|
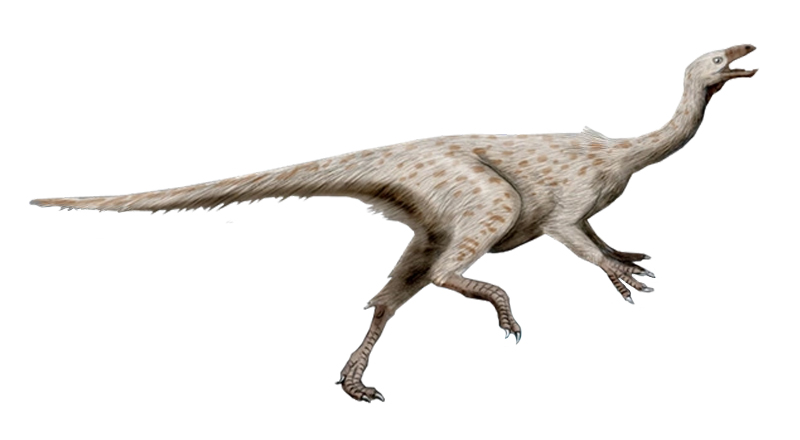
Paraxenisaurus
''Paraxenisaurus'' (meaning "strange lizard") is a genus of deinocheirid theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Mexico during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, 73 to 72.1 million years ago. Discovery and naming During the 1990s, ornithomimosaur fossils were discovered at three sites in the Cerro del Pueblo Formation of Coahuila state. Two decades later, these remains were identified as belonging to a distinct North American taxon. In 2020, they were named and described by Mexican paleontologists Claudia Inés Serrano-Brañas, Belinda Espinosa-Chávez, Sarah Augusta Maccracken, Cirene Gutiérrez-Blando, Claudio de León-Dávila and José Flores Ventura. The type species ''Paraxenisaurus normalensis''. The generic name is derived from the Greek ''paráxenos'', "strange". The specific name is after the Benemérita Escuela Normal de Coahuila, a teacher training institution, where the fossils had been deposited. They include the holotype BENC 2/2-001, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
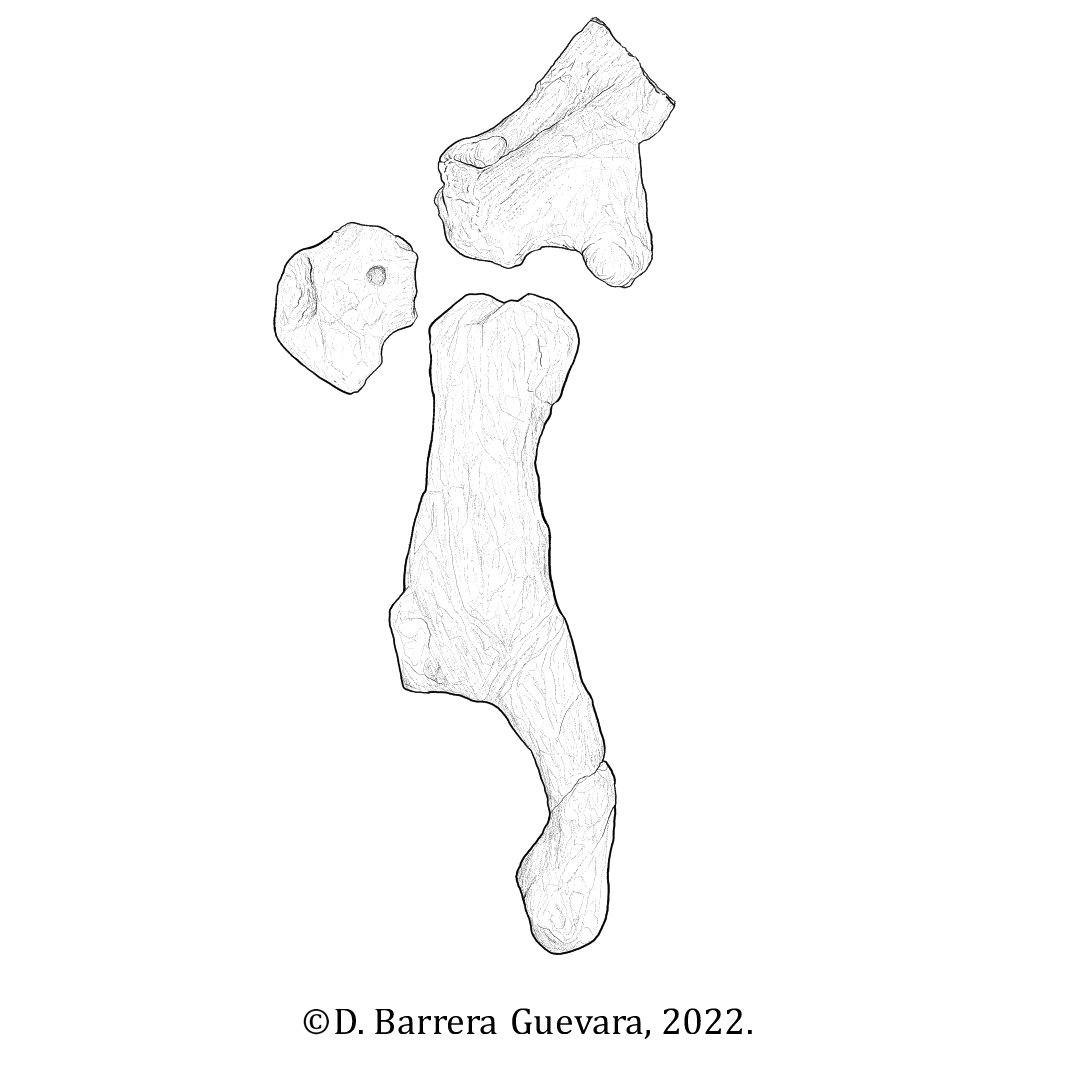
Paraxenisaurus Manual Claw
''Paraxenisaurus'' (meaning "strange lizard") is a genus of deinocheirid theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Mexico during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, 73 to 72.1 million years ago. Discovery and naming During the 1990s, ornithomimosaur fossils were discovered at three sites in the Cerro del Pueblo Formation of Coahuila state. Two decades later, these remains were identified as belonging to a distinct North American taxon. In 2020, they were named and described by Mexican paleontologists Claudia Inés Serrano-Brañas, Belinda Espinosa-Chávez, Sarah Augusta Maccracken, Cirene Gutiérrez-Blando, Claudio de León-Dávila and José Flores Ventura. The type species ''Paraxenisaurus normalensis''. The generic name is derived from the Greek ''paráxenos'', "strange". The specific name is after the Benemérita Escuela Normal de Coahuila, a teacher training institution, where the fossils had been deposited. They include the holotype BENC 2/2-001, a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Del Pueblo Formation
The Cerro del Pueblo Formation is a geological formation in Coahuila, Mexico whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, pp.574-588 The formation is believed to correlate with the '' Baculites reesidesi'' and '' Baculites jenseni'' ammonite zones, which dates it to 73.63-72.74 Ma. Dinosaurs Ornithischians Remains of the following ornithischians have been found in the formation: Ankylosaurs Ceratopsians Ornithopods Thescelosaurids Saurischians Remains of the following saurischians have been found in the formation: Theropods Other Fossils Pterosaurs Turtles Other vertebrates ;Fish * '' Lepisosteus sp.'' * Amiidae indet. ;Fossil eggs * '' Porituberoolithus sp.'' * '' Spheroolithus sp.'' * '' ?Prismatoolithus sp.'' ;Mammals * Multituberculata indet. See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations * List of fossiliferous strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2020. General research * A study aiming to determine how mass properties and body proportions relate to each other and locomotor posture in archosaurs is published online by Bishop ''et al.'' (2020). * A study on the brain growth in the American alligator and in the common ostrich throughout their ontogeny is published by Hu ''et al.'' (2020), who evaluate the implications of their findings for the knowledge of the development of the brain in non-avian dinosaurs. * A study on the evolution of metabolic rates along the bird stem lineage is published by Rezende ''et al.'' (2020). * A review of the anatomy of the respiratory systems and mechanics of breathing in living and fossil archosaurs, evaluating their physiological implications, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinocheirus
''Deinocheirus'' ( ) is a genus of large ornithomimosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous around 70 million years ago. In 1965, a pair of large arms, shoulder girdles, and a few other bones of a new dinosaur were first discovered in the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. In 1970, this specimen became the holotype of the only species within the genus, ''Deinocheirus mirificus''; the genus name is Greek for "horrible hand". No further remains were discovered for almost fifty years, and its nature remained a mystery. Two more complete specimens were described in 2014, which shed light on many aspects of the animal. Parts of these new specimens had been looted from Mongolia some years before, but were repatriated in 2014. ''Deinocheirus'' was an unusual ornithomimosaur, the largest of the clade at long, and weighing . Though it was a bulky animal, it had many hollow bones which saved weight. The arms were among the largest of any bipedal dinosaur at long, with large, blunt claws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garudimimus
''Garudimimus'' (meaning "Garuda mimic") is a genus of ornithomimosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous. The genus is known from a single specimen found in 1981 by a Soviet-Mongolian paleontological expedition in the Bayan Shireh Formation and formally described in the same year by Rinchen Barsbold; the only species is ''Garudimimus brevipes''. Several interpretations about the anatomical traits of ''Garudimimus'' were made in posterior examinations of the specimen, but most of them were criticized during its comprehensive redescription in 2005. Extensive undescribed ornithomimosaur remains at the type locality of ''Garudimimus'' may represent additional specimens of the genus. The only known specimen of ''Garudimimus'' was a medium-sized animal measuring nearly in length and weighing about . It was an ornithomimosaur with a mix of basal and derived features; unlike primitive ornithomimosaurs, both upper and lower jaws were toothless, a trait that is often reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinocheiridae
Deinocheiridae is a family of ornithomimosaurian dinosaurs, living in Asia and the Americas from the Albian until the Maastrichtian. The family was originally named by Halszka Osmólska and Roniewicz in 1970, including only the type genus ''Deinocheirus''. In a 2014 study by Yuong-Nam Lee and colleagues and published in the journal ''Nature'', it was found that Deinocheiridae was a valid family. Lee ''et al.'' found that based on a new phylogenetic analysis including the recently discovered complete skeletons of ''Deinocheirus'', the type genus, as well as ''Garudimimus'' and '' Beishanlong'', could be placed as a successive group, with ''Beishanlong'' as the most primitive and ''Deinocheirus'' as most derived. The family Garudimimidae, named in 1981 by Rinchen Barsbold, is now a junior synonym of Deinocheiridae as the latter family includes the type genus of the former. The group existed from 115 to 69 million years ago, with ''Beishanlong'' living from 115 to 100 mya, ''Garudi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithomimosauria
Ornithomimosauria ("bird-mimic lizards") are theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to the modern-day ostrich. They were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of Laurasia (now Asia, Europe and North America), as well as Africa and possibly Australia. The group first appeared in the Early Cretaceous and persisted until the Late Cretaceous. Primitive members of the group include '' Nqwebasaurus'', ''Pelecanimimus'', '' Shenzhousaurus'', '' Hexing'' and ''Deinocheirus'', the arms of which reached 2.4 m (8 feet) in length. More advanced species, members of the family Ornithomimidae, include ''Gallimimus'', '' Struthiomimus'', and '' Ornithomimus''. Some paleontologists, like Paul Sereno, consider the enigmatic alvarezsaurids to be close relatives of the ornithomimosaurs and place them together in the superfamily Ornithomimoidea (see classification below). Description The skulls of ornithomimosaurs were small, with large ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latirhinus
''Latirhinus'' (meaning "broad nose" from the Latin ''latus'' (broad) and Greek ῥίς, ''rhis'' (nose)) is an extinct genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Mexico. The type species, ''Latirhinus uitstlani'', was named in 2012 on the basis of a partial skeleton from the Campanian-age Cerro del Pueblo Formation. The specific name ''uitstlani'' means "southern" in the Náhuatl language of Mexico, a reference to the species' southern occurrence in the Cretaceous landmass Laramidia Laramidia was an island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period (99.6–66 Ma), when the Western Interior Seaway split the continent of North America in two. In the Mesozoic era, Laramidia was an island land mass separated from .... Classification ''Latirhinus'' was originally thought to be similar to the saurolophine '' Gryposaurus''. However, a 2012 study found its holotype, as originally defined, to be a chimera comprising both lambeosaurine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coahuilaceratops
''Coahuilaceratops'' (meaning "Coahuila horn face") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a chasmosaurine ceratopsian which lived during the Late Cretaceous period (late Campanian stage) in what is now southern Coahuila in northern Mexico. It is known from the holotype CPC 276, a partial skeleton of an adult individual which includes several skull elements. Another specimen, CPS 277, may represent a juvenile ''Coahuilaceratops''. All specimens of ''Coahuilaceratops'' were collected from a single location in the middle strata of the Cerro del Pueblo Formation, which dates to between 72.5 and 71.4 million years ago.Loewen, M.A., Sampson, S.D., Lund, E.K., Farke, A.A., Aguillón-Martínez, M.C., de Leon, C.A., Rodríguez-de la Rosa, R.A., Getty, M.A., Eberth, D.A., 2010, "Horned Dinosaurs (Ornithischia: Ceratopsidae) from the Upper Cretaceous (Campanian) Cerro del Pueblo Formation, Coahuila, Mexico", In: Michael J. Ryan, Brenda J. Chinnery-Allgeier, and Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the lateral and medial malleoli) that articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of its surface area covered by articular cartilage. It is also unusual in that it has a retrograde blood supply, i.e. arterial blood enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |