|
Paralysis Tick
''Ixodes holocyclus'', commonly known as the Australian paralysis tick, is one of about 75 species in the Australian tick fauna and is considered the most medically important. It can cause paralysis by injecting neurotoxins into its host. It is usually found in a 20-kilometre wide band following the eastern coastline of Australia. Within that range (biology), range, ''Ixodes holocyclus'' is the tick most frequently encountered by humans and their pets. Because the same area includes Australia's most densely populated regions, bites on people, pets and livestock are relatively common. Paralysis ticks are found in many types of habitat, particularly areas of high rainfall such as wet sclerophyll forest and temperate rainforest. The natural hosts for the paralysis tick include koalas, bandicoots, Phalangeriformes, possums and kangaroos. Common names The use of common names has led to many colloquial expressions for ''Ixodes holocyclus''. The most generally accepted name is ''Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Georges Neumann
Louis Georges Neumann (22 October 1846 – 28 June 1930) was a French veterinary parasitologist who specialized in ticks. He was a professor at the Veterinary School in Toulouse. Neumann was born in Paris and was orphaned at a young age. He studied veterinary medicine at the Maisons-Alfort National Veterinary School in 1868 and joined the French army working at the cavalry school in Saumur. He became a lecturer at the École nationale vétérinaire de Toulouse in 1878 and a professor two years later. He worked on helminth parasites initially but soon started examining the arthropods starting with some interest in the mallophaga but he gave the greatest attention to the ticks and became a leading expert on them. He published numerous descriptions of new species and received collections from around the world. He revised the taxonomy of ticks in the family Ixodidae as part of the German zoological volumes ''Tierreich''. In 1896 he wrote a book on the biographies of famous veterinarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conscutum
A scute () or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of birds. The term is also used to describe the anterior portion of the mesothorax in insects as well as some arachnids (e.g., the family Ixodidae, the scale ticks). Properties Scutes are similar to scales and serve the same function. Unlike the scales of lizards and snakes, which are formed from the epidermis, scutes are formed in the lower vascular layer of the skin and the epidermal element is only the top surface . Forming in the living dermis, the scutes produce a horny outer layer that is superficially similar to that of scales. Scutes will usually not overlap as snake scales (but see the pangolin). The outer keratin layer is shed piecemeal, and not in one continuous layer of skin as seen in snakes or lizards. The dermal base may contain bone and produce dermal armour. Scutes with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and Sublimation (phase transition), sublimes directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily as a cooling agent, but is also used in fog machines at theatres for dramatic effects. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of Ice, water ice and not leaving any residue (other than incidental frost from moisture in the atmosphere). It is useful for preserving frozen foods (such as ice cream) where Refrigeration, mechanical cooling is unavailable. Dry ice sublimes at at Earth atmospheric pressure. This extreme cold makes the solid dangerous to handle without protection from frostbite injury. While generally not very toxic, the outgassing from it can cause hypercapnia (abnormally elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood) due to a buildup in confined locations. Properties Dry ice is the soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
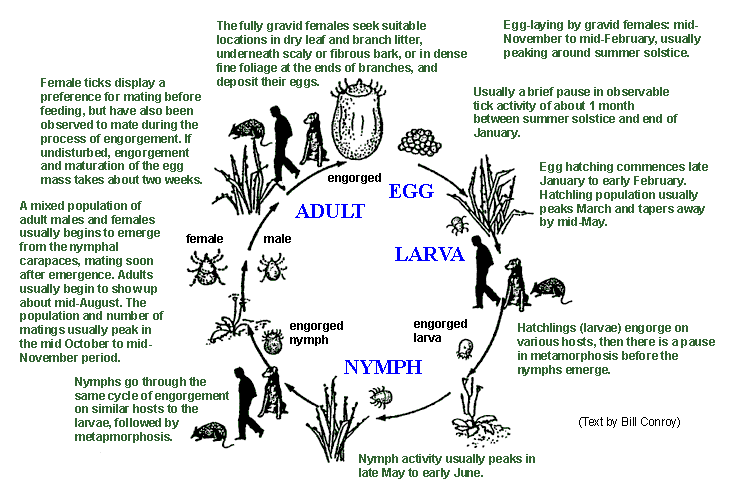
Lifecycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to: Science and academia *Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from conception to reproduction *Life-cycle hypothesis, in economics *Erikson's stages of psychosocial development, in psychoanalysis * Life-cycle of phonological processes, in linguistics Business *Enterprise life cycle, the process of changing a business enterprise *Project life cycle *Product lifecycle, the stages in the lifespan of a commercial or consumer product *New product development, the process of bringing a new product to market *Life-cycle assessment, the analysis of the environmental impacts associated with a product *Technology life cycle, the commercial gain of a product Software *Software development life cycle *Software release life cycle *Object lifetime of an object in object-oriented programming *Program lifecycle phases are the stages a computer program undergoe, from initial creation to deployments. Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent Flaccid paralysis, paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to what the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal–oral route, fecal–oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral–oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral Sea, Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory and Jervis Bay Territory are Enclave and exclave, enclaves within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. , the population of New South Wales was over 8.3 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Almost two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. The Colony of New South Wales was founded as a British penal colony in 1788. It originally comprised more than half of the Australian mainland with its Western Australia border, western boundary set at 129th meridian east in 1825. The colony then also includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Clunies Ross
Sir William Ian Clunies Ross (22 February 189920 June 1959) was an Australian veterinary scientist. He has been described as the "architect" of Australia's scientific boom, for his stewardship of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), the Australian scientific organisation. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Phillip
Port Phillip (Kulin languages, Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped bay#Types, enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel (geography), channel known as The Rip, and is completely surrounded by suburbs and localities (Australia), localities of Victoria's two largest cities — metropolitan Greater Melbourne in the bay's main eastern portion north of the Mornington Peninsula, and the city of Greater Geelong in the much smaller western portion (known as the Corio Bay) north of the Bellarine Peninsula. Geographically, the bay covers and the shore stretches roughly , with the volume of water around . Most of the bay is navigable, although it is extremely shallow for its size — the deepest portion is only and half the bay is shallower than . Its waters and coast are home to Pinniped, seals, whales, dolphins, corals and many kinds of seabirds and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |