|
Papa, Scotland
This is a list of places in Scotland called Papa or similar, which are so named after the Papar, monks from the Early Historic Period or from their connection to other, later priests. Orkney Islands * Papa Stronsay * Papa Westray (also known as "Papay") * Holm of Papay John of Fordun in his 14th century enumeration of these islands, has a ''Papeay tertia'' ("third Papey"), the location of which is unknown. Placenames * Paplay, South Ronaldsay * Paplay, Holm, Mainland * Papdale, an early name for Kirkwall Papleyhouse on Eday and Steevens of Papay on North Ronaldsay may not be genuinely related to the Papar.Thomson (2008) p. 15 Shetland * Papa, Shetland, one of the Scalloway Islands, lying north west of Burra and east of Oxna ** West Head of Papa, a tidal island off Papa, Shetland * Papa Little * Papa Stour (Great Papa) * Sound of Papa, a strait between Papa Stour and the Sandness peninsula. Hebrides Gaelic, ''Pabaigh'', () anglicised to "Pabay" or "Pabbay" means "priest island" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papar
The ''Papar'' (; from Latin , via Old Irish, meaning "father" or "pope") were Irish monks who took eremitic residence in parts of Iceland before that island's habitation by the Norsemen of Scandinavia. Their existence is attested by the early Icelandic sagas and recent archaeological findings. ''Papar'' in Iceland The first Norsemen began settling in Iceland in AD 874. The oldest Scandinavian source mentioning the existence of the ''Papar'', however, the '' Íslendingabók'' (Book of the Icelanders) by Icelandic chronicler Ari Þorgilsson, was written between 1122 and 1133, some time after the event. Ari writes of "Christian men", titled the ''Papar'' by the Norsemen, who departed the island because of their dislike of the 'heathen' Norse, pointing to the possibility of the ''Papar'' having arrived before the Norse. An earlier source that could possibly refer to the ''Papar'' is the work of Dicuil, an early 9th-century Irish monk and geographer, which included mention of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papa Little
Papa Little (; Old Norse: ''Papey Litla'', meaning "the little island of the priests") is an island in St Magnus Bay, Shetland, Scotland. The island lies at the head of Aith Voe in north west Mainland, Shetland, south of Muckle Roe. It is largely peat-covered and has been uninhabited since the 1840s. Its name means "little island of the papar" (as distinct from Papa Stour), who were Gaelic hermits or Culdees found as far north as Iceland Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi .... Notable people * Elizabeth Balfour (midwife) (1832-1918) Footnotes Uninhabited islands of Shetland Former populated places in Scotland {{Shetland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Uist
South Uist (, ; ) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the rest of the Hebrides, is one of the last remaining strongholds of the Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic language in Scotland. South Uist's inhabitants are known in Gaelic as ''Deasaich'' (Southerners). The population is about 90% Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic. The island is home to a nature reserve and a number of sites of archaeology, archaeological interest, including the only location in the British Isles where prehistoric mummy, mummies have been found. In the northwest, there is a missile testing range. In 2006 South Uist, together with neighbouring Benbecula and Eriskay, was involved in Scotland's biggest-ever community ownership, community land buyout by Stòras Uibhist. The group also owns the "biggest community wind farm in Scotland", Lochcarnan, on South Uist which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pabbay, Harris, Scotland
Pabbay () is an uninhabited island in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland which lies in the Sound of Harris between Harris and North Uist. The name comes from ''Papey'', which is Norse for "Island of the ''papar'' (Culdee)". The island was once very fertile, supporting a three-figure population and exporting corn, barley and illicit whisky. Most of the stewards of St Kilda were Pabbay men. St Kilda was part of a farm with Pabbay, and the islanders paid rent to the Macleod chiefs. The island was cleared for sheep in 1846. Pabbay is traditionally a home of Clan Morrison Clan Morrison is a Scottish clan. The Highland Clan Morrison is traditionally associated with the Lewis and Harris, Isle of Lewis and Harris (Leòdhas) around Ness, Lewis, Ness (Nis), Dun Pabbay, and Barvas (Barabhas), lands in Sutherland aroun .... Pabbay lies within the South Lewis, Harris and North Uist National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland which are defined so as to identify areas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop's Isles
The Barra Isles, also known as the Bishop's Isles, are a small archipelago in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. They lie south of the island of Barra, for which they are named. The group consists of nine islands and numerous rocky islets, skerry, skerries, and sea stacks. In 1427, the Lords of the Isles awarded the lairdship of Barra (and its associated islands) to Clan MacNeil of Barra. However, after acts of piracy by the MacNeils, King James VI of Scotland, James VI transferred ownership of the southern archipelago to the Bishop of the Isles, hence the islands became known as the ''Bishop's Isles''.Murray, W.H. (1966) ''The Hebrides''. London. Heinemann. p. 230 Murray writes that they belonged "to the Bishop of the Isles ''de jure'' although to Clan MacNeil, MacNeil ''de facto''". Many of the islands are extremely small; only the largest, Vatersay – which is now linked by the Vatersay Causeway to Barra – remains inhabited. Berneray, Barra, Scotland, Berneray (also known as B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pabbay, Barra, Scotland
Pabbay () is one of the Barra Isles at the southern tip of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The name comes from ''Papey'', which is Norse for "island of the ''papar''" (i.e. monks). At only , it never had a large population, and, after all the able-bodied men were killed in a fierce storm while out on a fishing trip on 1 May 1897, it was abandoned in the early twentieth century. The National Trust for Scotland has owned the island since 2000. With only two sheep left on the island in July 2007 and few, if any, other permanent mammalian residents, Pabbay is consequently home in summer to many ground-nesting birds due to the absence of predators. The island was the site of a Celtic hermitage, and a Pictish carved stone dates from that period. Remains of an Iron Age settlement can also been seen on Pabbay. The name of Pabbay is used for one of the three houses of Castlebay Secondary School. The other two are Mingulay and Sandray. Areas of Interest Bàgh Bàn is the name applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
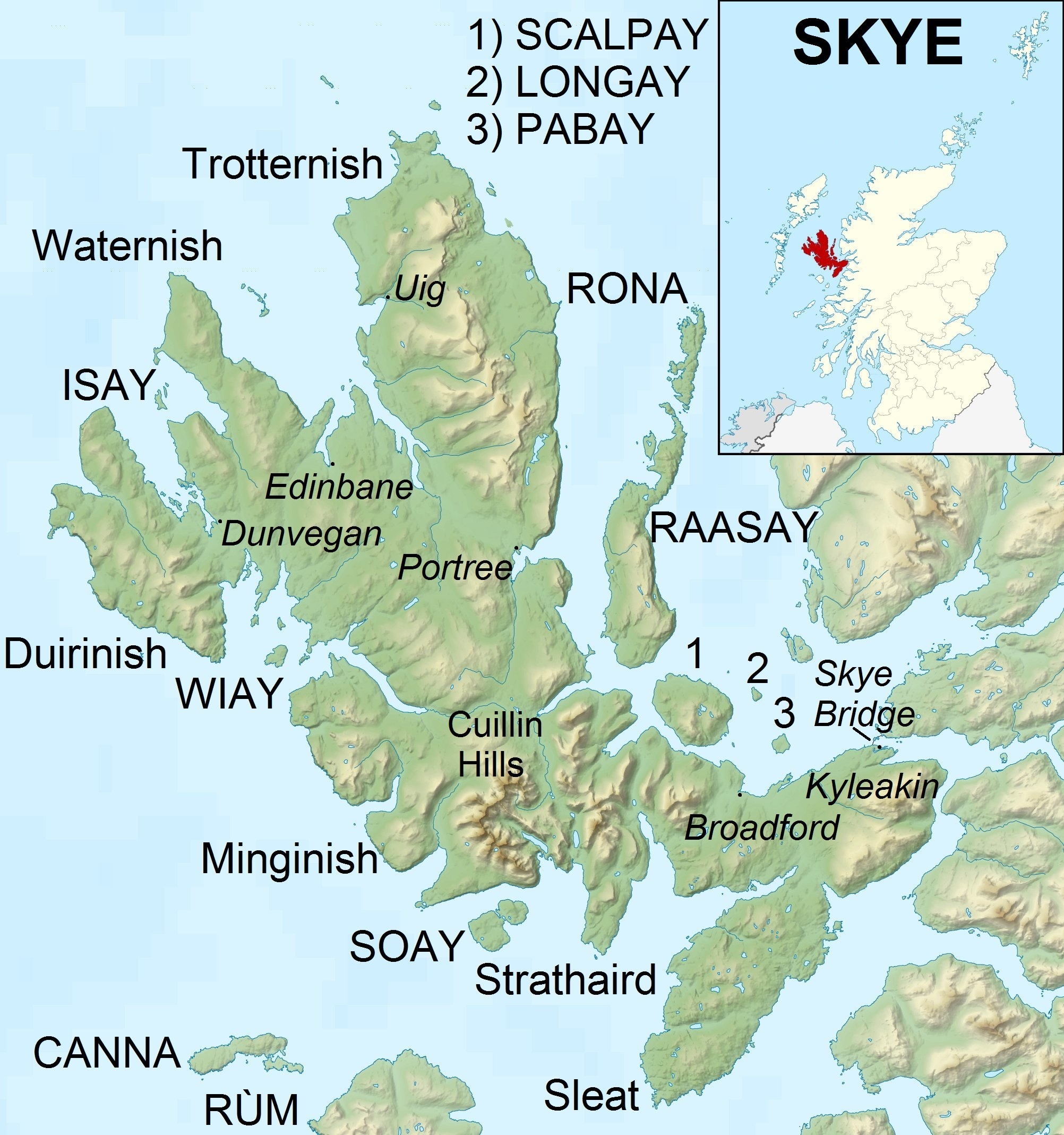
Pabay
Pabay is a Scottish island just off the coast of Skye. The name Pabay is derived from an old Norse word meaning "priest's isle" and there are the remains of a 13th-century chapel. Geography Pabay is an island in the Inner Sound of Skye, lying north of Broadford. It lies south of Longay and east of the larger Scalpay. Like most others of the name, is a low grassy island. It is in size, diamond-shaped and predominantly flat. The highest point is above sea level, with cliffs on the North and East shores. The island is formed of fossil-containing limestone, with some micaceous shale, named Pabba Shale. It forms a flat plateau with cliffs on the North and East shores. The surrounding low reefs encroach on its shores and double the area at low water. The island gives its name to a group of Jurassic Sedimentary rocks which are seen across the Inner Hebredian area-Pabba Shales. These were laid down at the bottom of a muddy sea 190 million years ago. Much later (about 60 milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Northmen) were a cultural group in the Early Middle Ages, originating among speakers of Old Norse in Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a Viking expansion, large-scale expansion in all directions, giving rise to the Viking Age. In English-language scholarship since the 19th century, Norse seafaring traders, settlers and warriors have commonly been referred to as Vikings. Historians of Anglo-Saxon England often use the term "Norse" in a different sense, distinguishing between Norse Vikings (Norsemen) from Norway, who mainly invaded and occupied the islands north and north-west of Britain as well as Ireland and western Britain, and Danish Vikings, who principally invaded and occupied eastern Britain. History of the terms ''Norseman'' and ''Northman'' The word ''Norseman'' first appears in English during the early 19th century: the earliest attestation given in the third edition of the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
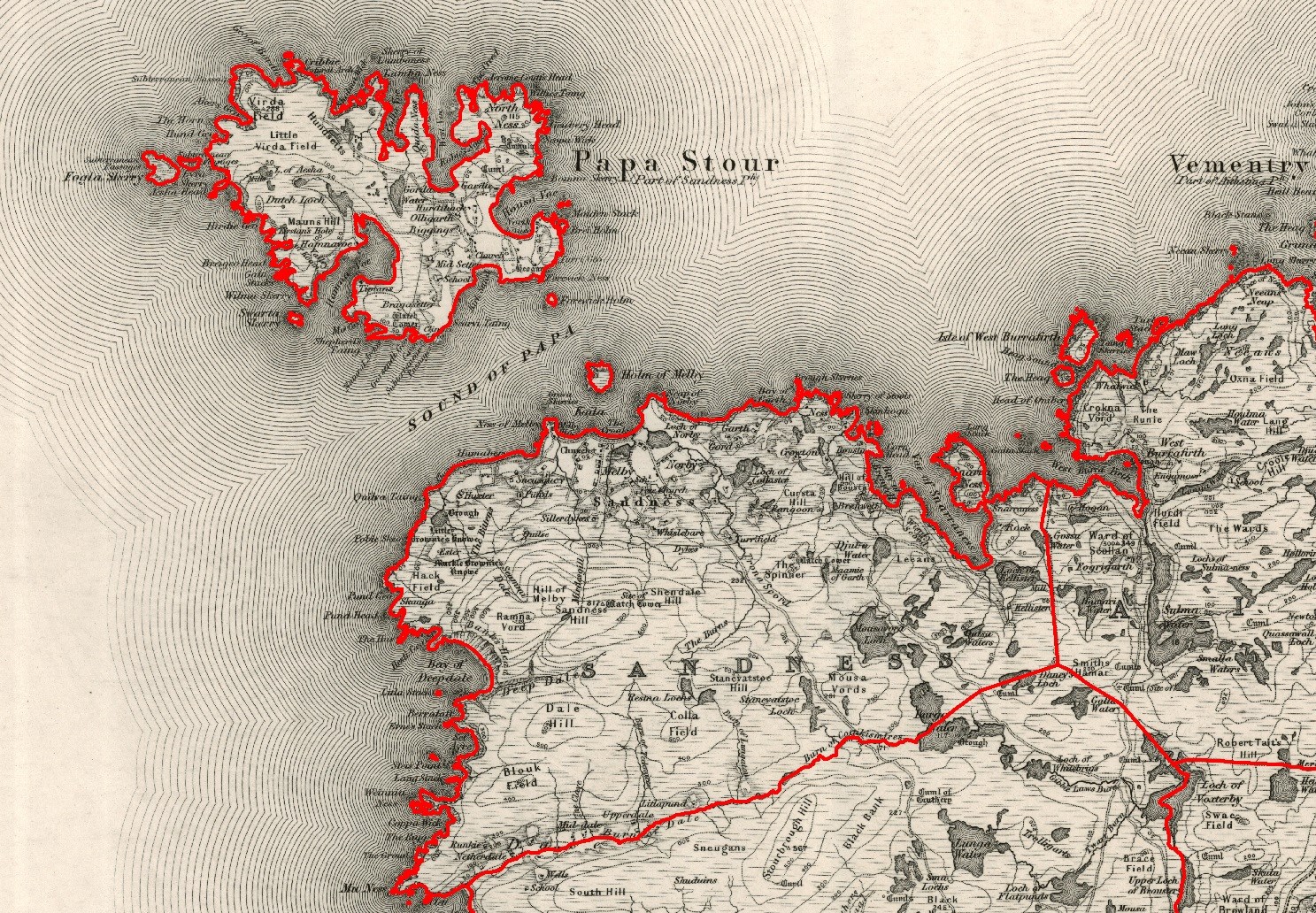
Sandness
Sandness (the "d" is not pronounced locally) is a headland and district in the west of Shetland Mainland, Scotland. Sandness was a civil parish, which also included the island of Papa Stour some 1600 metres northwest across ''Papa Sound''. In 1891, it was combined with Walls to the south, to form Walls and Sandness Parish, which had an administrative function until the abolition of Civil parishes in Scotland by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929 The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929 ( 19 & 20 Geo. 5. c. 25) reorganised local government in Scotland from 1930, introducing joint county councils, large and small burghs and district councils. The Act also abolished the Scottish poor law s ..., and had been a statistical regional unit since. Currently, the community council area of Sandness and Walls covers about the same area. The 1878 map of Sandness Parish shows that the parish to the east was Aithsting, before it was included into Sandsting to the south. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papa Stour
Papa Stour is one of the Shetland Islands in Scotland, with a population of fifteen people, some of whom immigrated after an appeal for residents in the 1970s. Located to the west of mainland Shetland and with an area of 828 hectares (3.2 square miles), Papa Stour is the ninth largest island in Shetland. Erosion of the soft volcanic rocks by the sea has created an extraordinary variety of caves, stacks, arches, blowholes, and cliffs. The island and its surrounding seas harbour diverse populations of wildlife. The west side of the island is a Site of Special Scientific Interest and the seas around the island are a Special Area of Conservation. The island has several Neolithic burial chamber sites, as well as the remains of Duke Hakon's 13th-century house dating from the Norse occupation of the island. The population reached 380 or more in the 19th century, when a fishing station was opened at Crabbaberry in West Voe. Subsequently, there was a steady decline in popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |