|
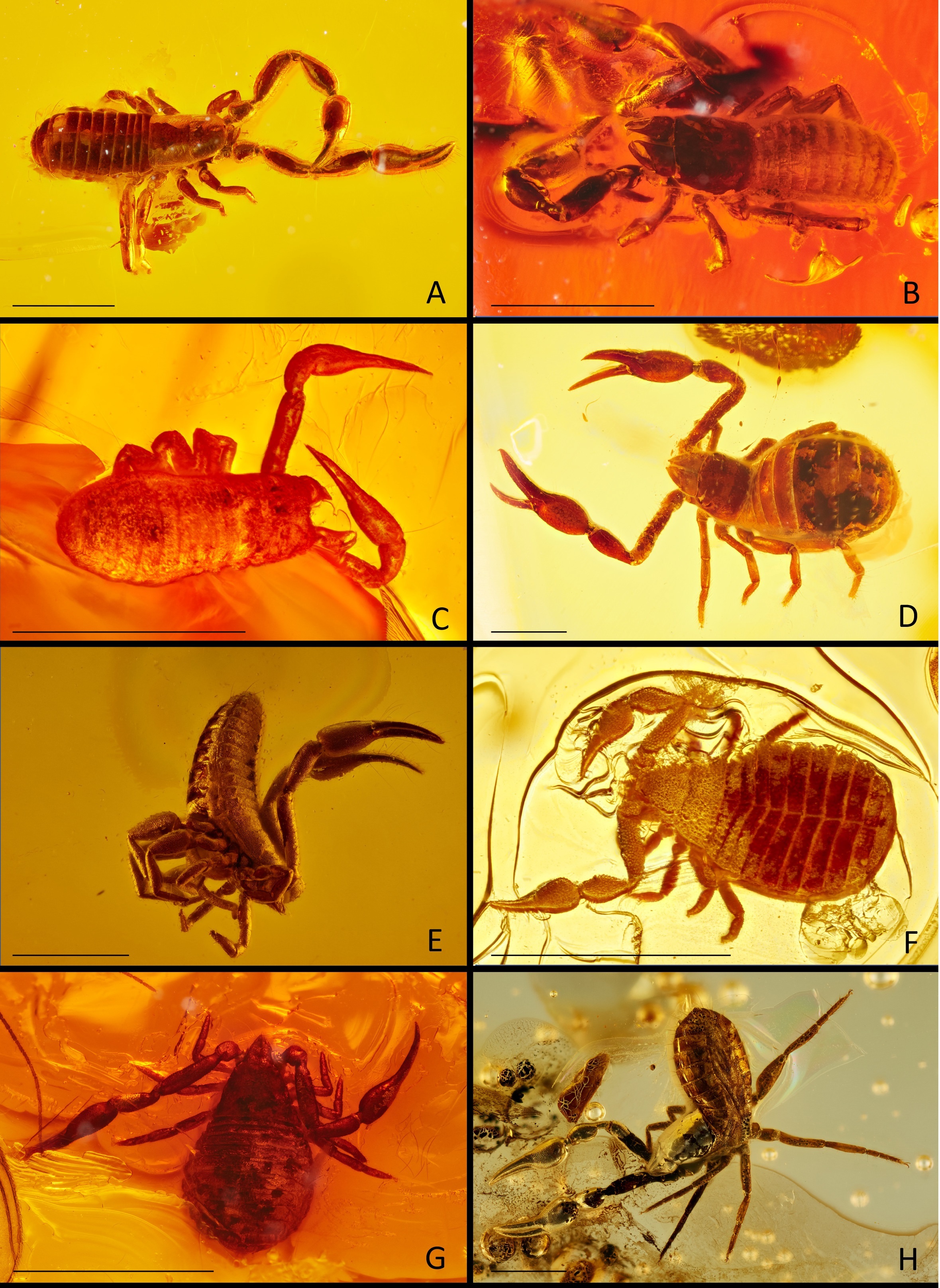
Paraustrochernes Novaeguineensis
''Paraustrochernes'' is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the Chernetidae family. It is native to Australasia, and was described in 1966 by Austrian arachnologist Max Beier. Species The genus contains the following species: * '' Paraustrochernes novaeguineensis'' Beier, 1975 – New Guinea * '' Paraustrochernes victorianus'' Beier, 1966 – Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ... References Chernetidae Pseudoscorpion genera Taxa described in 1966 Taxa named by Max Beier {{pseudoscorpion-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Beier
Max Beier (6 April 1903 in Spittal an der Drau – 4 July 1979 in Vienna) was an Austrian arachnologist and entomologist. He studied zoology at the University of Vienna, and obtained his doctorate there in 1927. He took up a post at the Natural History Museum, Vienna, Natural History Museum in Vienna, in the same year, developing an expertise in pseudoscorpions. He was appointed Director of the zoological department of the Vienna Museum in 1962, and retired in 1968. A list of Beier's 398 scientific papers was published, with an obituary, in ''Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien''. 252 were on pseudoscorpions. He described and named over 1200 pseudoscorpion species of which 1180 were still valid in 2007. He was editor of the ''Orthopterorum Catalogus'' and an updated edition of the volume on insects in the '. Awards Beier was awarded the Fabricius Medal in January 1967 of :de:Deutsche Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie, Deutsche Gesellschaft f� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscorpions
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida. Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans because they prey on clothes moth larvae, carpet beetle larvae, booklice, ants, mites, and small flies. They are common in many environments, but they are rarely noticed due to their small size. When people see pseudoscorpions, especially indoors, they often mistake them for ticks or small spiders. Pseudoscorpions often carry out phoresis, a form of commensalism in which one organism uses another for the purpose of transport. Characteristics Pseudoscorpions belong to the class Arachnida. They are small arachnids with a flat, pear-shaped body, and pincer-like pedipalps that resemble those of scorpions. They usually range from in length.Pennsylvania State University, DepartmentEntomological Notes: Pseudoscorpion Fact Sheet/ref> The large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernetidae
Chernetidae is a family of pseudoscorpions, first described by Anton Menge in 1855. Genera , the ''World Pseudoscorpiones Catalog'' accepts the following 119 genera: * '' Acanthicochernes'' Beier, 1964 * '' Acuminochernes'' Hoff, 1949 * '' Adelphochernes'' Beier, 1937 * ''Allochernes ''Allochernes'' is a genus of pseudoscorpion Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida. Pseudo ...'' Beier, 1932 * '' Americhernes'' Muchmore, 1976 * '' Anaperochernes'' Beier, 1964 * '' Anthrenochernes'' Lohmander, 1939 * '' Antillochernes'' Muchmore, 1984 * '' Apatochernes'' Beier, 1948 * '' Asterochernes'' Beier, 1955 * '' Atherochernes'' Beier, 1954 * '' Attaleachernes'' Mahnert, 2009 * '' Austinochernes'' Harvey, 2021 * '' Austrochernes'' Beier, 1932 * '' Balgachernes'' Harvey, 2018 * '' Barbaraella'' Harvey, 1995 * '' Bipeltochernes'' Dashda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnology
Arachnology is the science, scientific study of arachnids, which comprise spiders and related invertebrates such as scorpions, Pseudoscorpionida, pseudoscorpions, Opiliones, harvestmen, Tick, ticks, and mites. Those who study spiders and other arachnids are arachnologists. More narrowly, the study of spiders alone (Order (biology), order Araneae) is known as araneology. The word "wiktionary:arachnology, arachnology" derives from the Ancient Greek words , ''arachnē'', "spider"; and , ''-logia'', "the study of a particular subject". The greek word for "spider" itself refers to Arachne, the female protagonist of an ancient tale of the Greek mythology, Greek Mythology. Arachnology as a science Arachnologists are primarily responsible for biological classification, classifying arachnids and studying aspects of their biology. In the popular imagination, they are sometimes referred to as spider experts. Disciplines within arachnology include naming species and determining their phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraustrochernes Novaeguineensis
''Paraustrochernes'' is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the Chernetidae family. It is native to Australasia, and was described in 1966 by Austrian arachnologist Max Beier. Species The genus contains the following species: * '' Paraustrochernes novaeguineensis'' Beier, 1975 – New Guinea * '' Paraustrochernes victorianus'' Beier, 1966 – Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ... References Chernetidae Pseudoscorpion genera Taxa described in 1966 Taxa named by Max Beier {{pseudoscorpion-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraustrochernes Victorianus
''Paraustrochernes'' is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the Chernetidae family. It is native to Australasia, and was described in 1966 by Austrian arachnologist Max Beier. Species The genus contains the following species: * '' Paraustrochernes novaeguineensis'' Beier, 1975 – New Guinea * '' Paraustrochernes victorianus'' Beier, 1966 – Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ... References Chernetidae Pseudoscorpion genera Taxa described in 1966 Taxa named by Max Beier {{pseudoscorpion-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscorpion Genera
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida. Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans because they prey on clothes moth larvae, carpet beetle larvae, booklice, ants, mites, and small flies. They are common in many environments, but they are rarely noticed due to their small size. When people see pseudoscorpions, especially indoors, they often mistake them for ticks or small spiders. Pseudoscorpions often carry out phoresis, a form of commensalism in which one organism uses another for the purpose of transport. Characteristics Pseudoscorpions belong to the class Arachnida. They are small arachnids with a flat, pear-shaped body, and pincer-like pedipalps that resemble those of scorpions. They usually range from in length.Pennsylvania State University, DepartmentEntomological Notes: Pseudoscorpion Fact Sheet/ref> The large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |