|
Pathophysiology Of Nerve Entrapment
Nerve compression syndrome, Nerve entrapment involves a cascade of physiological changes caused by compression and tension. Some of these changes are irreversible. The magnitude and duration of the forces determines the extent of injury. In the acute form, mechanical injury and metabolic blocks impede nerve function. In the chronic form, there is a sequence of changes starting with a breakdown of the blood-nerve-barrier, followed by edema with connective tissue changes, followed by diffuse Demyelinating disease, demyelination, and finally followed by axonmetesis. The injury will often be a mixed lesion where mild/moderate compression is a combination of a metabolic block and Neurapraxia, neuropraxia, while severe compression combines elements of neuropraxia and axonmetesis. Peripheral nerve anatomy Nerve cell Neuron, Nerve cells comprise a small cell body and a very long segment called the axon. The cell body resides in the spinal cord and the axon extends all the way to the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section Normal Nerve And Atrophied Nerve
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross shape has been widely officially recognized as an absolute and exclusive religious symbol of Christianity from an early period in that religion's history.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 Before then, it was used as a religious or cultural symbol throughout Europe, in West Asia, west and south Asia (the latter, in the form of the original Swastika); and in Ancient Egypt, where the Ankh was a hieroglyph that represented "life" and was used in the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
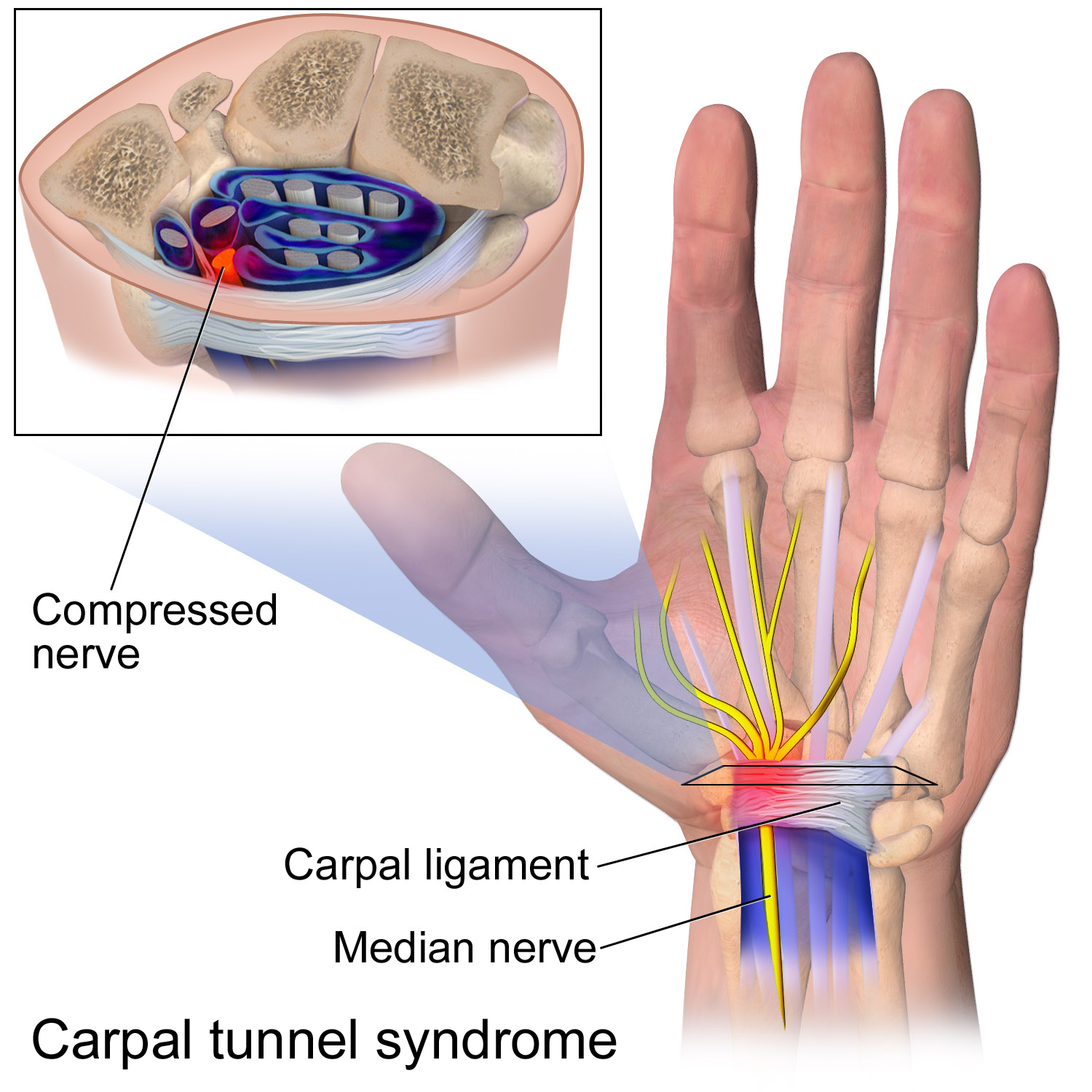
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome usually has no known cause, but there are environmental and medical risk factors associated with the condition.> CTS can affect both wrists. Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, the resulting swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial membrane, synovial lining of the tendons causes compression. The main symptoms are numbness and Paresthesia, tingling of the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the thumb side of the ring finger, as well as pain in the hand and fingers. Symptoms are typically most troublesome at night. Many people sleep with their wrists bent, and the ensuing symptoms may lead to awake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adduction
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves (nerve plexus) formed by the anterior rami of the lower four Spinal nerve#Cervical nerves, cervical nerves and first Spinal nerve#Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve (cervical spinal nerve 5, C5, Cervical spinal nerve 6, C6, cervical spinal nerve 7, C7, cervical spinal nerve 8, C8, and thoracic spinal nerve 1, T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the axilla, armpit, it supplies Afferent nerve fiber, afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. Structure The brachial plexus is divided into five ''roots'', three ''trunks'', six ''divisions'' (three anterior and three posterior), three ''cords'', and five ''branches''. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Gluteal Syndrome
Deep gluteal syndrome describes the non- discogenic extrapelvic entrapment of the sciatic nerve in the deep gluteal space. In simpler terms this is sciatica due to nerve irritation in the buttocks rather than the spine or pelvis. It is an extension of non-discogenic sciatic nerve entrapment beyond the traditional model of piriformis syndrome. Where sciatic nerve irritation in the buttocks was once thought of as only piriformis muscle, it is now recognized that there are many other causes. Symptoms are pain or dysthesias (abnormal sensation) in the buttocks, hip, and posterior thigh with or without radiating leg pain. Patients often report pain when sitting. The two most common causes are piriformis syndrome and fibrovascular bands (scar tissue), but many other causes exist. Diagnosis is usually done through physical examination, magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance neurography, and diagnostic nerve blocks. Surgical treatment is an endoscopic sciatic nerve decompression wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Sacroiliac Ligament
The posterior sacroiliac ligament is situated in a deep depression between the sacrum and ilium behind; it is strong and forms the chief bond of union between the bone A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...s. It consists of numerous fasciculi, which pass between the bones in various directions. * The ''upper part'' (''short posterior sacroiliac ligament'') is nearly horizontal in direction, and pass from the first and second transverse tubercles on the back of the sacrum to the tuberosity of the ilium. * The ''lower part'' (''long posterior sacroiliac ligament'') is oblique in direction; it is attached by one extremity to the third transverse tubercle of the back of the sacrum, and by the other to the posterior superior spine of the ilium. See also * Anterior sacro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Cluneal Nerves
The medial clunial nerves innervate the skin of the buttocks closest to the midline of the body. Those nerves arise from the posterior rami of spinal sacral nerves A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into t ... (S1, S2, and S3). Additional images Image:Gray801.png, Diagram of the distribution of the cutaneous branches of the posterior divisions of the spinal nerves. Image:Gray803.png, The posterior divisions of the sacral nerves. External links * * - "Superficial Anatomy of the Lower Extremity: Cutaneous Nerves of the Posterior Aspect of the Lower Extremity" Spinal nerves Buttocks {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop. Structure The inguinal ligament runs from the anterior superior iliac crest of the ilium to the pubic tubercle of the pubic bone. It is formed by the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis and is continuous with the fascia lata of the thigh. There is some dispute over the attachments. Structures that pass deep to the inguinal ligament include: * Psoas major, iliacus, pectineus * Femoral nerve, artery, and vein * Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh *Lymphatics Function The ligament serves to contain soft tissues as they course anteriorly from the trunk to the lower extremity. This structure demarcates the superior border of the femoral triangle. It demarcates the inferior border of the inguinal triangle. The midpoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Of Thigh
The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve) is a cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It originates from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves from the lumbar plexus. It passes under the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin on the lateral part of the thigh by an anterior branch and a posterior branch. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh can be investigated using ultrasound. Local anaesthetic can be injected around the nerve for skin grafts and surgery around the outer thigh. Nerve compression (usually around the inguinal ligament) can cause meralgia paraesthetica. Structure The nerve is usually 1-2 mm thick. Origin The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a nerve of the lumbar plexus. It arises from the anterior rami of the second and third lumbar nerves (L2-L3). Course and relations It passes through psoas major muscle, and emerges from its lateral border. It cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |