|
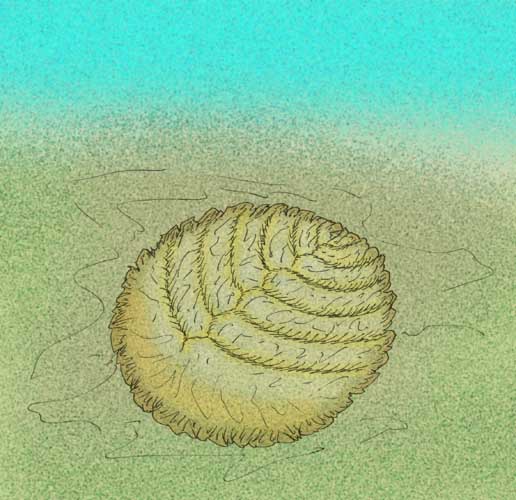
Paravendia Janae
''Paravendia'' is an extinct genus of proarticulate vendiamorph that lived in the Ediacaran period, about 553 million years ago. It shares the Vendiidae family with ''Vendia'' and ''Karakhtia''. It is a monotypic genus, with the species ''Paravendia janae''. Description It is an animal that presents 'bilateral' symmetry, similar in appearance to the previously mentioned genus '' Vendia '', with new isomers replacing the older ones. Distribution Ediacaran of the Russian Federation (Arkhangelsk). See also *List of ediacaran genera The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the chal ... References Notes Zakrevskaya, Maria. Paleoecological reconstruction of the Ediacaran benthic macroscopic communities of the White Sea (Russia). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last period of the Proterozoic geologic eon, Eon as well as the last of the so-called "Precambrian supereon", before the beginning of the subsequent Cambrian Period marks the start of the Phanerozoic Eon, where recognizable fossil evidence of life becomes common. The Ediacaran Period is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia, where trace fossils of a diverse community of previously unrecognized lifeforms (later named the Ediacaran biota) were first discovered by geologist Reg Sprigg in 1946. Its status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period took namesake from the Ediacara Hills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendiamorpha
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulates. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. Typically, the first few, or largest initial isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulates have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Some vendiamorphs (e.g., ''Vendia'' and ''Paravendia'') supposedly demonstrate a digestive-distributive sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendiamorpha
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulates. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. Typically, the first few, or largest initial isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulates have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Some vendiamorphs (e.g., ''Vendia'' and ''Paravendia'') supposedly demonstrate a digestive-distributive sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendia
''Vendia'' is an extinct vendiamorph from the late Ediacaran, estimated to be around 567 - 550 Ma years old, it contains two species, ''V. sokolovi'' and ''V. rachiata'', both of which are restricted to the Ust' Pinega Formation in Northwestern Russia. Discovery and naming The first fossil materials of ''Vendia'' were found in a core from a Yarensk borehole that was collected from the Ust' Pinega Formation of the Arkhangelsk Oblast, northwestern Russia in 1963,V. V. Menner. (1963). "The Other Problematical Organic Remains". In: "Stratigraphy of the USSR: Upper Precambrian" Gos. Nauchno-Tekh. Izd., Moscow. pp. 504-507. (In Russian) and was formally described and named in 1969 as ''Vendia sokolovi''.B. M. Keller. (1969). "Imprint of unknown animal from Valdai Series of Russian Platform". In: A. Y. Rozanov and et al. (Eds.), "Tommotian Stage and the Cambrian lower boundary problem". ''Geol. Inst. Trans''. Vol. 206, p. 175. (In Russian) A Further two species were found and named i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakhtia
''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a species of Proarticulate from the Ediacaran period, around 555 Million Years Ago. K. nessovi is the only species in the genus ''Karakhtia''. The genus '' Haootia'' has been compared minorly to ''Karakhtia'' in the way that the fossils of ''Haootia'' superficially resemble the crumpled margins of ''Karakhtia''. Discovery and name The holotype fossil of ''Karakhtia'' was found from the Ustʹ Pinega Formation, in the White Sea of Russia, and described in 2004. The generic name ''Karakhtia'' is derived from the place name ''Karakhta River'', near to where the fossil material was found. The specific name ''nessovi'' is derived from the surname of ''L.A. Nessov'', a Leningrad paleontologist. Description ''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a Proarticulate from the Vendiidae family, growing up to in length, and like other members of its family, it has a headshield-like structure. Unlike anything seen in other Proarticulates, it features a margin with radial fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river and numerous islands of its river delta, delta. Arkhangelsk was the chief seaport of medieval and early modern Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly founded Saint Petersburg. A Northern Railway (Russia), railway runs from Arkhangelsk to Moscow via Vologda and Yaroslavl, and air travel is served by the Talagi Airport and the smaller Vaskovo Airport. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, the city's population was 301,199. Coat of arms The arms of the city display the Michael (archangel), Archangel Michael in the act of defeating the Devil. Legend states that this victory took place near where the city stands, hence its name, and that Michael still stands watch over the city to prevent the Devil's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ediacaran Genera
The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the challenge it posed for his theory of evolution. While reports of Precambrian organisms have been made since Alexander Murray's 1868 discovery of ''Aspidella'', it wasn't until the discovery of ''Charnia'' in 1956 that considerable evidence of Precambrian life had been presented. The period immediately preceding the Cambrian, the Ediacaran, is now widely accepted of containing animal life. It spans from 635 to 540 million years ago, and covers approximately 2% of Earth's history. Taxonomists have purported a total of 245 described genera from the Ediacaran, 162 of which are accepted as valid. Key * Valid genus - Genera that are accepted by the scientific community * Synonym (taxonomy), Junior synonym - Alternative name for an already existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |