|
Paratrimastix Pyriformis
''Paratrimastix pyriformis'' is a species of free-living (non-parasitic) anaerobic freshwater bacteriovorous flagellated protists formerly known as '' Trimastix pyriformis'' and '' Tetramitus pyriformis''. History of knowledge This species was first described by G. A. Klebs in 1892 as '' Tetramitus pyriformis''. Under this name, it has been frequently discussed in the context of sewage, sewage treatment, and water quality during the 20th century. It was also observed on Elephant Island, South Shetland Islands. More than 100 years after its description, in 1999, it was transferred to the genus '' Trimastix'' based on its morphology. The first ultrastructural study using transmission electron microscopy was published the same year, which reported a discovery of hydrogenosome-like organelles in the species. A molecular phylogenetic study based on small-subunit ribosomal RNA placed the genus '' Trimastix'' (then including ''P. pyriformis'') as sister to the oxymonad Pyrsonympha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands, Antarctic islands located in the Drake Passage with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories. According to British government language on the topic, "the whole of Antarctica is protected in the interests of peace and science." The islands have been claimed by three countries, beginning with the United Kingdom since 1908 (since 1962 as part of the equally unrecognized British Antarctic Territory). The islands are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province), and by Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocercomonoides
''Monocercomonoides'' is a genus of flagellate Excavata belonging to the order Oxymonadida. It was established by Bernard V. Travis and was first described as those with "polymastiginid flagellates having three anterior Flagellum, flagella and a trailing one originating at a single basal granule located in front of the anteriorly positioned cell nucleus, nucleus, and a more or less well-defined axostyle". It is the first eukaryotic genus to be found to completely lack Mitochondrion, mitochondria, and all hallmark proteins responsible for mitochondrial function. The genus also lacks any other Mitochondrion#Origin and evolution, mitochondria related organelles (MROs) such as hydrogenosomes or mitosomes. Data suggests that the absence of mitochondria is not an ancestral feature, but rather due to secondary loss. ''Monocercomonoides ''sp. was found to obtain energy through an enzymatic action of nutrients absorbed from the environment. The genus has replaced the Iron–sulfur protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamonad
The metamonads are a large group of flagellate amitochondriate microscopic eukaryotes. They include the retortamonads, diplomonads, parabasalids, oxymonads, and a range of more poorly studied taxa, most of which are free-living flagellates. All metamonads are anaerobic (many being aerotolerant anaerobes), and most members of the four groups listed above are symbiotes or parasites of animals, as is the case with ''Giardia lamblia'' which causes diarrhea in mammals. Characteristics A number of parabasalids and oxymonads are found in termite guts, and play an important role in breaking down the cellulose found in wood. Some other metamonads are parasites. These flagellates are unusual in lacking aerobic mitochondria. Originally they were considered among the most primitive eukaryotes, diverging from the others before mitochondria appeared. However, they are now known to have lost aerobic mitochondria secondarily, and retain both organelles and nuclear genes derived ultimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaeromonadea
Anaeromonadea, also known as Preaxostyla, is a class of excavate protists, comprising the oxymonads, ''Trimastix'', and ''Paratrimastix''. This group is studied as a model system for reductive evolution of mitochondria, because it includes both organisms with anaerobic mitochondrion-like organelles (''Trimastix'' and ''Paratrimastix''), and those that have completely lost their mitochondria ( oxymonads ''Monocercomonoides'', ''Streblomastix A symbiotic eukaryote that lives in the hindgut of termites, ''Streblomastix'' is a protist associated with a community of ectosymbiotic bacteria. Motility ''Streblomastix'' moves by beating its anterior flagella. Morphology These protists ...'', and '' Blattamonas''). Phylogeny and Taxonomy Based on the work of Zhang et al. 2015. References External links Tree of Life: Preaxostyla Metamonads {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrsonympha
''Pyrsonympha'' is a genus of Excavata. It includes the species ''Pyrsonympha vertens''. Species List of ''Pyrsonympha'' species. * ''P. affinis'' Fedorowa 1923 * ''P. elongata'' Georgevitch 1932 * ''P. flagellata'' Grassé 1894 * ''P. grandis'' Koidzumi 1921 * ''P. granulata'' Powell 1928 * ''P. havilalldi'' Das 1972 * ''P. major'' Powell 1928 * ''P. minor'' Powell 1928 * ''P. modesta'' Koidzumi 1921 * ''P. omblensis'' Georgevitch 1951 * ''P. rostrata'' Mukherjee & Maiti 1988 * ''P. tirapi'' Mukherjee & Maiti 1988 * ''P. vertens'' Leidy 1877 References Metamonads Metamonad genera {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxymonad
The Oxymonads (or Oxymonadida) are a group of flagellated protists found exclusively in the intestines of animals, mostly termites and other Xylophagy, wood-eating insects. Along with the similar parabasalid flagellates, they harbor the Symbiosis, symbiotic bacterium, bacteria that are responsible for breaking down cellulose. There is no evidence for presence of Mitochondrion, mitochondria (not even anaerobic mitochondrion-like organelles like hydrogenosomes or mitosomes) in oxymonads and three species have been shown to completely lack any molecular markers of mitochondria. It includes e.g. ''Dinenympha'', ''Pyrsonympha'', ''Oxymonas'', ''Streblomastix'', ''Monocercomonoides'', and ''Blattamonas''. Characteristics Most Oxymonads are around 50 μm in size and have a single cell nucleus, nucleus, associated with four Flagellum, flagella. Their Basal body, basal bodies give rise to several long sheets of microtubules, which form an organelle called an axostyle, but different in st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between Prokaryote, prokaryotes and Eukaryote, eukaryotes. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetics, phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to the Human body, body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bounded organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bounded organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some functional units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst (these could be referred to as membrane bound in the sense that they are attached to (or bound to) the membrane). Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
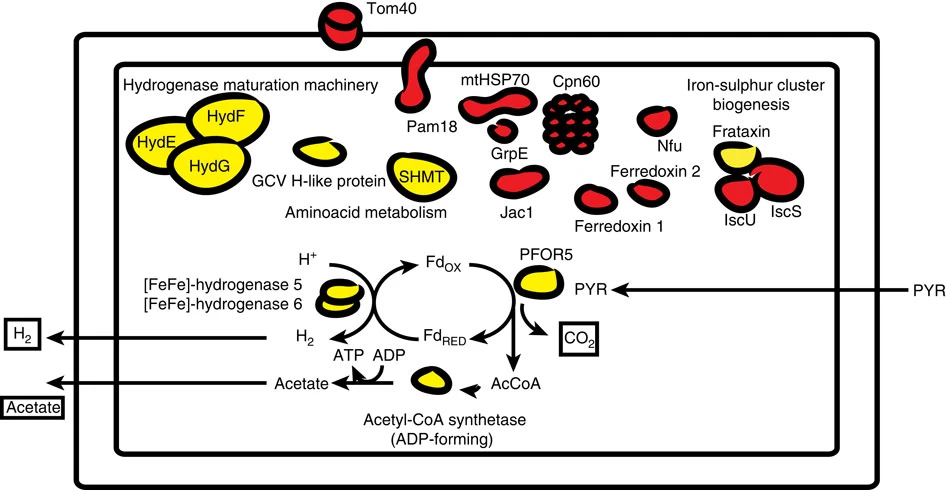
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some Anaerobic organism, anaerobic Ciliate, ciliates, Flagellate, flagellates, Fungus, fungi, and three species of Loricifera, loriciferans. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protoMitochondrion, mitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenosomes were discovered in 1973 by D. G. Lindmark and M. Müller. Because hydrogenosomes hold evolutionary lineage significance for organisms living in anaerobic or oxygen-stressed environments, many research institutions have since documented their findings on how the organelle differs in various sources. History Hydrogenosomes were isolated, purified, biochemically characterized and named in the early 1970s by Lindmark and Müller at Rockefeller University. In addition to this seminal study on hydrogenosomes, they also demonstrated for the first time the presence of Pyruvate:fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |