|
Pathupattu
The Ten Idylls, known as Pattuppāṭṭu () or Ten Lays, is an anthology of ten longer poems in the Sangam literature – the earliest known Tamil literature. They range between about 100 and 800 lines, and the collection includes the celebrated Nakkīrar's ''Tirumurukāṟṟuppaṭai'' (lit. "Guide to Lord Murukan"). The collection was termed as "Ten Idylls" during the colonial era, though this title is considered "very incorrect" by Kamil Zvelebil – a scholar of Tamil literature and history. He suggests "Ten Lays" as the more apt title. Five of these ten ancient poems are lyrical, narrative bardic guides (''arruppatai'') by which poets directed other bards to the patrons of arts such as kings and chieftains. The others are guides to religious devotion (Murugan) and to major towns, sometimes mixed with akam- or puram-genre poetry. The ''Pattuppāṭṭu'' collection is a later dated collection, with its earliest layer composed sometime between 2nd and 3rd century CE, the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthology
In book publishing, an anthology is a collection of literary works chosen by the compiler; it may be a collection of plays, poems, short stories, songs, or related fiction/non-fiction excerpts by different authors. There are also thematic and genre-based anthologies.Chris Baldrick''The Oxford Dictionary of Literary Terms'' 3rd. ed (2008) Complete collections of works are often called " complete works" or "" (Latin equivalent). Etymology The word entered the English language in the 17th century, from the Greek word, ἀνθολογία (''anthologic'', literally "a collection of blossoms", from , ''ánthos'', flower), a reference to one of the earliest known anthologies, the ''Garland'' (, ''stéphanos''), the introduction to which compares each of its anthologized poets to a flower. That ''Garland'' by Meléagros of Gadara formed the kernel for what has become known as the Greek Anthology. '' Florilegium'', a Latin derivative for a collection of flowers, was used in mediev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
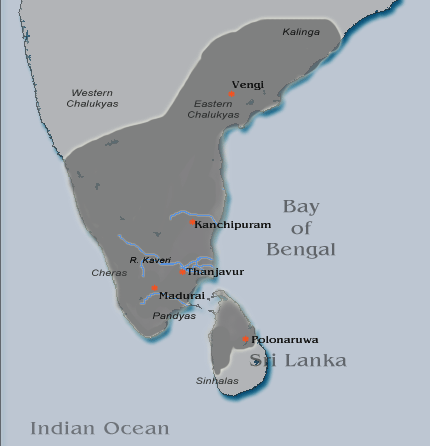
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil language, Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam''), historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil language, Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ''), connotes the early classical Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition links it to Legendary Tamil Sangams, legendary literary gatherings around Madurai in the ancient Pandya dynasty, Pandya kingdom. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the historical Sangam literature era, also known as the Sangam period, spanned from 100 BCE to 250 CE, on the basis of linguistic, epigraphic, archaeological, numismatic and historical data; though some scholars give a broader range of 300 BCE to 300 CE. The Eighteen Greater Texts (Patiṉeṇmēlkaṇakku), along with the Tamil grammar work Tolkāppiyam, Tolkappiyam, are collectively considered as Sangam literature. These tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumurukāṟṟuppaṭai
''Tirumurukātṟuppatai'' (, meaning ''Guide to Lord Murugan'') is an ancient devotional Tamil poem in the Sangam literature genre entirely dedicated to the god Murugan. Murugan is described as the nephew of the god Vishnu, who is called Mayon or the ruler of the worlds. Authored by Nakkiranar, it is the first poem in the Ten Idylls (''Pattuppāṭṭu'') anthology. The poem is generally dated to the late classical period (2nd to 4th century CE), with some scholars suggesting it may have been composed a few centuries later. The anthologies and poems of the Sangam literature have numerous references and verses to Murugan – also known as Subrahmanya, Kumara, Skanda, Kartikeya in other parts of India. The ''Tirumurukarruppatai'' poem is exclusively about different manifestations and shrines of Murugan. It describes different major temples dedicated to him in the Tamil region, six locations, the natural scenes, worship practices and the culture of the people. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lai (poetic Form)
A ''lai'' (or ''lay lyrique'', "lyric lay", to distinguish it from a '' lai breton'') is a lyrical, narrative poem written in octosyllabic couplets that often deals with tales of adventure and romance. ''Lais'' were mainly composed in France and Germany, during the 13th and 14th centuries. The English term '' lay'' is a 13th-century loan from Old French ''lai''. The origin of the French term itself is unclear; perhaps it is itself a loan from German '' Leich'' (reflected in archaic or dialectal English ''lake A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...'', "sport, play" and in modern Swedish (att leka = to play). The terms ''note'', ''nota'' and ''notula'' (as used by Johannes de Grocheio) appear to have been synonyms for ''lai''. The poetic form of the ''lai'' usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poruṇarāṟṟuppaṭai
__NOTOC__ ''Porunarāṟṟuppaṭai'' (, ''lit.'' "guide for war bards") is an ancient Tamil poem and the second lay of the ''Pattuppattu'' anthology in the Sangam literature. It contains 248 lines, mostly in the ''akaval'' meter. It is one of five ''arruppatai'' genre poems, possibly the oldest one, aimed as a guide to other bards seeking a patron for their art. Set in the early Chola kingdom, describes about Uraiyur, the capital of Cholas and the Powerful King of early cholas Karikala Cholan, his early life and how he brought up the King of Chola Kingdom. It was composed by Mutattamakkanniyar sometime around 180–190 CE, states Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar. The ''Porunararruppatai'' poem, also called ''Porunarattrupadai'', is set in the context of a meeting of the poet with a "war bard" (''porunar'') and his wife, wherein the poet guides his hosts on how to go about meeting the Chola king, the background information about the king and his kingdom. The poem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivite
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the supreme being. It is the second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in Southern India), Sri Lanka, and Nepal.Keay, p.xxvii. The followers of Shaivism are called Shaivas or Shaivites. According to Chakravarti, Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Aryan religions and traditions, Vedic Rudra, and post-Vedic traditions, accommodating local traditions and Yoga, puja and bhakti. According to Bisschop, early shaivism is rooted in the worship of vedic deity Rudra. The earliest evidence for sectarian Rudra-Shiva worship appears with the Pasupata (early CE), possibly owing to the Hindu synthesis, when many local traditions were aligned with the Vedic-Brahmanical fold. The Pāśupata movement rapidly expanded throughout North India, giving rise to different forms of Shaivism, which led to the emergence of variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, sixth largest by population, Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, who speak the Tamil language—the state's official language and one of the longest surviving Classical languages of India, classical languages of the world. The capital and largest city is Chennai. Located on the south-eastern coast of the Indian peninsula, Tamil Nadu is straddled by the Western Ghats and Deccan Plateau in the west, the Eastern Ghats in the north, the Eastern Coastal Plains lining the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait to the south-east, the Laccadive Sea at the southern Cape (geography), cape of the peninsula, with the river Kaveri bisecting the state. Politically, Tamil Nadu is bound by the Indian sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajaraja I
Rajaraja I ( Middle Tamil: ''Rājarāja Cōḻaṉ''; Classical Sanskrit: ''Rājarāja Śōḷa''; 3 November 947 – January/February 1014), also known as Rajaraja the Great, was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 to 1014. He was known for his conquests of southern India and Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka, as well as increasing Chola influence across the Indian Ocean. Rajaraja's birth name is variously given as Arul Mozhi Varman and Arul Moli Varman. Rajaraja's empire encompassed vast territories, including regions of the Pandya country, the Chera country, and northern Sri Lanka. He also extended his influence over strategic islands such as Lakshadweep, Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and parts of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. His conquests weren't limited to the south; he also launched successful campaigns against the Western Gangas and the Western Chalukyas, extending Chola authority as far as the Tungabhadra River. In the east, Rajaraja faced fierce opposition fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapilar
Kapilar or Kabilar ( Tamil: கபிலர்) was the most prolific Tamil poet of the Sangam period (c. 3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE). He contributed 206 poems, or a little less than 10% of the entire Sangam-era classical corpus by 473 ancient poets. Held in high regard by other poets of the Sangam era, as well as the post-Sangam era, he is variously dated to have lived between c. 50–125 CE, or 140–200 CE. He was a contemporary of Karikala Chola, Irunkōvēl and Vēl Pāri, and the close friend, confidant and alleged favorite of Vēl Pāri, one of the Vēlir kings.''Studies in Tamil Literature and History by Ramachandra Dikshitar'', pages 55-59 He authored the Inna Narpathu, a didactic work of the Sangam literature. Verse 5 of the Tiruvalluva Maalai is also attributed to him. Early life Kapilar was born in Thiruvadhavur in the Pandyan Kingdom. Initially a poet at the Pandyan court, he left Madurai at an early age to travel across various kingdoms. Kapilar hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengam
Chengam (or Chengamma as on British records) is an important market town and a taluk headquarter in the Foot hills of Eastern ghats in Tiruvannamalai district of Tamil Nadu, India. Chengam is the gateway to the Chengam pass in the Eastern ghats between Javvadhu hills to the north and Chennakesava hills to the south. The town is also the centre for various industrial activities which includes Sathanur dam hydro-electric project, Aavin milk processing plant and Periya Kolappadi SIDCO estate. History The book Malaipadukadam in the Sangakkala literature mentions that Nannansei Nannan was a short-lived king who ruled from the Palkunrakottam hill with his capital as his capital. Many rare historical sources such as inscriptions and archeological finds have been found to prove this. Researchers also say that Nannan-ruled Navira Hill now refers to the Jawadhu Hills and some to the mountains near the sea. Initially Chengam was an assembly constituency (SC) of Tiruppattur (Lok Sabha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |