|
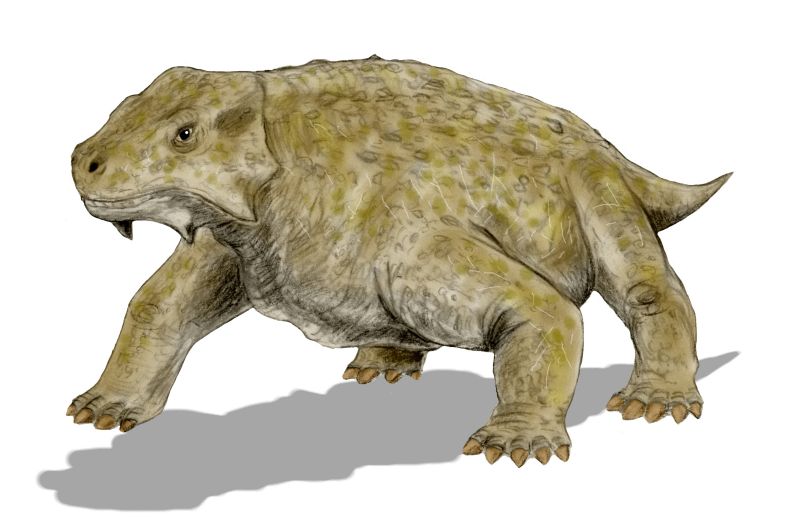
Pareiasuchus
''Pareiasaurus'' (from , "cheek" and , "lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ... had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurus Serridens
''Pareiasaurus'' (from , "cheek" and , "lizard") is an extinct genus of Pareiasauromorpha, pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family (biology), family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, South Africa. This early form is one of the first representatives of the genus. It was originally included under the genus ''Pareiasuchus''. The snout is heavily armoured, and bears a horn-like boss. The teeth are equipped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurus Serridens Skeleton
''Pareiasaurus'' (from , "cheek" and , "lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ... had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasauromorpha
Pareiasauromorpha is a group of parareptilian amniotes from the Permian. It includes genera found all over the world, with many genera from Asia and South Africa. The clade was first used as a group by Linda A. Tsuji in 2011, in order to group the family Nycteroleteridae (nycteroleters) and the superfamily Pareiasauroidea (pareiasaurs). Pareiasauromorpha is considered to be a monophyletic node, the sister group to procolophonoids. Classification ''Pareiasauromorpha'' was first used to define a group of parareptilians in 2011 by Linda A. Tsuji. The next year, Tsuji and her colleagues used Pareiasauromorpha as a node inside Procolophonia. In their 2012 publication, Tsuji ''et al.'' defined it as a monophyletic node containing "nycteroleters" (the family Nycteroleteridae) and "pareiasaurs" (in the superfamily Pareiasauroidea). Nycteroleteridae Nycteroleteridae is a family, commonly called "nycteroleters", classified in Pareiasauromorpha. The group includes the genera '' Emero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurids
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with osteoderms which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, some reaching sizes over , equivalent to the largest contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct in the end-Permian mass extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, with some species estimated to exceed in body mass. The limbs of many parieasaurs were extremely robust, likely to account for the increased stress on their limbs caused by their typically sprawling posture. The cow-sized ''Bunostegos'' differed from other pareiasaurs by having a more upright limb posture, being amongst the first amniotes to develop this trait. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasauria
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with osteoderms which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, some reaching sizes over , equivalent to the largest contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct in the end-Permian mass extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, with some species estimated to exceed in body mass. The limbs of many parieasaurs were extremely robust, likely to account for the increased stress on their limbs caused by their typically sprawling posture. The cow-sized '' Bunostegos'' differed from other pareiasaurs by having a more upright limb posture, being amongst the first amniotes to develop this trait. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchiapingian
In the geologic timescale, the Wuchiapingian or Wujiapingian (from in the Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province ) is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the lower or earlier of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Wuchiapingian spans the time between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Capitanian and followed by the Changhsingian. Regional stages with which the Wuchiapingian is coeval or overlaps include the Djulfian or Dzhulfian, Longtanian, Rustlerian, Saladoan, and Castilian. Stratigraphic definitions The Wuchiapingian was first used in 1962, when the Lopingian Series of southwestern China was divided in the Changhsingian and Wuchiapingian Formations. In 1973 the Wuchiapingian was first used as a chronostratigraphic unit (i.e. a stage, as opposed to a formation, which is a lithostratigraphic unit). The base of the Wuchiapingian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the conodont specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchiapingian Genus First Appearances
In the geologic timescale, the Wuchiapingian or Wujiapingian (from in the Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province ) is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the lower or earlier of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Wuchiapingian spans the time between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Capitanian and followed by the Changhsingian. Regional stages with which the Wuchiapingian is coeval or overlaps include the Djulfian or Dzhulfian, Longtanian, Rustlerian, Saladoan, and Castilian. Stratigraphic definitions The Wuchiapingian was first used in 1962, when the Lopingian Series of southwestern China was divided in the Changhsingian and Wuchiapingian Formations. In 1973 the Wuchiapingian was first used as a chronostratigraphic unit (i.e. a stage, as opposed to a formation, which is a lithostratigraphic unit). The base of the Wuchiapingian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the conodont species ''Clarkina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changhsingian Life
In the geologic time scale, the Changhsingian or Changxingian is the latest age or uppermost stage of the Permian. It is also the upper or latest of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Changhsingian lasted from to 251.9 Ma ago. It is preceded by the Wuchiapingian age/stage and is followed by the Induan age/stage (Early Triassic epoch). The greatest mass extinction in the Phanerozoic eon, the Permian–Triassic extinction event, occurred around the end of this age. Stratigraphic definitions The Changhsingian is named after Changxing () in northern Zhejiang, China. The stage was named for the Changhsing Limestone. The name was first used for a stage in 1970 and was anchored in the international timescale in 1981.. The base of the Changhsingian Stage is at the first appearance of the conodont species '' Clarkina wangi''. The global reference profile is profile D at Meishan, in the type area in Changxing, just below the Changhsingian foraminifer index fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchiapingian Life
In the geologic timescale, the Wuchiapingian or Wujiapingian (from in the Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province ) is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the lower or earlier of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured. The moment of epoch is usually decided b ... or Series. The Wuchiapingian spans the time between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Capitanian and followed by the Changhsingian. Regional stages with which the Wuchiapingian is coeval or overlaps include the Djulfian or Dzhulfian, Longtanian, Rustlerian, Saladoan, and Castilian. Stratigraphic definitions The Wuchiapingian was first used in 1962, when the Lopingian Series of southwestern China was divided in the Changhsingian and Wuchiapingian Formations. In 1973 the Wuchiapin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopingian Life
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic. The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal terms late Permian or upper Permian. The name was introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1931 and derives from Leping, Jiangxi in China. It consists of two stages/ ages. The earlier is the Wuchiapingian and the later is the Changhsingian. The International Chronostratigraphic Chart (v2018/07) provides a numerical age of 259.1 ±0.5 Ma. If a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) has been approved, the lower boundary of the earliest stage determines numerical age of an epoch. The GSSP for the Wuchiapingian has a numerical age of 259.8 ± 0.4 Ma. Evidence from Milankovitch cycles suggests that the length of an Earth day during this epoch was approximately 22 hours. Geography During the Lopingian, most of the earth was in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1876
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |