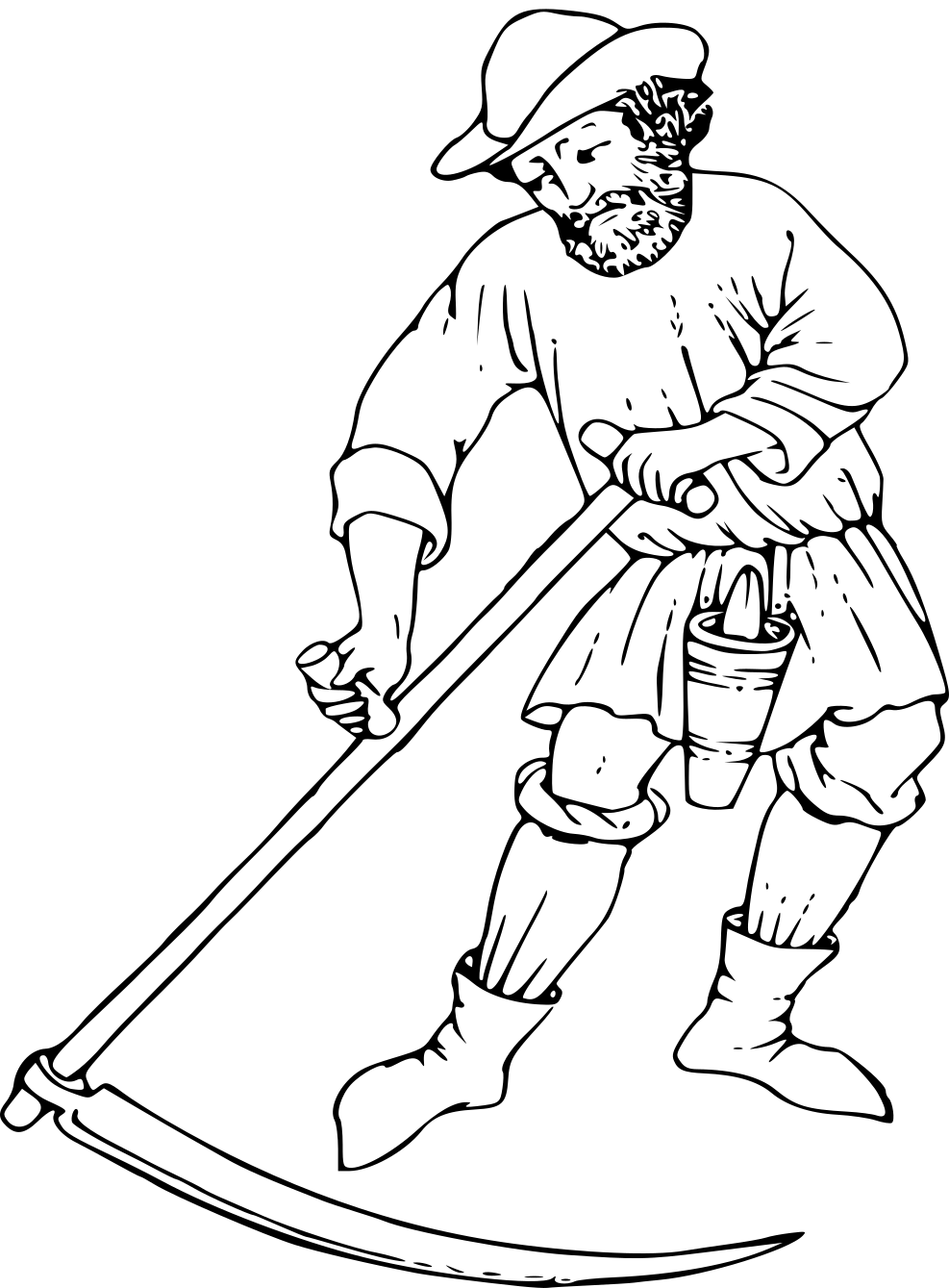
Scythe
A scythe (, rhyming with ''writhe'') is an agriculture, agricultural hand-tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It was historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains before they underwent the process of threshing. Horse-drawn and then tractor machinery largely replaced the scythe, but it is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting action of the scythe, and sometimes include subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelled ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) that the word was related to the Latin (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered, and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the List of German states by area, tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of , and the List of German states by population, sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants. The term Saxony (other), Saxony has been in use for more than a millennium. It was used for the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Saxony, and twice for a republic. The first Free State of Saxony was established in 1918 as a constituent state of the Weimar Republic. After World War II, it was under Soviet occupation before it became part of communist East Germany and was abolished by the government in 1952. Following German reunificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern German
Early New High German (ENHG) is a term for the period in the history of the German language generally defined, following Wilhelm Scherer, as the period 1350 to 1650, developing from Middle High German and into New High German. The term is the standard translation of the German (Frnhd., Fnhd.), introduced by Scherer. The term ''Early Modern High German'' is also occasionally used for this period (but the abbreviation EMHG is generally used for ''Middle High German, Early Middle High German''). Periodisation The start and end dates of ENHG are, like all linguistic periodisations, somewhat arbitrary. In spite of many alternative suggestions, Scherer's dates still command widespread acceptance. Linguistically, the mid-14th century is marked by the phonological changes to the vowel system that characterise the modern standard language; the mid-17th sees the loss of status for regional forms of language, and the triumph of German over Latin as the dominant, and then sole, language f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Armour
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, especially in the context of the Hundred Years' War, from the coat of plates (popular in late 13th and early 14th century) worn over mail (armour), mail suits during the 14th century, a century famous for the Transitional armour, in that plate gradually replaced mail. In Europe, full plate armour reached its peak in the 15th and 16th centuries. The full suit of armour, also referred to as a panoply, is thus a feature of the very end of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance period. Its popular association with the "Middle Ages in popular culture, medieval knight” is due to the specialised jousting armour which developed in the 16th century. Full suits of Gothic plate armour and Milanese plate armour were worn on the battlefields of the Burgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounted Combat
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Books * '' Mount!'', a 2016 novel by Jilly Cooper Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To prepare dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial By Combat
Trial by combat (also wager of battle, trial by battle or judicial duel) was a method of Germanic law to settle accusations in the absence of witnesses or a confession in which two parties in dispute fought in single combat; the winner of the fight was proclaimed to be right. In essence, it was a judicially sanctioned duel. It remained in use throughout the European Middle Ages, gradually disappearing in the course of the 16th century. History Origins Unlike trial by ordeal in general, which is known to many cultures worldwide, trial by combat is known primarily from the customs of the Germanic peoples. The practice was "almost universal in Europe" according to medievalist Eric Jager. It was in use among the ancient Burgundians, Ripuarian Franks, Alamans, Lombards, and Swedes. It was unknown in Anglo-Saxon law and Roman law and it does not figure in the traditions of Middle Eastern antiquity such as the code of Hammurabi or the Torah. However, it is recorded in the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
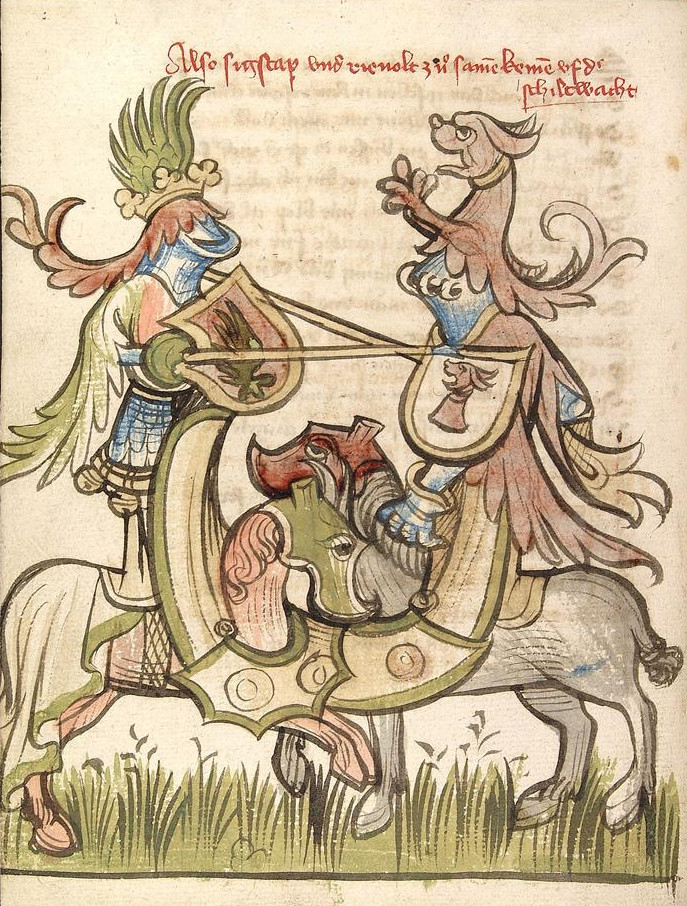
Tournament (medieval)
A tournament, or tourney (from Old French ''torneiement'', ''tornei''), was a mock fight that was common in the Middle Ages">Mock_combat.html" ;"title="chivalry">chivalrous competition or Mock combat">mock fight that was common in the Middle Ages and Renaissance (12th to 16th centuries), and is a type of hastilude. Tournaments included Melee, mêlée, hand-to-hand combat, contests of strength or History of archery, accuracy, and sometimes Jousting, jousts. Some considered the tournaments to be frivolous pursuits of celebrity, even a potential threat to public order. But the shows were popular and often put on in honor of coronations, marriages, or births; to celebrate recent conquests or peace treatises; or to welcome ambassadors, lords, or others considered to be of great importance. Other times tournaments were held for no particular reason at all, simply for entertainment. Certain tournaments are depicted throughout the ''Codex Manesse''. Etymology The word ''tournamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joust
Jousting is a medieval and renaissance martial game or hastilude between two combatants either on horse or on foot. The joust became an iconic characteristic of the knight in Romantic medievalism. The term is derived from Old French , ultimately from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , ultimately from Latin "to approach, to meet". The word was loaned into Middle English around 1300, when jousting was a very popular sport among the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman knighthood. The synonym tilt (as in tilting at windmills) dates . Jousting on horse is based on the military use of the lance by heavy cavalry. It transformed into a specialized sport during the Late Middle Ages, and remained popular with the nobility in England and Wales, Germany and other parts of Europe throughout the whole of the 16th century (while in France, it was discontinued after the death of King Henry II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Axe
A battle axe (also battle-axe, battle ax, or battle-ax) is an axe specifically designed for combat. Battle axes were designed differently to utility axes, with blades more akin to cleavers than to wood axes. Many were suitable for use in one hand, while others were larger and were deployed two-handed. Axes designed for warfare ranged in weight from just over , and in length from just over to upwards of , as in the case of the Danish axe or the sparth axe. Cleaving weapons longer than would arguably fall into the category of polearms. Overview Through the course of human history, commonplace objects have been pressed into service as weapons. Axes, by virtue of their ubiquity, are no exception. Besides axes designed for combat, there were many battle axes that doubled as tools. Axes could be modified into deadly projectiles as well (see the francisca for an example).Underwood, Richard (1999). ''Anglo-Saxon Weapons and Warfare''. p.35-37. Tempus Publishing. . Axes were ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |