|
Parental Care
Parental care is a behavioural and evolutionary strategy adopted by some animals, involving a parental investment being made to the evolutionary fitness of offspring. Patterns of parental care are widespread and highly diverse across the animal kingdom.Kokko, H. & Jennions, M.D. (2008) Parental investment, sexual selection and sex ratios. ''Journal of Evolutionary Biology,'' 21, pp.919–948. There is great variation in different animal groups in terms of how parents care for offspring, and the amount of resources invested by parents. For example, there may be considerable variation in the amount of care invested by each sex, where females may invest more in some species, males invest more in others, or investment may be shared equally. Numerous hypotheses have been proposed to describe this variation and patterns in parental care that exist between the sexes, as well as among species.Gonzalez-Voyer, A. and Kolm, N. (2010). Parental Care and Investment. ''Encyclopedia of Life Scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
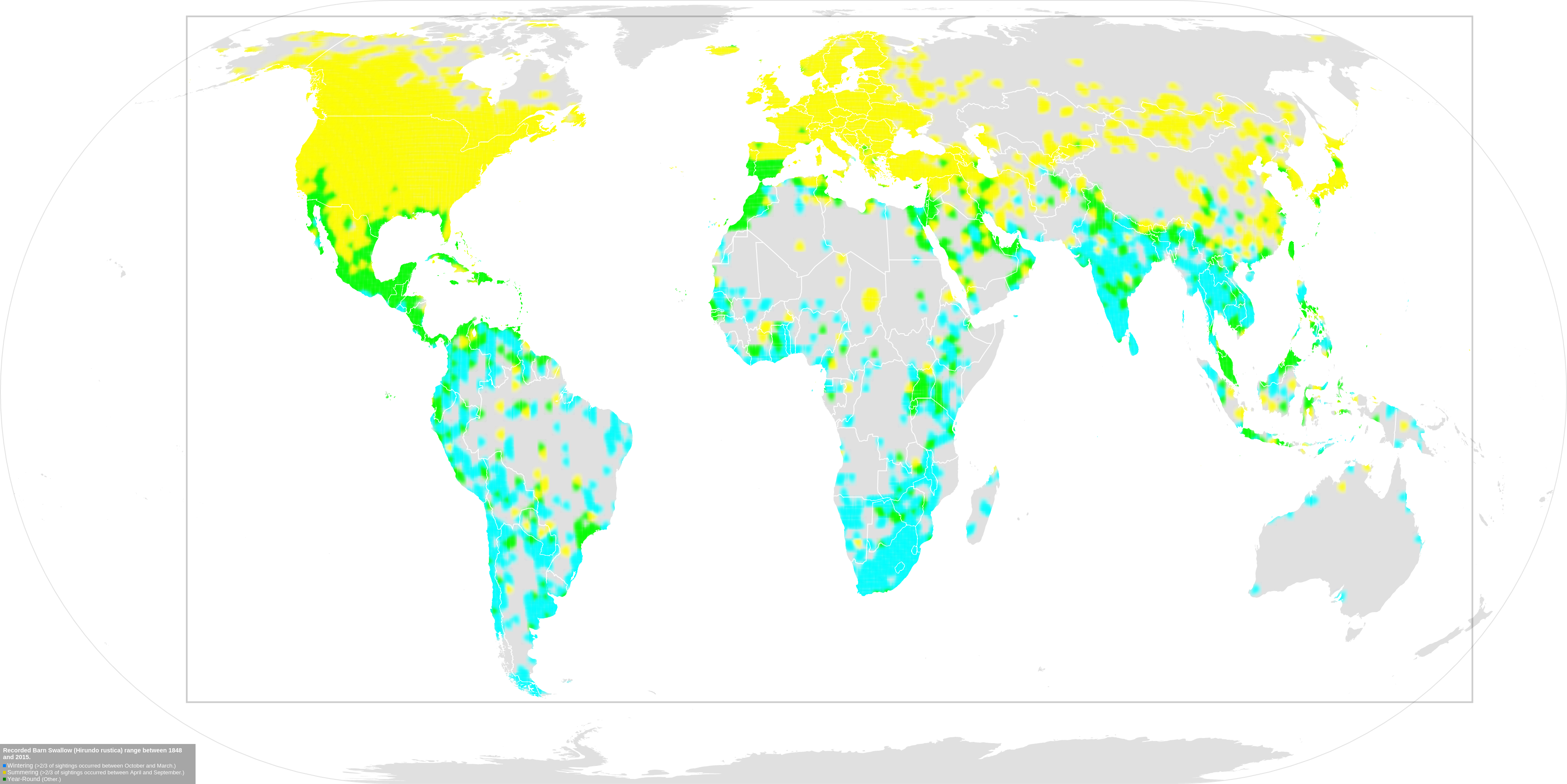
Hirundo Rustica (Linnaeus, 1758)
The barn swallow (''Hirundo rustica'') is the most widespread species of swallow in the world, occurring on all continents, with vagrants reported even in Antarctica. It is a distinctive passerine bird with blue upperparts and a long, deeply forked tail. In English-speaking world, Anglophone Europe, it is just called the swallow; in northern Europe, it is the only member of family Hirundinidae called a "swallow" rather than a "Martin (bird), martin". There are six subspecies of barn swallow, which breed across the Northern Hemisphere. Two subspecies, (''H. r. savignii and H. r. transitiva'') have fairly restricted ranges in the Nile valley and eastern Mediterranean, respectively. The other four are more widespread, with winter ranges covering much of the Southern Hemisphere. The barn swallow is a bird of open country that normally nests in man-made structures and consequently has spread with human expansion. It builds a cup bird nest, nest from mud pellets in barns or similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterly Review Of Biology
''The Quarterly Review of Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of biology. It was established in 1926 by Raymond Pearl. In the 1960s it was purchased by the Stony Brook Foundation when the editor H. Bentley Glass became academic vice president of Stony Brook University. The editor-in-chief is Liliana M. Dávalos (Stony Brook University). It is currently published by the University of Chicago Press. Aims and scope The ''QRB'' has presented insightful historical, philosophical, and technical treatments of important biological topics since 1926. As the premier review journal in biology, the ''QRB'' publishes outstanding review articles of generous length that are guided by an expansive, inclusive, and often humanistic understanding of biology. Beyond the core biological sciences, the ''QRB'' is also an important review journal for scholars in related areas, including policy studies and the history and philosophy of science. A comprehensive section o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiptera
Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising more than 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from to around , and share a common arrangement of piercing-sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is sometimes limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Entomologists reserve the term ''bug'' for Hemiptera or Heteroptera,Gilbert Waldbauer. ''The Handy Bug Answer Book.'' Visible Ink, 1998p. 1. which does not include other arthropods or insects of other orders such as ants, bees, beetles, or butterflies. In some varieties of English, all terrestrial arthropods (including non-insect arachnids and myriapods) also fall under the colloquial understanding of ''bug''. Many insects with "bug" in their common name, especially in American English, belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the Maybug and ladybug are beetles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUniverse
iUniverse, founded in October 1999, is an American self-publishing company based in Bloomington, Indiana.Kevin Abourezk"iUniverse to move to Indiana" incoln Journal Star, January 22, 2008 It has been owned by Author Solutions since 2008 (which has been owned by Najafi Companies since 2015). History iUniverse focuses on print-on-demand self-publishing and a service the company refers to as "assisted self-publishing" which critics say is indicative of vanity press since authors are asked to pay from to $15,000 for additional services. Soon after they were founded, Barnes & Noble purchased a 49% stake in the company. As part of the agreement, Barnes & Noble offered select iUniverse titles both in their online bookstore and at their physical stores. In 2004, Amy Fisher's memoir, ''If I Knew Then'', about serving seven years in prison on first-degree aggravated assault charges for shooting Mary Jo Buttafuoco, became the best-selling book in iUniverse's history, selling more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bledius Spectabilis
''Bledius spectabilis'', commonly known as the magnificent salt beetle, is a species of small rove beetle. Description This beetle is 5 to 7 millimetres long and has brightly coloured legs. The wing covers are brownish and as wide as they are long. Distribution ''Bledius spectabilis'' inhabits the sea shores of the Caspian Sea, Caspian and Black Seas, the coasts of the Mediterranean from Asia Minor to Spain and Morocco, and the Atlantic coast as far north as the Irish Sea and the North Sea. Behaviour ''Bledius spectabilis'', shows very unusual behaviour for an insect in that it actively protects its larvae from the parasitic wasp ''Barycnemis blediator'' and from the predatory ''Dicheirotrichus gustavii''. References External linksImages representing ''Bledius spectabilis'' at Barcode of Life Data System {{Taxonbar, from=Q2114623 Staphylinidae Beetles of Europe Beetles described in 1857 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burying Beetle
Burying beetles or sexton beetles, genus ''Nicrophorus'', are the best-known members of the family Silphidae (carrion beetles). Most of these beetles are black with red markings on the Elytron, elytra (forewings). Burying beetles are true to their name—they bury the carcasses of small vertebrates such as birds and rodents as a Necrophagy, food source for their larvae; this makes them carnivorous. They are unusual among insects in that both the male and female parents take Bi-parental care, care of the brood. The genus name is sometimes spelled ''Necrophorus'' in older texts: this was an unjustified Emendation (taxonomy), emendation by Carl Peter Thunberg (1789) of Fabricius's original name, and is not valid under the ICZN. The American burying beetle (''Nicrophorus americanus'') has been on the U.S. Endangered species, endangered species list since 1989. This species was native to 35 U.S. states but now is only known to exist in 9. Reproduction Burying beetles have large clu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeybee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to mainland Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of perennial colonial nests from wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only 8 surviving species of honey bees are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees. The best-known honey bee is the wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potter Wasp
Potter wasps (or mason wasps), the Eumeninae, are a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan wasp group currently considered a subfamily of Vespidae, but sometimes recognized in the past as a separate family, Eumenidae. Mud dauber wasps, which also build their nests with mud, are in the families Sphecidae and Crabronidae and not discussed here. Recognition Most eumenine species are black or brown, and commonly marked with strikingly contrasting patterns of yellow, white, orange, or red (or combinations thereof), but some species, mostly from Tropics, tropical regions, show faint to strong blue or green Metallic color, metallic highlights in the background colors. Like most vespids, their wings are folded longitudinally at rest. They are particularly recognized by the following combination of characteristics: # a posterolateral projection known as a parategula on both sides of the Mesothorax#Mesoscutum, mesoscutum; # tarsal claws cleft; # hind Arthropod leg, coxae with a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they reach adulthood. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term because species in this order have membranous wings. However, a key characteristic of this order is that the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PubMed Identifier
PubMed is an openly accessible, free database which includes primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintains the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval. From 1971 to 1997, online access to the MEDLINE database was provided via computer and phone lines primarily through institutional facilities, such as university libraries. PubMed, first released in January 1996, ushered in the era of private, free, home- and office-based MEDLINE searching. The PubMed system was offered free to the public starting in June 1997. Content In addition to MEDLINE, PubMed provides access to: * older references from the print version of ''Index Medicus'', back to 1951 and earlier * references to some journals before they were indexed in Index Medicus and MEDLINE, for instance ''Science'', '' BMJ'', and ''Annals of Surgery'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviparity
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings known as hatchlings with little or no embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method used by most animal species, as opposed to viviparous animals that develop the embryos internally and metabolically dependent on the maternal circulation, until the mother gives birth to live juveniles. Ovoviviparity is a special form of oviparity where the eggs are retained inside the mother (but still metabolically independent), and are carried internally until they hatch and eventually emerge outside as well-developed juveniles similar to viviparous animals. Modes of reproduction The traditional modes of reproduction include oviparity, taken to be the ancestral condition, traditionally where either unfertilised oocytes or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |