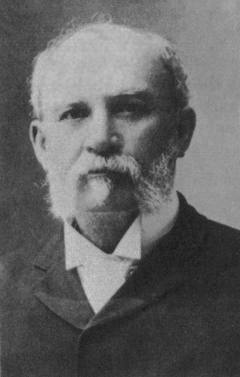|
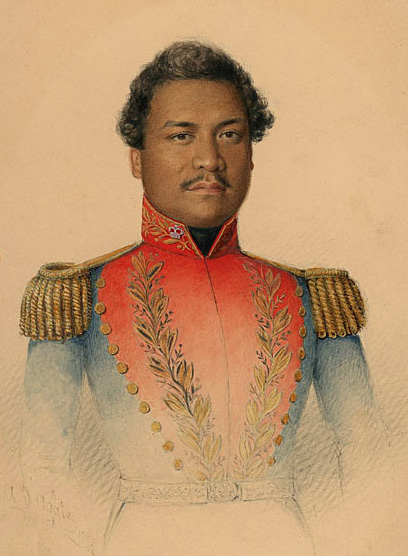
Paulo Kanoa
Paul (Paulo) Kanoa ( – November 10, 1885) was a Hawaiian high chief who served many political posts in the Kingdom of Hawaii, including Governor of Kauaʻi from 1847 to 1877. Biography Kanoa was born around the year 1802 in Kahaluu in South Kona on the island of Hawaii. His parents were Kapuohoula and Kepaa. His family descended from the Molokai chiefess Kaneʻalai. Kekūanaōʻa, the father of Kamehameha IV and Kamehameha V, and Boaz Mahune, the author of the Hawaiian Declaration of Rights of 1839, were his cousins. In his youth, Kanoa lived for a time with Gerrit P. Judd, an American missionary and advisor to King Kamehameha III, and also accompanied Rev. Hiram Bingham I on two missionary trips to Kauaʻi. He started his political career as a secretary of his cousin Kekūanaōʻa, the Governor of Oʻahu. In 1842, Kanoa was elected along with L. Kolona Halaʻi as Oʻahu's representative to Legislature of Hawaii at Lahaina, the capital at the time. Kanoa served as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Kauai
The Governor of Kauai () was the royal governor or viceroy of the island of Kauai and island of Niihau during the Kingdom of Hawaii. The governor was usually a male Hawaiian chief or prince, but several women also held the office. The governor had authority over the islands of Kauai and Niihau, and it was up to the governor to appoint lieutenant governors to assist them. The governor had replaced the old alii aimokus of the islands, but the sovereignty remained with the king. The first governor was the last king of Kaumualii, and it was not until his death in 1824 that Queen Kaahumanu and King Kamehameha II took control from his sons. The island governors were under the jurisdiction of the Ministers of the Interiors. Role In the 1840 Constitution of the Kingdom of Hawaii it states: ''There shall be four governors over these Hawaiian Islands - one for Hawaii - one for Maui and the Islands adjacent - one for Oahu, and one for Kauai and the adjacent Islands. All the governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamehameha IV
Kamehameha IV (Alekanetero ʻIolani Kalanikualiholiho Maka o ʻIouli Kūnuiākea o Kūkāʻilimoku; Anglicisation, anglicized as Alexander Liholiho) (February 9, 1834 – November 30, 1863), reigned as the List of Hawaiian monarchs, fourth monarch of Hawaii under the title ''Ke Aliʻi o ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻAina'' of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kingdom of Hawaii from January 11, 1855, to November 30, 1863. Early life Alexander was born on February 9, 1834, in Honolulu on the island of Oahu, Oʻahu. His father was Kekūanaōʻa, High Chief Mataio Kekūanaōʻa, Royal Governor of Oʻahu. His mother was Kīnaʻu, Princess Elizabeth Kīnaʻu the ''Kuhina Nui'' or Prime Minister of the Kingdom. He was the grandson of Kamehameha I, first monarch of all the islands. Alexander had three older brothers, David Kamehameha, Moses Kekūāiwa and Lot Kapuāiwa, and a younger sister, Victoria Kamāmalu. As a toddler, Alexander was adopted by his uncle, King Kamehameha III who decreed Alexander heir to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hyde Rice
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Isenberg
Paul Isenberg (April 15, 1837 – January 16, 1903) was a German businessman who developed the sugarcane business in the Kingdom of Hawaii. Life Paul Heinrich Friedrich Carl Isenberg was born April 15, 1837, in Dransfeld, Kingdom of Hanover, Germany. His father was Lutheran minister Daniel Isenberg (1807–1875), and mother was Dorothea (Strauch) Isenberg (1808–1871). He came to the Hawaiian Islands in 1858. Isenberg moved to the island of Kauai and first worked in Wailua. In October 1861 he married Hannah "Maria" Rice, daughter of William Harrison Rice (February 17, 1842—April 7, 1867). They had two children, Mary Dorothea Rice Isenberg (1862–1949) and Daniel Paul Rice Isenberg (1866–1919), known as "Paul Jr." He traveled back to Germany in 1869 where he married Beta Margarete Glade (born 1846) before returning to Hawaii. They had six more children: Johannes "John" Carl Isenberg (born September 12, 1870), Heinrich Alexander Isenberg (born January 17, 1872), Julie Mari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliʻi
The aliʻi were the traditional nobility of the Hawaiian islands. They were part of a hereditary line of rulers, the ''noho aliʻi''. Cognates of the word ''aliʻi'' have a similar meaning in other Polynesian languages; in Māori it is pronounced " ariki" and in Tahitian ari'i. Background In ancient Hawaiian society, the ''aliʻi'' were hereditary nobles (a social class or caste). The ''aliʻi'' consisted of the higher and lesser chiefs of the various levels on the islands. The ''noho aliʻi'' were the ruling chiefs. The ''aliʻi'' were believed to be descended from the deities. There were eleven classes of ''aliʻi'', of both men and women. These included the '' kahuna'' (priestesses and priests, experts, craftsmen, and canoe makers) as part of four professions practiced by the nobility. Each island had its own aliʻi nui, who governed their individual systems. ''Aliʻi'' continued to play a role in the governance of the Hawaiian islands until 1893, when Queen Liliʻuoka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerk (legislature)
The clerk, chief clerk, secretary, or secretary general (British English: ; American English: ) of a legislative chamber is the senior administrative officer responsible for ensuring that its business runs smoothly. This may encompass keeping custody of documents Laying before the house, lain before the house, received, or produced; making records of proceedings; allocating office space; enrolling of members, and administering an oath of office. During the first sitting of a newly elected legislature, or when the current presiding officer steps down, they may preside over an election of a new presiding officer. The clerk sometimes has a ceremonial role. A clerk may also advise the speaker (politics), speaker or members on parliamentary procedure, acting in American parlance as a "Parliamentarian (consultant), parliamentarian". In the anglosphere, English speaking world, a parliamentary, legislative or congressional clerk is often used to refer to other officials who are involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahaina, Hawaii
Lahaina (; ) or Lāhainā is a census-designated place (CDP) in Maui County, Hawaii, United States. On the northwest coast of the island of Maui, it encompasses Lahaina town and the Kaanapali and Kapalua beach resorts. At the 2020 census (before the 2023 wildfire), Lahaina had a resident population of 12,702. The CDP spans the coast along Hawaii Route 30 from a tunnel at the south end, through Olowalu, and to the CDPs of Kaanapali and Napili-Honokowai to the north. A series of wildfires destroyed approximately 80% of Lahaina in 2023, resulting in the deaths of 102 people. History Name Both ''Lahaina'' and ''Lāhainā'' are correct orthography in modern Hawaiian Modern name, etymology and pronunciations Protestant missionaries sent by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM) began organizing a way to write the Hawaiian language with English letters between 1820–1826 after they reached Hawaii. According to ''Thrums Hawaiian Annual'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislature Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The Legislature of the Hawaiian Kingdom () was the bicameral (later unicameral) legislature of the Hawaiian Kingdom. A royal legislature was first provided by the 1840 Constitution and the 1852 Constitution was the first to use the term Legislature of the Hawaiian Islands, and the first to subject the monarch to certain democratic principles. Prior to this the monarchs ruled under a Council of Chiefs (ʻAha Aliʻi). Structure The Legislature from 1840 to 1864 was bicameral and originally consisted of a lower House of Representatives and an upper House of Nobles as provided for under the Constitutions of the Kingdom of 1840 and 1852, until abolished by the 1864 Constitution which then provided for a unicameral Legislature. House of Nobles The members of the upper House of Nobles (Hale ʻAhaʻōlelo Aliʻi) were appointed by the Monarch with the advice of his Privy Council. It also served as the court of impeachment for any royal official. Members were usually Hawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Oahu
The Governor of Oahu () was the royal governor or viceroy of the island of Oahu in the Kingdom of Hawaii. The Governor of Oahu resided at Honolulu and was usually a Hawaiian chief or prince and could even be a woman. The governor had authority over the island of Oahu and Honolulu, the kingdom's capital, and it was up to the governor to appoint lieutenant governors to assist them. The governor had replaced the old alii aimokus of the islands, but sovereignty remained with the king. The island governors were under the jurisdiction of the Ministers of the Interiors. Either the governor or the monarch had the power to call in foreign assistance in time of troubles. This occurred a few times, including the uprising of the Emmaites in 1874 when John Owen Dominis called for British and American assistance. Neither the governor nor monarch called for foreign assistance in January 1893 when John L. Stevens sent American troops into Honolulu. Role In the 1840 Constitution of the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kauai
Kauai (), anglicized as Kauai ( or ), is one of the main Hawaiian Islands. It has an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest of the islands and the 21st-largest island in the United States. Kauai lies 73 miles (117 km) northwest of Oahu, across the Kauai Channel. The island's 2020 population was 73,298. Styling itself the "Garden Isle", Kauai is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park and Nā Pali Coast State Park. It forms the bulk of Kauai County, which includes Niihau as well as the small nearby islands of Kaula and Lehua. Etymology and language Hawaiian narrative derives the name's origin from the legend of Hawaiiloa, the Polynesian navigator credited with discovering the Hawaiian Islands. The story relates that he named the island after a favorite son; a possible translation of Kauai is "place around the neck", describing how a father would carry his child. Another possible translation is "food season". Kauai was known for its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram Bingham I
Hiram Bingham, formally Hiram Bingham I (October 30, 1789 – November 11, 1869), was the leader of the first group of American Protestant missionaries to introduce Christianity to the Hawaiian Islands. Like most of the missionaries, he was from New England. Life Bingham was descended from Deacon Thomas Bingham, who emigrated to the American colonies in 1650 and settled in Connecticut Colony. He was born October 30, 1789, in Bennington, Vermont, one of thirteen children of his mother, Lydia, and father, Calvin Bingham. He attended Middlebury College and the Andover Theological Seminary. He had as private tutor Rev. Elisha Yale, who taught him Greek and Latin and prepared him for higher education. After breaking his first engagement Bingham found a new bride, Sybil Moseley. He needed to be married to be accepted as a missionary. On October 23, 1819, the young couple sailed out of Boston aboard the brig ''Thaddeus'' along with Asa and Lucy Goodale Thurston to lead a mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name was Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa Kalani Waiakua Kalanikau Iokikilo Kīwalaō i ke kapu Kamehameha when he ascended the throne. Under his reign, Hawaii evolved from an absolute monarchy to a constitutional monarchy with the signing of both the 1840 Constitution, which was the first Hawaiian Language Constitution, and the 1852 Constitution. He was the longest reigning monarch in the history of the Kingdom, ruling for 29 years and 192 days, although in the early part of his reign he was under a regency by Queen Kaahumanu and later by Kaahumanu II. His goal was the careful balancing of modernization by adopting Western ways while keeping his nation intact. Early life Kauikeaouli was born at Keauhou Bay, on Hawaii island, the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |