|
Paul Gerson Unna
Paul Gerson Unna, (September 8, 1850, Hamburg – January 29, 1929, Hamburg) was a German physician specialized in dermatologist, dermatology and one of the pioneers in dermatopathology. Biography Paul Unna was born to German Jewish parents Moritz Adolph Unna, a physician from Hamburg. Unna was educated at the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums and Ida Gerson, who descended from a long line of physicians. He began to study medicine at the University of Heidelberg, but had to interrupt it in order to fight in the Franco-Prussian war, where he was severely wounded. In 1871, he resumed his studies in Heidelberg and later went to the University of Leipzig, finally attaining a doctorate under Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in Strasbourg. His doctoral work was on the subject of the histology and development of the Epidermis (skin), epidermis, and was published in 1876. The thesis contained a set of new ideas and aspects that were met with hard criticism. They were accepted only after some corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Kaposi
Moritz Kaposi (, ; 23 October 1837 – 6 March 1902) was a physician and dermatologist from the Austro-Hungarian Empire who discovered the skin tumor that received his name (Kaposi's sarcoma). Biography Early life and name Born in Kaposvár, Hungary, Austrian Empire, to a Jewish family, originally his surname was Kohn; but, with his conversion to the Catholic faith, he changed it to Kaposi in 1871, in reference to his town of birth. One purported reason behind this is that he wanted to marry a daughter of current dermatology chairman, Ferdinand Ritter von Hebra, and advance in the society, which he could not have done being of Jewish faith. This seems unlikely because he married Martha Hebra and converted to Catholicism several years prior to changing his name, by which time he was already well established in the Vienna University faculty and a close associate of her father, Ferdinand. A more plausible explanation is based on his own comments to colleagues that he changed his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
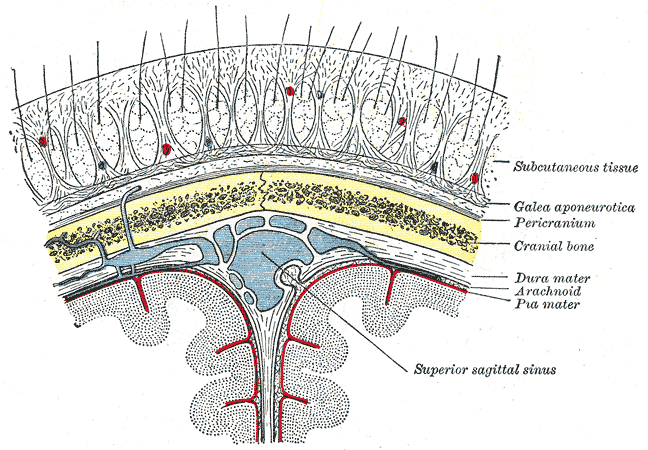
Scalp
The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology. Structure Layers The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can be remembered using the mnemonic 'SCALP': * S: Skin. The skin of the scalp contains numerous hair follicles and sebaceous glands. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: Aponeurosis. The epicranial aponeurosis or galea aponeurotica is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which anchors the above layers in place. It runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
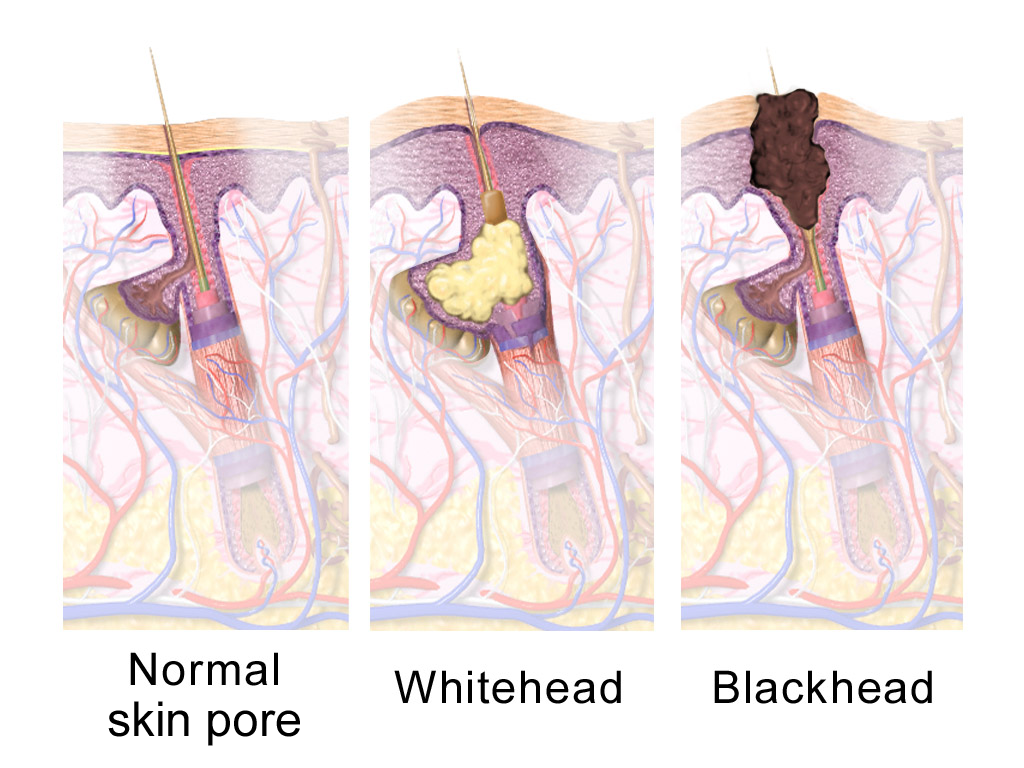
Seborrhea
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unna's Disease
Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of skin disorders characterized by abnormal thickening (scleroderma) of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles. Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been described in medical literature. Types Clinically, three distinct patterns of palmoplantar keratoderma may be identified: diffuse, focal, and punctate. Diffuse Diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is a type of palmoplantar keratoderma that is characterized by an even, thick, symmetric hyperkeratosis over the whole of the palm and sole, usually evident at birth or in the first few months of life. Restated, diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is an autosomal dominant disorder in which hyperkeratosis is confined to the palms and soles. The two major types can have a similar clinical appearance: * ''Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma'' (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma cum degeneratione granulosa Vörner", "Vörner's epidermo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hamburg
The University of Hamburg (, also referred to as UHH) is a public university, public research university in Hamburg, Germany. It was founded on 28 March 1919 by combining the previous General Lecture System ('':de:Allgemeines Vorlesungswesen, Allgemeines Vorlesungswesen''), the Hamburg Colonial Institute ('':de:Hamburgisches Kolonialinstitut, Hamburgisches Kolonialinstitut''), and the Academic College ('':de:Akademisches Gymnasium (Hamburg), Akademisches Gymnasium''). The main campus is located in the central district of Rotherbaum, with affiliated institutes and research centres distributed around the city-state. Seven Nobel Prize winners and one Wolf Prize winner are affiliated with UHH. History Founding At the beginning of the 20th century, wealthy individuals made several unsuccessful petitions to the Hamburg Senate and Parliament requesting the establishment of a university. Senator Werner von Melle worked towards the merging of existing institutions into one university, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf
The University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (German: Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf, UKE) is the teaching hospital of the University of Hamburg and the largest hospital in Hamburg, Germany. The UKE has 1,738 beds and 121 day-care places and is listed to provide the capacity to dispatch emergency medical services. Research & Training Research at the UKE is focused on 5 major areas. This increasing scientific focus is supported by the Faculty of Medicine and is reflected in the research centers and joint projects at national and European level: # Neuroscience (Hamburg Center for NeuroscienceHCNS # Inflammation, infection and immunity # Oncology research (University Cancer Center Hamburg, UCCH) # Cardiovascular research (Cardiovascular Research Center, CVRC) # Health care research and public health The next generation of biomedical researchers is trained in the structured training program 'UKE Academy of Biomedical and Health Sciences', consisting of the following gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eppendorf, Hamburg
Eppendorf () is one of thirteen quarters in the Hamburg-Nord borough of Hamburg, Germany, and lies north of the Außenalster. In 2023 the population was 25,253. History Eppendorf, first mentioned as ''Eppenthorp'' in 1140, is Hamburg's oldest village. Its name originates either from the old Germanic ''epen'' (on the water) or from the personal name Ebbo/Eppo. It is possible, but unlikely, that it was named after Ebbo, the archbishop of Reims. During the restoration of the St. Johannis Church, which was first mentioned in 1267, ruins of an older stone tower were found. In the 19th century, Eppendorf gained popularity among the affluent of Hamburg. The low-lying, moist land was banked up and built on. The last area of moorland, the Eppendorfer Moor, was placed under nature protection in 1982. In 1894, Eppendorf was transferred to Hamburg. Geography In 2007 according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, the quarter Eppendorf has an area of 2,7 km2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of Hamburg
The government of Hamburg is divided into executive, legislative and judicial branches. Hamburg is a city-state and municipality, and thus its governance deals with several details of both state and local community politics. It takes place in two ranks – a citywide and state administration ( Senate of Hamburg), and a local rank for the boroughs. The head of the city-state's government is the First Mayor and President of the Senate. A ministry is called ''Behörde'' (office) and a state minister is a ''Senator'' in Hamburg. The legislature is the state parliament, called '' Hamburgische Bürgerschaft'', and the judicial branch is composed of the state supreme court and other courts. The seat of the government is Hamburg Rathaus. The President of the Hamburg Parliament is the highest official person of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg.constitution of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, § 18 This is a traditional difference to the other German states. The presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Granulosum
The stratum granulosum (or granular layer) is a thin layer of cells in the epidermis lying above the stratum spinosum and below the stratum corneum ( stratum lucidum on the soles and palms).James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005) ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 2. . Keratinocytes migrating from the underlying stratum spinosum become known as granular cells in this layer. These cells contain keratohyalin granules, which are filled with histidine- and cysteine-rich proteins that appear to bind the keratin filaments together. Therefore, the main function of keratohyalin granules is to bind intermediate keratin filaments together.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 7. . At the transition between this layer and the stratum corneum, cells secrete lamellar bodies (containing lipids and proteins) into the extracellular space. This results ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a medical sign characterised by brown-to-black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is usually found in body folds, such as the posterior and lateral folds of the neck, the armpits, groin, navel, forehead and other areas. It is associated with endocrine dysfunction, especially insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia, as seen in diabetes mellitus. This activates the insulin-like growth factor receptors, which leads to proliferation of keratinocytes, fibroblasts and other cells in the skin. Activation of other growth factor receptors such as fibroblast growth factor receptors or epidermal growth factor receptor can also be responsible. Signs and symptoms Acanthosis nigricans appears as dark brown-black, poorly defined, velvety patches of skin, typically affecting the face, neck, underarms, genitals, groin, elbows, knees, anus, umbilicus and nasal crease. Causes It typically occurs in individuals younger than age 40, is associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resorcinol
Resorcinol (or resorcin) is a phenolic compound. It is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or ''meta- (chemistry), meta''-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether, but insoluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide. Production Resorcinol is produced in several steps from benzene, starting with dialkylation with propylene to give 1,3-Diisopropylbenzene, 1,3-diisopropylbenzene. Oxidation and Hock rearrangement of this disubstituted arene gives acetone and resorcinol. Resorcinol is a relatively inexpensive chemical. It is produced in only a very few locations around the world (as of 2010 only four commercial plants were known to be operative: in the United States, Germany, China, and Japan), and is the determining factor in the cost of Phenol formaldehyde resin, PRF adhesives. Production in the United States ended in 2017 with the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |