|
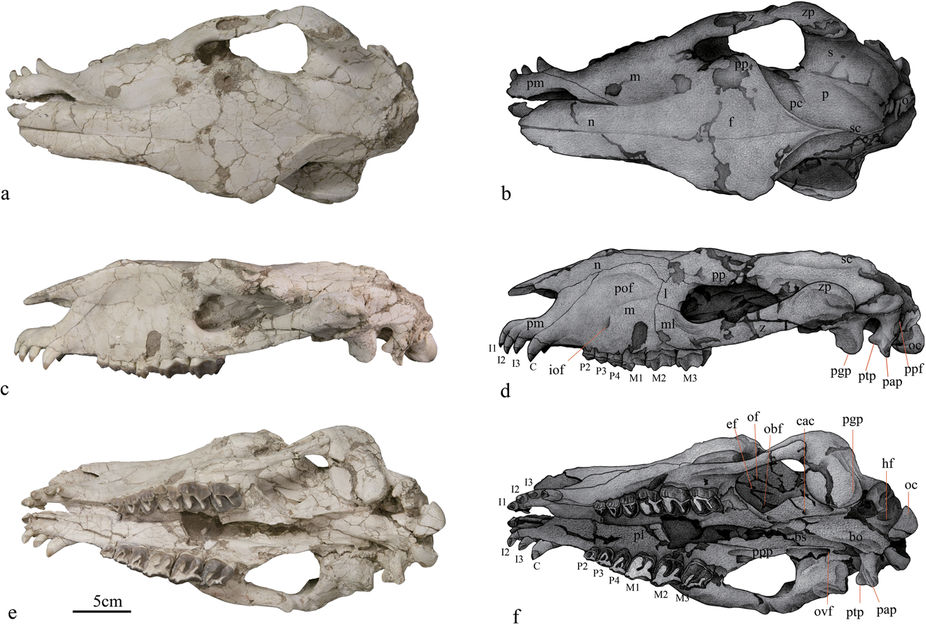
Pappaceras
''Pappaceras'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros from the Early Eocene of Asia belonging to Paraceratheriidae. Taxonomy In 1963, material including a partial skull containing cheek teeth was unearthed in Late Eocene deposits of Mongolia. These remains were identified as from a true rhinoceros by Wood, who found them an important discovery with the scant amount of previous cranial material of early rhinocerotids available. On July 25, the same year, a paper was published by Wood concerning the taxonomy and osteology of these remains, in which he named them a new genus and species (or binomial) as well as re-ranking a previously named family as a subfamily containing the new taxon. The binomial created was ''Pappaceras confluens'', classified as a close relative of ''Forstercooperia'' within Forstercooperiinae (before Forstercooperiidae, named in 1940 by Kretzoi). Wood noted that the generic name is derived from the Latin word ''πaππos'', "grandfather", and the Greek words ''alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
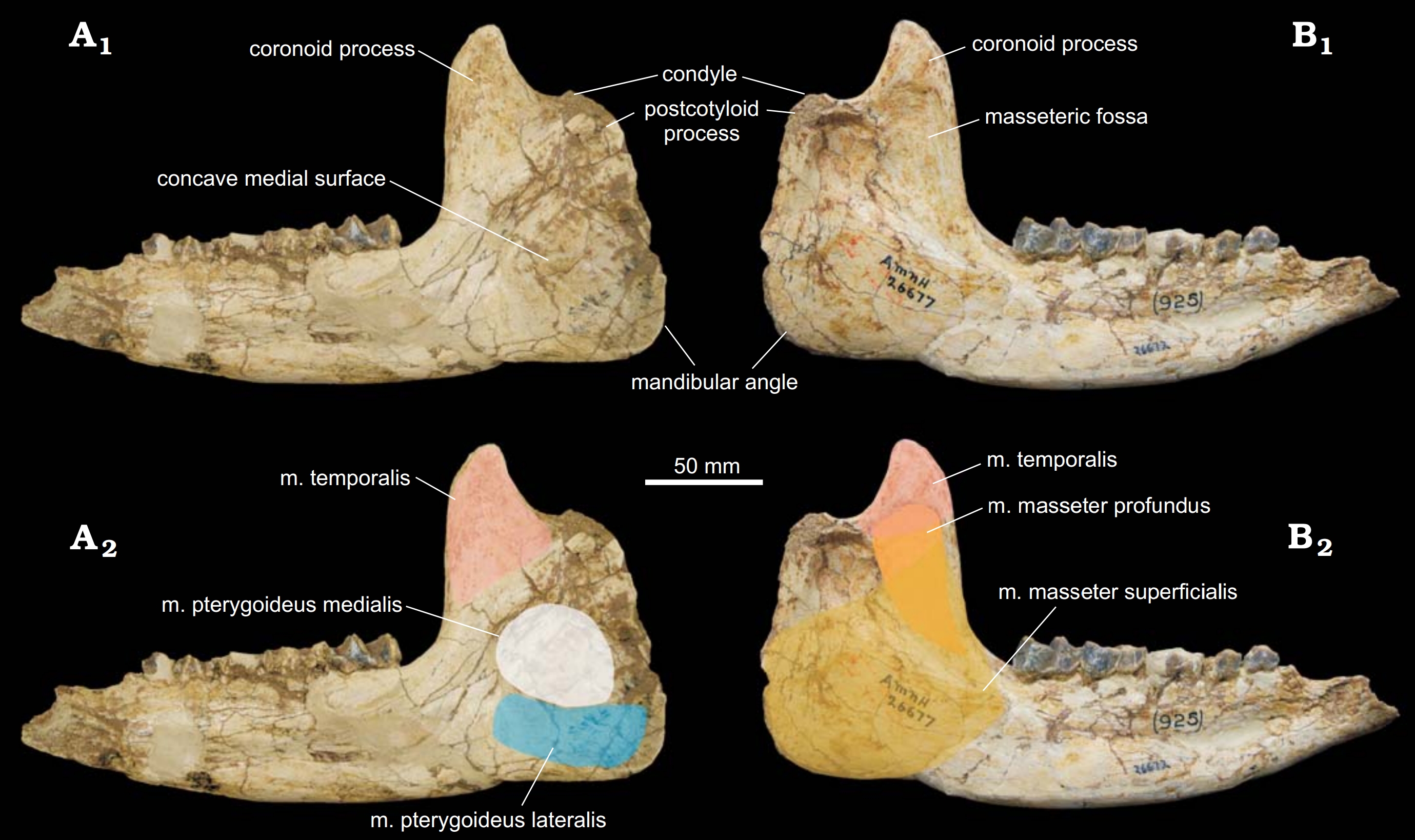
Pappaceras ,mandible Wang Et Al 2017
''Pappaceras'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros from the Early Eocene of Asia belonging to Paraceratheriidae. Taxonomy In 1963, material including a partial skull containing cheek teeth was unearthed in Late Eocene deposits of Mongolia. These remains were identified as from a true rhinoceros by Wood, who found them an important discovery with the scant amount of previous cranial material of early rhinocerotids available. On July 25, the same year, a paper was published by Wood concerning the taxonomy and osteology of these remains, in which he named them a new genus and species (or binomial) as well as re-ranking a previously named family as a subfamily containing the new taxon. The binomial created was ''Pappaceras confluens'', classified as a close relative of ''Forstercooperia'' within Forstercooperiinae (before Forstercooperiidae, named in 1940 by Kretzoi). Wood noted that the generic name is derived from the Latin word ''πaππos'', "grandfather", and the Greek words ''alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinocerotoidea
Rhinocerotoidea is a superfamily consisting of three family groups of odd-toed ungulates, three of which, the Amynodontidae, Hyracodontidae, and Paraceratheriidae, are extinct. The only extant family group is the Rhinocerotidae (true rhinoceroses), which survives as five living species. The extinct members of this superfamily are often called "rhinoceroses" alongside members of the family Rhinocerotidae, though they include genera, such as ''Paraceratherium'', which do not closely resemble modern rhinoceroses. Taxonomy The cladogram below follows a phylogenetic analysis In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... by Bai ''et al.'' (2020): References {{Taxonbar, from=Q15487229 Odd-toed ungulates Mammal superfamilies Taxa named by John Edward Gray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indricotheriinae
Paraceratheriidae is an extinct family of long-limbed, hornless rhinocerotoids, commonly known as paraceratheres or indricotheres, that originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the early Miocene. The first paraceratheres were only about the size of large dogs, growing progressively larger in the late Eocene and Oligocene. They were most common in the rainforest floodplain region which is now Kazakhstan, India, and southwest China, and lived further inland throughout northern and central Asia as well. The paraceratheres reached the peak of their evolution from the middle Oligocene to the early Miocene, where they became very large, herbivorous mammals. Most genera were about the size of modern draft horses and the extinct giant horse ''Equus giganteus'', with some growing significantly larger. The largest genus was ''Paraceratherium'', which was more than twice as heavy as a bull African elephant, and was one of the largest land mammals that ever lived. However, they remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Eocene
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the lower Eocene. Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. Stratigraphic definition The Ypresian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Belgium, Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The Ypresian is named after the Flanders, Flemish city of Ypres in Belgium (spelled ''Ieper'' in Dutch). The definitions of the original stage were totally different from the modern ones. The Ypresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inner Mongolia is geographically divided into eastern and western divisions. The eastern division is often included in Northeastern China (Dongbei) with major cities including Tongliao, Chifeng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two. Consider a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Manning
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant " chieftain", particularly a chieftain set to rule a territory in a king's stead. After the Norman Conquest, it became the equivalent of the continental count (in England in the earlier period, it was more akin to a duke; in Scotland, it assimilated the concept of mormaer). Alternative names for the rank equivalent to "earl" or "count" in the nobility structure are used in other countries, such as the ''hakushaku'' (伯爵) of the post-restoration Japanese Imperial era. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ''countess'' is used. Etymology The term ''earl'' has been compared to the name of the Heruli, and to runic ''erilaz''. Proto-Norse '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Schoch
Robert Milton Schoch is an American associate professor of Natural Sciences at the College of General Studies, Boston University. Schoch co-authored and expanded the fringe Sphinx water erosion hypothesis since 1990. Education Schoch received a BA in Anthropology and a BS in Geology from George Washington University in 1979. He was awarded MS and PhD degrees in Geology and Geophysics from Yale University (PhD, 1983). Schoch's PhD dissertation, ''Systematics, Functional Morphology and Macroevolution of the Extinct Mammalian Order Taeniodonta'', was published in 1986 by the Peabody Museum of Natural History. Teaching Schoch has taught at Boston University since 1984. He is an associate professor of Natural Sciences at the College of General Studies, a two-year core curriculum for bachelor's degree candidates. He teaches undergraduate science courses, including biology, geology, environmental science, geography, and science and public policy. He has received his college's Peyton R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolpak Formation , a Hasidic fur hat
{{disambig ...
Kolpak may refer to: * Kolpak ruling, a European Court of Justice decision involving Maros Kolpak that set a precedent about foreigners in professional sports * an alternate spelling of kalpak, a type of hat People with the surname * Maros Kolpak (born 1971), a Slovak handball player * Sydir Kovpak (1887–1967), a Soviet partisan leader in Ukraine during World War II See also * *Kolpik In Ashkenazi Jewish tradition, a kolpik is a type of traditional headgear worn in families of some Chassidic ''rebbes'' (Hasidic rabbis) of Galician or Hungarian dynastic descent, by their unmarried children on the Sabbath (Shabbat), and by so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 In Paleontology
Plants Cycadophytes Cycadophyte research *Hopkins and Johnson briefly report the first occurrence of cycad leaves from the Eocene Okanagan Highlands Klondike Mountain Formation which will later be identified to the family Zamiaceae. Angiosperms Fungi newly named Arthropoda Insects Plesiosaurs Newly Named Plesiosaurs Archosauromorphs Pterosaurs Newly Named Pterosaurs Non-avian dinosauromorphs * Paleontologist Karen Chin received a coprolite that was excavated during 1995 from strata dating back to the Maastrichtian in Saskatchewan, Canada. The specimen was about 17 inches (44 cm) long and contained fragments of bone. Due to its size, contents and age, the coprolite was believed to have been the remains of ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' feces. This discovery was announced in a 1998 paper published in the journal ''Nature''. * A Saharan expedition under the leadership of Paul Sereno yielded fruit when a team member stumbled on the bones and skull of '' Nigersaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg/1200px-Siège_de_Beijing_(1213-1214).jpeg)


.jpg)