|
Particle In A Spherically Symmetric Potential
In quantum mechanics, a spherically symmetric potential is a system of which the potential only depends on the radial distance from the spherical center and a location in space. A particle in a spherically symmetric potential will behave accordingly to said potential and can therefore be used as an approximation, for example, of the electron in a hydrogen atom or of the formation of chemical bonds. In the general time-independent case, the dynamics of a particle in a spherically symmetric potential are governed by a Hamiltonian of the following form:\hat = \frac + V() Here, m_0 is the mass of the particle, \hat is the momentum operator, and the potential V(r) depends only on the vector magnitude of the position vector, that is, the radial distance from the origin (hence the spherical symmetry of the problem). To describe a particle in a spherically symmetric system, it is convenient to use spherical coordinates; denoted by r, \theta and \phi. The time-independent Schrödin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bound State
A bound state is a composite of two or more fundamental building blocks, such as particles, atoms, or bodies, that behaves as a single object and in which energy is required to split them. In quantum physics, a bound state is a quantum state of a particle subject to a potential energy, potential such that the particle has a tendency to remain localized in one or more regions of space. The potential may be external or it may be the result of the presence of another particle; in the latter case, one can equivalently define a bound state as a state representing two or more particles whose interaction energy exceeds the total energy of each separate particle. One consequence is that, given a potential vanish at infinity, vanishing at infinity, negative-energy states must be bound. The energy spectrum of the set of bound states are most commonly discrete, unlike scattering states of Free particle, free particles, which have a continuous spectrum. Although not bound states in the stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle In A Box
In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes the movement of a free particle in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example, a particle trapped inside a large box can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never "sit still". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes. The particle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baker–Campbell–Hausdorff Formula
In mathematics, the Baker–Campbell–Hausdorff formula gives the value of Z that solves the equation e^X e^Y = e^Z for possibly noncommutative and in the Lie algebra of a Lie group. There are various ways of writing the formula, but all ultimately yield an expression for Z in Lie algebraic terms, that is, as a formal series (not necessarily convergent) in X and Y and iterated commutators thereof. The first few terms of this series are: Z = X + Y + \frac ,Y+ \frac ,[X,Y + \frac [Y,[Y,X + \cdots\,, where "\cdots" indicates terms involving higher Commutator#Identities_(ring_theory)">commutators of X and Y. If X and Y are sufficiently small elements of the Lie algebra \mathfrak g of a Lie group G, the series is convergent. Meanwhile, every element g sufficiently close to the identity in G can be expressed as g = e^X for a small X in \mathfrak g. Thus, we can say that ''near the identity'' the group multiplication in G—written as e^X e^Y = e^Z—can be expressed in purely Lie alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, an Austrian physicist, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933. Conceptually, the Schrödinger equation is the quantum counterpart of Newton's second law in classical mechanics. Given a set of known initial conditions, Newton's second law makes a mathematical prediction as to what path a given physical system will take over time. The Schrödinger equation gives the evolution over time of the wave function, the quantum-mechanical characterization of an isolated physical system. The equation was postulated by Schrödinger based on a postulate of Louis de Broglie that all matter has an associated matter wave. The equati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Coordinates
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system specifies a given point in three-dimensional space by using a distance and two angles as its three coordinates. These are * the radial distance along the line connecting the point to a fixed point called the origin; * the polar angle between this radial line and a given ''polar axis''; and * the azimuthal angle , which is the angle of rotation of the radial line around the polar axis. (See graphic regarding the "physics convention".) Once the radius is fixed, the three coordinates (''r'', ''θ'', ''φ''), known as a 3-tuple, provide a coordinate system on a sphere, typically called the spherical polar coordinates. The plane passing through the origin and perpendicular to the polar axis (where the polar angle is a right angle) is called the ''reference plane'' (sometimes '' fundamental plane''). Terminology The radial distance from the fixed point of origin is also called the ''radius'', or ''radial line'', or ''radial coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1960) ''Physics'', Section 7-5, Wiley International Edition The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, or force ( F) in the direction of motion times its displacement ( s), needed to accelerate the object from rest to its given speed. The same amount of work is done by the object when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. The SI unit of energy is the joule, while the English unit of energy is the foot-pound. In relativistic mechanics, \fracmv^2 is a good approximation of kinetic energy only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις ''kinesis'', meaning "motion". The dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenfunction
In mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator ''D'' defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that, when acted upon by ''D'', is only multiplied by some scaling factor called an eigenvalue. As an equation, this condition can be written as Df = \lambda f for some scalar eigenvalue \lambda. The solutions to this equation may also be subject to boundary conditions that limit the allowable eigenvalues and eigenfunctions. An eigenfunction is a type of eigenvector. Eigenfunctions In general, an eigenvector of a linear operator ''D'' defined on some vector space is a nonzero vector in the domain of ''D'' that, when ''D'' acts upon it, is simply scaled by some scalar value called an eigenvalue. In the special case where ''D'' is defined on a function space, the eigenvectors are referred to as eigenfunctions. That is, a function ''f'' is an eigenfunction of ''D'' if it satisfies the equation where λ is a scalar. The solutions to Equation may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
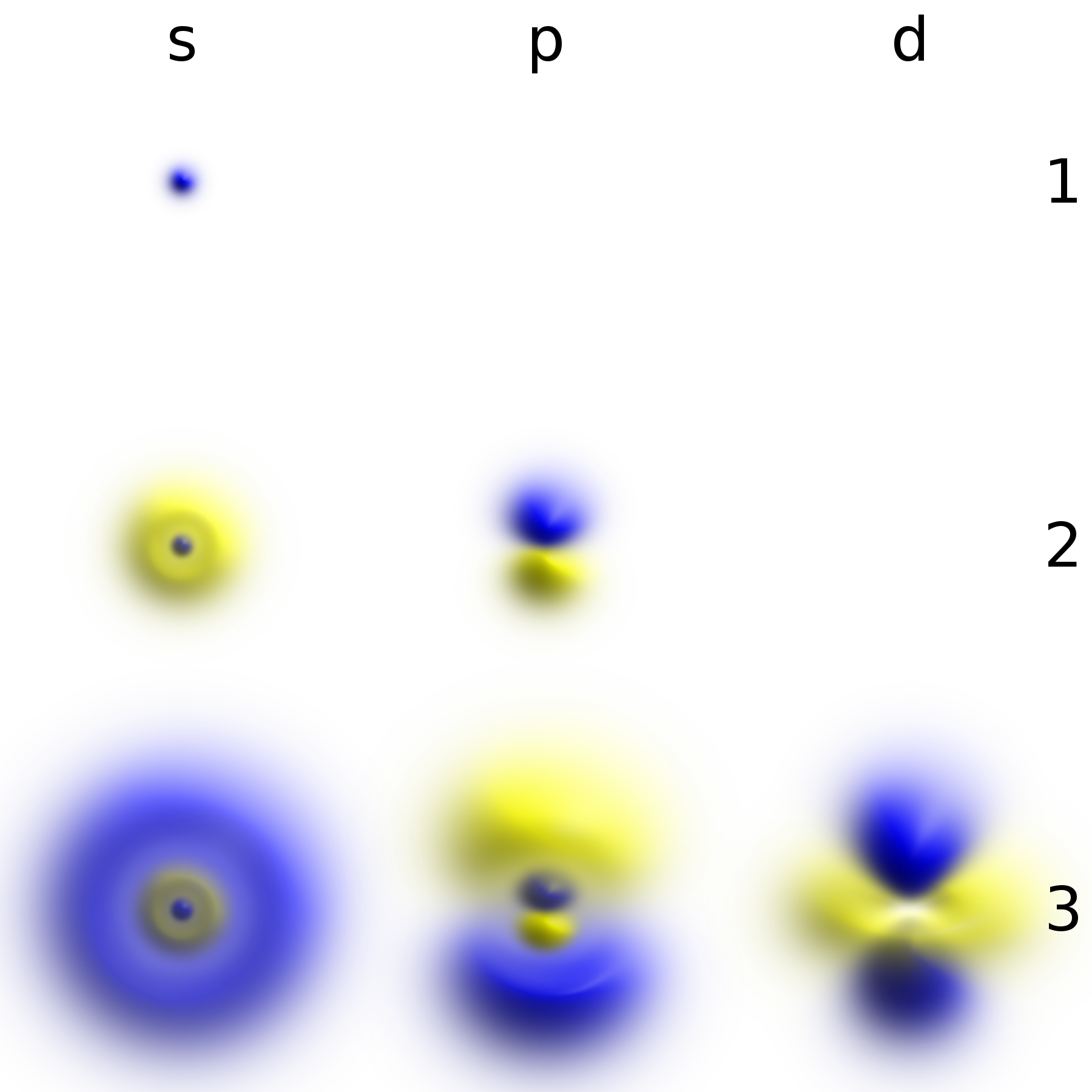
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The table of spherical harmonics contains a list of common spherical harmonics. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, every function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |