|
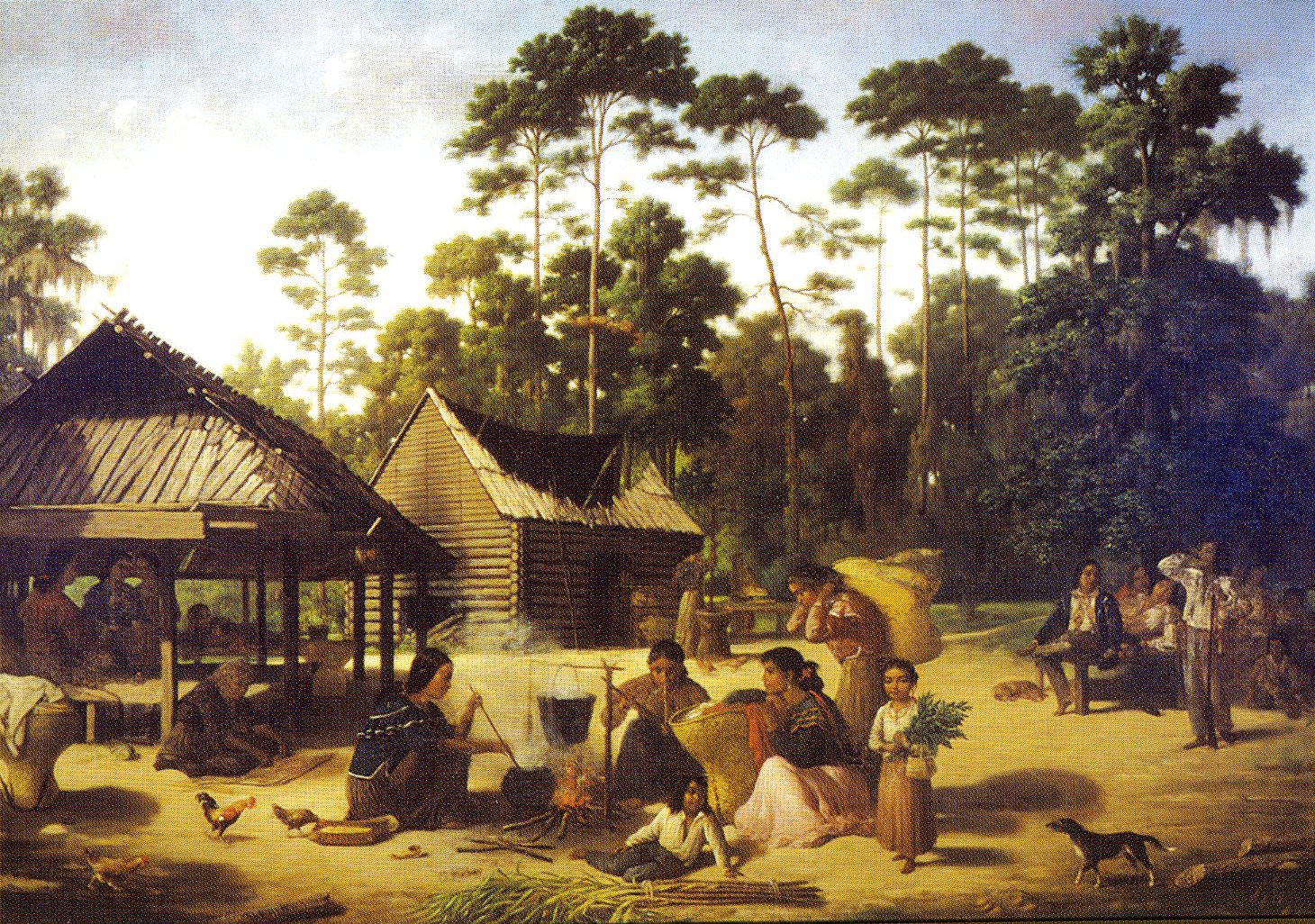
Pascagoula Formation
The Pascagoula (also Pascoboula, Pacha-Ogoula, Pascagola, Pascaboula, Paskaguna) were an indigenous group living in coastal Mississippi on the Pascagoula River. The name ''Pascagoula'' is a Choctaw term meaning "bread eater". Choctaw native Americans using the name Pascagoula are named after the words for "bread eaters". History Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville encountered the tribe in 1699 and was impressed by the beauty of Pascagoula women. According to local Euro-American legend, the peace-loving tribe walked single file into the river because the local Biloxi tribe were planning to attack. Anola, a Biloxi "princess", eloped with the Pascagoula chief Altama, although she was engaged to a Biloxi chieftain. Anola's angry would-be husband led his soldiers into battle with the Pascagoula. Outnumbered and fearing enslavement by the Biloxi, the tribe joined hands and walked into the river singing a death song. The river became known as the "Singing River" because of this death song, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the southwest, and Arkansas to the northwest. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River, or its historical course. Mississippi is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 32nd largest by area and List of U.S. states by population, 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income. Jackson, Mississippi, Jackson is both the state's List of capitals in the United States, capital and largest city. Jackson metropolitan area, Mississippi, Greater Jackson is the state's most populous Metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan area, with a population of 591,978 2020 United States census, in 2020. Other major cities include Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Southaven, Mississippi, South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascagoula River
The Pascagoula River is a river, about 80 miles (130 km) long, in southeastern Mississippi in the United States. The river drains an area of about 8,800 square miles (23,000 km²) and flows into Mississippi Sound of the Gulf of Mexico. The Pascagoula River Basin is managed by the Pat Harrison Waterway District. It is significant as the only unaffected (or nearly so) river with a discharge of over per year flowing from the United States into the Gulf of Mexico, and indeed the only one in the humid subtropical climate, Cfa Köppen climate classification zone anywhere in the world, with the nearest approaches being the Juquiá River, Juquiá and Itajaí-Açu River, Itajaí in Southeast Region, Brazil, southeastern Brazil (The Red River (Asia), Yuan Jiang and Shinano Gawa are comparable to those Brazilian rivers but are only marginally in the Cfa zone). As a result, the Pascagoula has, in modern times, been the focus of a great deal of effort regarding its conservation to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. Choctaw descendants are also members of other tribes. Etymology The Choctaw autonym is Chahta. "Choctaw" is an anglicized spelling. According to anthropologist John R. Swanton, the Choctaw derived their name from an early leader of the Choctaw people. Language The Choctaw language belongs to the Muskogean language family. The Choctaw language was well known among the American frontiersmen of the early 19th century. In 1870, a Christian Missionary and fluent Choctaw speaker Cyrus Byington published a Choctaw Dictionary ''Grammar of the Choctaw Language.'' Revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Singing River, The Famous Singing River, Pascagoula Located On U
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Le Moyne D'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French colonist parents. Early life Pierre Le Moyne was born in July 1661 at Fort Ville-Marie (now Montreal), in the French colony of Canada, the third son of Charles le Moyne de Longueuil et de Châteauguay, a native of Dieppe or of Longueuil near Dieppe, Normandy in France and lord of Longueuil in Canada, and of (called Catherine Primot in some sources) from Rouen. He is also known as ''Sieur d'Iberville'' (''et d'Ardillières''). He had eleven brothers, most of whom became soldiers. One, Jacques Le Moyne de Sainte-Hélène, led French and Indian forces in the Schenectady massacre in present-day New York's Mohawk Valley. Charles le Moyne de Longueuil, Baron de Longueuil, was governor of Montreal. Another, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne Bienville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Princess
The Indian princess or Native American princess is usually a stereotypical and inaccurate representation of a Native American or other Indigenous woman of the Americas. The term "princess" was often mistakenly applied to the daughters of tribal chiefs or other community leaders by early American colonists who mistakenly believed that Indigenous people shared the European system of royalty. This inaccurate portrayal has continued in popular animation, with characters that conform to European standards of beauty, with the most famous misrepresentation being that of Pocahontas. Frequently, the "Indian Princess" stereotype is paired with the "Pocahontas theme" in which the princess "offers herself to a captive Christian knight, a prisoner of her father, and after rescuing him, she is converted to Christianity and lives with him in his native land." - a false narrative which misrepresents the events of Matoaka's life. The phrase "''Indian princess''", when used in this way, is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Sibley (doctor)
John Sibley (1757–1837) was an American surgeon. After serving as a surgeon's assistant in the American Revolutionary War, he moved to Natchitoches, Louisiana to work as a contract surgeon. From 1805 to 1815, Sibley was also the official United States Indian agent of . Later in life, he served as a Senator in the Louisiana State Senate, as well as a colonel of a militia, a cattle farmer, a cotton planter, and a salt manufacturer. Early life Born in 1757, Sibley lived in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, until moving to Louisiana in 1803. In 1780, he married Elizabeth Hopkins, a daughter of theologian Samuel Hopkins. John and Elizabeth had two sons, George Champlin Sibley (April 1, 1782 – January 31, 1863), an American explorer and educator, and Samuel Hopkins Sibley, father of Confederate General Henry Hopkins Sibley. During the Revolutionary War, John Sibley was a surgeon's assistant, giving him the experience to continue his practice after the war; however, in 1784, John moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobilian Jargon
Mobilian Jargon (also Mobilian trade language, Mobilian Trade Jargon, Chickasaw–Choctaw trade language, Yamá) was a pidgin used as a lingua franca among Native American groups living along the north coast of the Gulf of Mexico around the time of European settlement of the region. It was the main language among Native tribes in this area, mainly Louisiana. There is evidence indicating its existence as early as the late 17th to early 18th century. The Native groups that are said to have used it were the Alabama, Apalachee, Biloxi, Chacato, Pakana, Pascagoula, Taensa, Tunica, Caddo, Chickasaw, Houma, Choctaw, Chitimacha, Natchez, and Ofo. The name is thought to refer to the Mobile Indians of the central Gulf Coast, but did not originate from this group; Mobilian Jargon is linguistically and grammatically different from the language traditionally spoken by the Mobile Indians. Mobilian Jargon facilitated trade between tribes speaking different languages and European sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine-Simon Le Page Du Pratz
Antoine-Simon Le Page du Pratz (1695?–1775)John C. Van Horne, "Memoir of a French Visitor: du Pratz, History of Louisiana" , Discovering Lewis & Clark was a French ethnographer, historian, and who is best known for his ''Histoire de la Louisiane''. It was first published in twelve installments from 1751 to 1753 in the ''Journal Economique'', then completely in three volumes in Paris in 1758. After their victory in the |
Native American Tribes In Mississippi
Native may refer to: People * '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood * '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes * List of Australian plants termed "native", whose common name is of the form "native . . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |