|
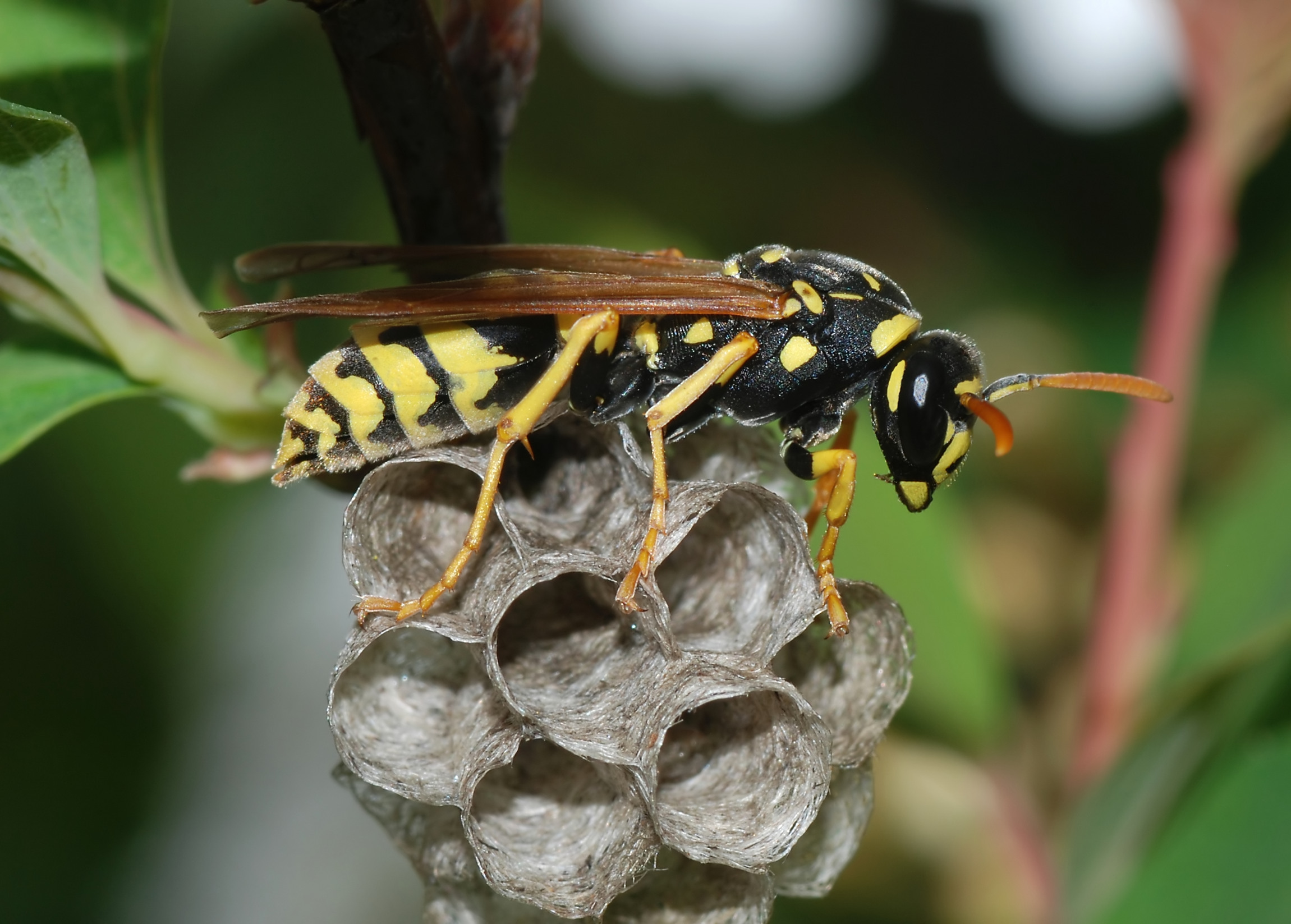
Paper Wasp
Paper wasps are a type of Eusociality, social vespid wasps. The term is typically used to refer to members of the Vespidae, vespid subfamily Polistinae, though it often colloquially includes members of the subfamilies Vespinae (hornets and yellowjackets) and Stenogastrinae, which also make nests out of paper. Paper wasp nests are characterized by open combs with down pointing cells. Some types of paper wasps are occasionally referred to as umbrella wasps due to the distinctive design of their nests."Paper Wasp" Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. Species Approximately 300 species of ''Polistes'' paper wasps have been identified worldwide. The most common paper wasp in Europe is ''Polistes dominula''. The Old World tribe Ropalidiini contains another 300 species ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polistes Dominula
The European paper wasp (''Polistes dominula'') is one of the most common and well-known species of social wasps in the genus ''Polistes''. Its diet is more diverse than those of most ''Polistes'' species—many genera of insects versus mainly caterpillars in other ''Polistes''—giving it superior survivability compared to other wasp species during a shortage of resources. The dominant females are the principal egg layers, while the subordinate females ("auxiliaries") or workers primarily forage and do not lay eggs. This hierarchy is not permanent, though; when the queen is removed from the nest, the second-most dominant female takes over the role of the previous queen. Dominance in females is determined by the severity of the scatteredness in the coloration of the Clypeus (arthropod anatomy), clypeus (face), whereas dominance in males is shown by the variation of spots of their abdomens. ''P. dominula'' is common and cosmopolitan due to their exceptional survival features such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polistes Gallicus
''Polistes gallicus'' is a species of paper wasp found in various parts of Europe, excluding England, Denmark, and Scandinavia, from warmer climates to cooler regions north of the Alps. Nests of these social insects are created in these various conditions. The ''Polistes'' species use an oral secretion to construct their nests, which consist of a combination of saliva and chewed plant fibers. This structural mixture physically protects the nest from various harsh elements and from weathering over time. Description and identification ''P. gallicus'', like other members of the subgenus ''Polistes (Polistes)'', has recognizable, bright yellow and black markings. They have smaller bodies than many of its allies that overlap in range, and their bodies are largely hairless. The species may be separated from allies through the following traits. Females are identified by having 12 antennal segments and 6 abdominal segments. The antennae are orange and paler on the ventral surface than i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiponini
The Epiponini (formerly known as Polybiini) are a large and diverse tribe of social wasps inhabiting the Neotropical region, with some species' ranges extending into the Nearctic The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface. The Nearctic realm covers most of North America, including Greenland, Central Florida, and the highlands of Mexico. The parts of North America ... region. Selected species * '' Apoica pallens'' * '' Leipomeles dorsata'' * '' Parachartergus apicalis'' * '' Parachartergus colobopterus'' * '' Polybia sericea'' * '' Protopolybia exigua'' * '' Synoeca cyanea'' * '' Brachygastra mellifica'' References Vespidae Hymenoptera tribes {{Vespidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microstigmus
''Microstigmus'', or the thin-waisted social wasps, is a small genus of wasps in the family Pemphredonidae. Species of the genus are found in the Neotropical realm from Central to South America. They build nests and live in colonies ranging in size from 1 to 18 members. ''Microstigmus'' is widely considered to be the only true eusociality, eusocial species of Apoidea, apoid wasp. Biology The species of ''Microstigmus'' ranges in length from . Unlike other Hymenoptera, the head and thorax lack branched or plumose hairs.Allaby, Michael. A Dictionary of Zoology. 1999. The wasps also have their posterior metatarsus modified into a cleaning mechanism. Apoid wasps also have a silk gland in the abdomen, which in the Pemphredonidae is used for nest building. In ''Microstigmus'', the gland cells ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crabronidae
The Crabronidae is a large family of wasps within the superfamily Apoidea. Taxonomy and phylogeny This family has historically been treated as a subfamily in the now-defunct Spheciformes group under the family Sphecidae. The Spheciformes included well over 200 genera, containing well over 9000 species. Revision of these taxa resulted resulted in the restriction of the Sphecidae to what was once the subfamily Sphecinae. As a result, the former Crabroninae was elevated to family status as Crabronidae. Subsequent revision has further restricted the Crabronidae. Several of the subfamilies of the Crabronidae are often treated as families in their own right, as is true of the most recent phylogenies. Of these lineages of Apoidea, only three were not included within Crabronidae in the past: Ampulicidae, Sphecidae, and Anthophila. The following phylogenetic tree is based on Sann ''et al.'', 2018, which used phylogenomics to demonstrate that both the bees ( Anthophila) and the Sphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusociality
Eusociality ( Greek 'good' and social) is the highest level of organization of sociality. It is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society, sometimes called castes. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform behaviors characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality has evolved among the insects, crustaceans, trematoda and mammals. It is most widespread in the Hymenoptera (ants, bees, and wasps) and in Isoptera (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the sole reproducers, while soldiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liostenogaster Flavolineata
''Liostenogaster'' is a genus of hover wasps from the subfamily Stenogastrinae of the family Vespidae which has a distribution centred on south-east Asia. It was named by the Dutch entomologist Jacobus van der Vecht from material collected by Japanese scientists on an expedition to Thailand, Malaysia Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ... and Cambodia which took place in 1966. Species The following species are currently assigned to ''Liostenogaster'': * '' Liostenogaster abstrusa'' Turillazzi 1999 * '' Liostenogaster bimaculata'' Selis, 2018 * '' Liostenogaster campanulae'' Turillazzi 1999 * '' Liostenogaster filicis'' Turillazzi 1999 * '' Liostenogaster flaviplagiata'' (Cameron, 1902) * '' Liostenogaster flavolineata'' (Cameron, 1902) * '' Liostenogaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chick (young bird), chicks hatched from one clutch (eggs), clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the brood (honeybee), honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring (lineal descendant, descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petiole , the narrow waist of some hymenopteran insects
{{disambiguation ...
Petiole may refer to: *Petiole (botany), the stalk of a leaf, attaching the blade to the stem *Petiole (insect anatomy) In entomology, petiole is the technical term for the narrow waist of some hymenopteran insects, especially ants, bees, and wasps in the suborder Apocrita. The petiole can consist of either one or two segments, a characteristic that separates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lingual lipase and amylase), and antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Saliva has specialized purposes for a variety of animal species beyond predigestion. Certain swifts construct nests with their sticky saliva. The foundation of bird's nest soup is an aerodramus nest. Venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Stems
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, engages in photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue. The stem can also be called the culm, halm, haulm, stalk, or thyrsus. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes: * The nodes are the points of attachment for leaves and can hold one or more leaves. There are sometimes axillary buds between the stem and leaf which can grow into branches (with leaves, conifer cones, or flowers). Adventitious roots (e.g. brace roots) may also be produced from the nodes. Vines may produce tendrils from nodes. * The internodes distance one node from another. The term "shoots" is often confused with "stems"; "shoots" generally refers to new fresh plant growth, including both stems and other structures like leaves or flowers. In most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |