|
Paralinguistics
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using suprasegmental techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relating to nonphonemic properties only. Paralanguage may be expressed consciously or unconsciously. The study of paralanguage is known as paralinguistics and was invented by George L. Trager in the 1950s, while he was working at the Foreign Service Institute of the U.S. Department of State. His colleagues at the time included Henry Lee Smith, Charles F. Hockett (working with him on using descriptive linguistics as a model for paralanguage), Edward T. Hall developing proxemics, and Ray Birdwhistell developing kinesics. Trager published his conclusions in 1958, 1960 and 1961. His work has served as a basis for all later research, especially those investigating the relationship between paralanguage and culture (since paralan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Birdwhistell
Ray L. Birdwhistell (September 29, 1918 – October 19, 1994) was an American anthropologist who founded kinesics as a field of inquiry and research.Danesi, M (2006). Kinesics. ''Encyclopedia of language & linguistics''. 207-213. Birdwhistell coined the term ''kinesics'', meaning "facial expression, gestures, posture and gait, and visible arm and body movements". He estimated that "no more than 30 to 35 percent of the social meaning of a conversation or an interaction is carried by the words." Stated more broadly, he argued that "words are not the only containers of social knowledge." He proposed other technical terms, including kineme, and many others less frequently used today. Birdwhistell had at least as much impact on the study of language and social interaction generally as just nonverbal communication because he was interested in the study of communication more broadly than is often recognized. Birdwhistell understood body movements to be culturally patterned rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesics
Kinesics is the interpretation of body communication such as facial expressions and gestures, nonverbal behavior related to movement of any part of the body or the body as a whole. The equivalent popular culture term is body language, a term Ray Birdwhistell, considered the founder of this area of study, neither used nor liked (on the grounds that what can be conveyed with the body does not meet the linguist's definition of language). Birdwhistell's work Kinesics was first used in 1952 by an anthropologist named Ray Birdwhistell. Birdwhistell wished to study how people communicate through posture, gesture, stance and movement. His ideas over several decades were synthesized and resulted in the book ''Kinesics and Context.'' Interest in kinesics specifically and nonverbal behaviour generally was popularized in the late 1960s and early 1970s by such popular mass-market (nonacademic) publications as ''How to Read a Person Like a Book''. Part of Birdwhistell's work involved filming p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phone (phonetics)
In phonetics (a branch of linguistics), a phone is any distinct speech sound. It is any surface-level or unanalyzed sound of a language, the smallest identifiable unit occurring inside a stream of speech. In spoken human language, a phone is thus any vowel or consonant sound (or semivowel sound). In sign language, a phone is the equivalent of a unit of gesture. Phones versus phonemes Phones are the segment (linguistics), segments of speech that possess distinct physical or perceptual properties, regardless of whether the exact sound is critical to the meanings of words. Whereas a phone is a Abstract and concrete, concrete sound used across various spoken languages, a phoneme is more abstract and narrowly defined: any class of phones that the users of a particular language nevertheless ''perceive'' as a single basic sound, a single unit, and that distinguishes words from other words. If a phoneme is swapped with another phoneme inside a word, it can change the meaning of that word, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formant
In speech science and phonetics, a formant is the broad spectral maximum that results from an acoustic resonance of the human vocal tract. In acoustics, a formant is usually defined as a broad peak, or local maximum, in the spectrum. For harmonic sounds, with this definition, the formant frequency is sometimes taken as that of the harmonic that is most augmented by a resonance. The difference between these two definitions resides in whether "formants" characterise the production mechanisms of a sound or the produced sound itself. In practice, the frequency of a spectral peak differs slightly from the associated resonance frequency, except when, by luck, harmonics are aligned with the resonance frequency, or when the sound source is mostly non-harmonic, as in whispering and vocal fry. A room can be said to have formants characteristic of that particular room, due to its resonances, i.e., to the way sound reflects from its walls and objects. Room formants of this nature reinforc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Voice
The human voice consists of sound Voice production, made by a human being using the vocal tract, including Speech, talking, singing, Laughter, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of Voicelessness, unvoiced consonants, Click consonant, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
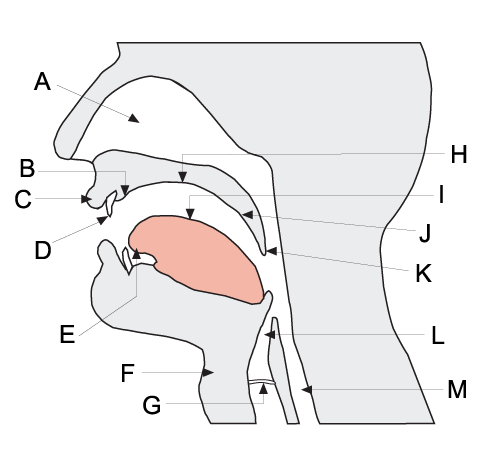
Speech Organ
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Localization
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. Other animals, such as birds and reptiles, also use them but they may use them differently, and some also have localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the Pinna (anatomy), pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadoma
Tadoma is a method of communication utilized by Deafblindness, deafblind individuals, in which the listener places their little finger on the speaker's lips and their fingers along the jawline. The middle three fingers often fall along the speaker's cheeks with the little finger picking up the vibrations of the speaker's throat. It is sometimes referred to as ''tactile lipreading'', as the listener feels the movement of the lips, the vibrations of the vocal cords, expansion of the cheeks and the warm air produced by Nasal consonant, nasal phonemes such as 'N' and 'M'. Hand positioning can vary, and it is a sometimes also used by Hearing loss, hard-of-hearing people to supplement their remaining hearing. In some cases, especially if the speaker knows sign language, the deafblind listener may use the Tadoma method with one hand on the speaker's face, and their other hand on the speaker’s signing hand to hear the words. In this way, the two methods reinforce each other, increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGurk Effect
The McGurk effect is a perceptual phenomenon that demonstrates an interaction between hearing and vision in speech perception. The illusion occurs when the auditory component of one sound is paired with the visual component of another sound, leading to the perception of a third sound. The visual information a person gets from seeing a person speak changes the way they hear the sound. If a person is getting poor-quality auditory information but good-quality visual information, they may be more likely to experience the McGurk effect. Integration abilities for audio and visual information may also influence whether a person will experience the effect. People who are better at sensory integration have been shown to be more susceptible to the effect. Many people are affected differently by the McGurk effect based on many factors, including brain damage and other disorders. Background It was first described in 1976 in a paper by Harry McGurk and John MacDonald, titled "Hearing Lip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lip Reading
Lip reading, also known as speechreading, is a technique of understanding a limited range of speech by visually interpreting the movements of the lips, face and tongue without sound. Estimates of the range of lip reading vary, with some figures as low as 30% because lip reading relies on context, language knowledge, and any residual hearing. Although lip reading is used most extensively by deaf and hard-of-hearing people, most people with normal hearing process can infer some speech information by observing a speaker's mouth. Process Although speech perception is considered to be an auditory skill, it is intrinsically multimodal, since producing speech requires the speaker to make movements of the lips, teeth and tongue which are often visible in face-to-face communication. Information from the lips and face supports aural comprehension and most fluent listeners of a language are sensitive to seen speech actions (see McGurk effect). The extent to which people make use of seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Language
A spoken language is a form of communication produced through articulate sounds or, in some cases, through manual gestures, as opposed to written language. Oral or vocal languages are those produced using the vocal tract, whereas sign languages are produced with the body and hands. Definition The term "spoken language" is sometimes used to mean only oral languages, especially by linguists, excluding sign languages and making the terms 'spoken', 'oral', 'vocal language' synonymous. Others refer to sign language as "spoken", especially in contrast to written transcriptions of signs. Relation between spoken and written language The relationship between spoken language and written language is complex. Within the fields of linguistics, the current consensus is that speech is an innate human capability, and written language is a cultural invention. However, some linguists, such as those of the Prague school, argue that written and spoken language possess distinct qualities which would ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langue And Parole
''Langue'' and ''parole'' is a theoretical linguistic dichotomy distinguished by Ferdinand de Saussure in his '' Course in General Linguistics''. The French term ''langue'' (' n individuallanguage') encompasses the abstract, systematic rules and conventions of a signifying system; it is independent of, and pre-exists, the individual user. It involves the principles of language, without which no meaningful utterance, or ''parole'', would be possible. In contrast, ''parole'' ('speech') refers to the concrete instances of the use of ''langue'', including texts which provide the ordinary research material for linguistics. Background and significance Structural linguistics, as proposed by Saussure, assumes a non-biological standpoint of culture within the nature–nurture divide. Langue and parole make up two thirds of Saussure's speech circuit (French: ''circuit de la parole''); the third part being the brain, where the individual's knowledge of language is located. The ''speech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |