|
Pangasinan Language
Pangasinan (''Pangasinense'') is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary and predominant language of the entire province of Pangasinan and northern Tarlac, on the northern part of Luzon's central plains geographic region, most of whom belong to the Pangasinan ethnic group. Pangasinan is also spoken in southwestern La Union, as well as in the municipalities of Benguet, Nueva Vizcaya, Nueva Ecija, and Zambales that border Pangasinan. A few Aeta groups and most Sambal in Central Luzon's northern part also understand and even speak Pangasinan as well. Classification The Pangasinan language belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian languages branch of the Austronesian languages family. Pangasinan is similar to other closely related Philippine languages, Malay in Malaysia (as Malaysian), Indonesia (as Indonesian), Brunei, and Singapore, Hawaiian in Hawaii, Māori in New Zealand, and Malagasy in Madagascar. The Pangasinan l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in Island groups of the Philippines, three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. With a population of over 110 million, it is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, twelfth-most-populous country. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It has Ethnic groups in the Philippines, diverse ethnicities and Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Cordilleran Languages
The Meso-Cordilleran languages are a group of languages spoken in or near the Cordillera Central (Luzon), Cordillera Central mountain range in Northern Luzon. Its speakers are culturally very diverse, and include the lowland Pangasinan people, Pangasinense, the Igorot highlanders (including bugkalot people, Bugkalot), and Alta language, Alta-speaking Aeta people, Aeta groups. Languages Classification per Himes (2005):Himes, Ronald S. 2005. The Meso-Cordilleran Group of Philippine Languages. In Hsiu-chuan Liao and Carl R. Galvez Rubino (eds.), Current Issues in Philippine Linguistics and Anthropology: Parangal kay Lawrence A. Reid, 81-92. Manila, Philippines: Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL Philippines. *Meso-Cordilleran **Northern Alta language, Northern Alta **Southern Alta language, Southern Alta **South-Central Cordilleran ***Central Cordilleran languages, Central Cordilleran ****Isinai language, Isinai ****North Central Cordilleran *****Kalinga–Itneg ******It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay ( , ; , Jawi alphabet, Jawi: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken primarily by Malays (ethnic group), Malays in several islands of Maritime Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula on the mainland Asia. The language is an official language of Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore. Indonesian language, Indonesian, a standardized variety of Malay, is the official language of Indonesia and one of the working languages of East Timor. Malay is also spoken as a regional language of Malays (ethnic group), ethnic Malays in Indonesia and the Thai Malays, southern part of Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 60 million people across Maritime Southeast Asia. The language is pluricentric and a ISO 639 macrolanguage, macrolanguage, i.e., a group of Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible speech varieties, or dialect continuum, that have no traditional name in common, and which may be considered distinct languages by their speakers. Several varieties of it ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
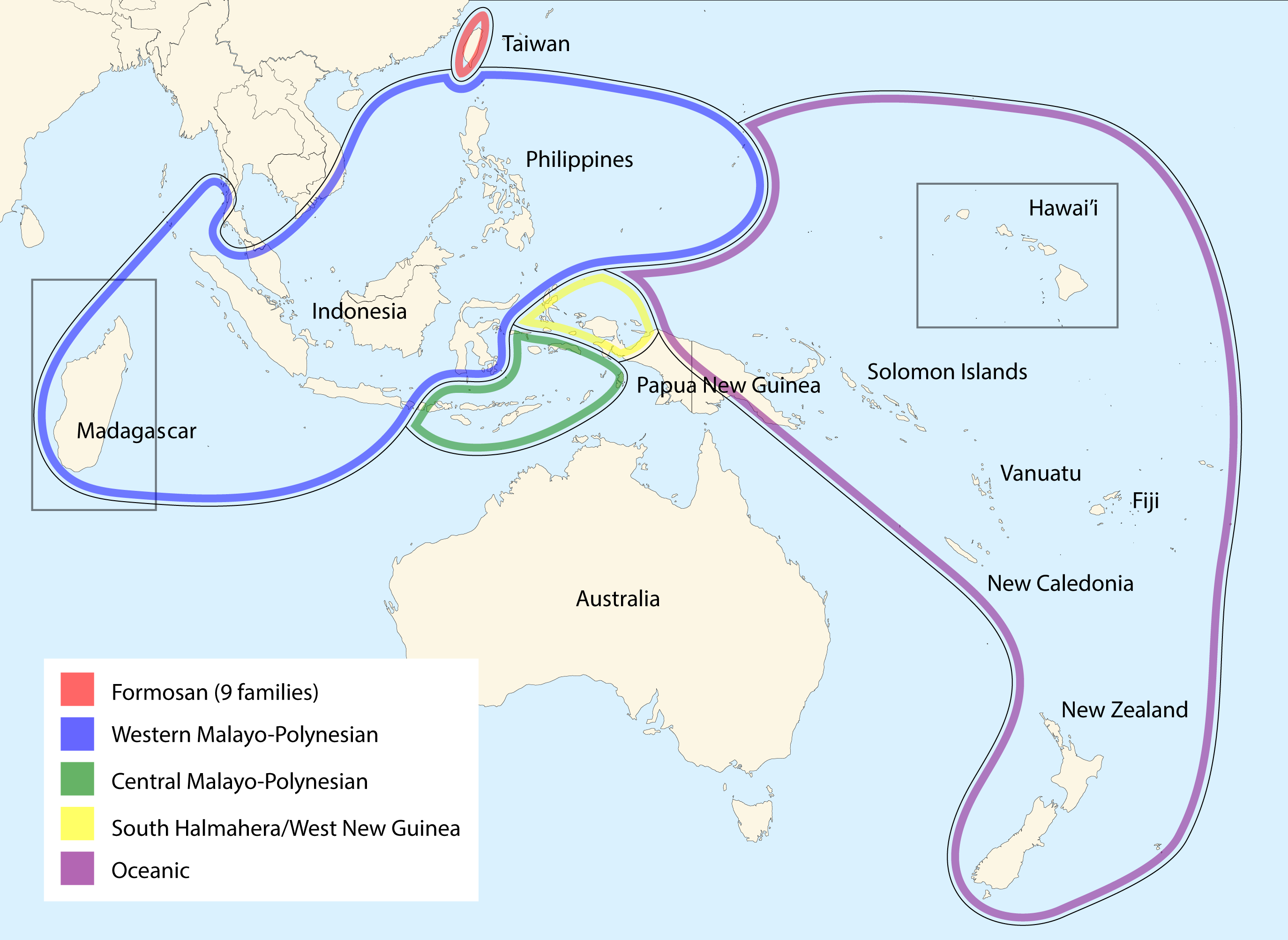
Austronesian Languages
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken by about 328 million people (4.4% of the world population). This makes it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages include Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, Sundanese, Tagalog (standardized as Filipino), Malagasy and Cebuano. According to some estimates, the family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family. In 1706, the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland first observed similarities between the languages spoken in the Malay Archipelago and by peoples on islands in the Pacific Ocean. In the 19th century, researchers (e.g. Wilhelm von Humboldt, Herman van der Tuuk) started to apply the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
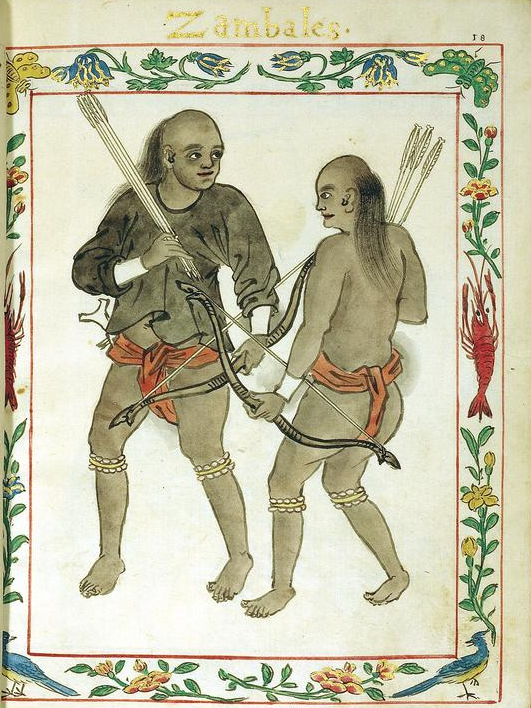
Sambal People
The Sambal people are a Filipino ethnolinguistic group living primarily in the province of Zambales and the Pangasinense municipalities of Bolinao, Anda, and Infanta. The term may also refer to the general inhabitants of Zambales. They were also referred to as the Zambales (singular Zambal) during the Spanish colonial era. In 1950s, hundreds of Sambal from the northern municipalities of Zambales migrated to and established a settlement in Quezon, Palawan; this settlement was named Panitian. The residents call themselves ''Palawenyong Sambal'' ( Spanish: ''zambales palaweños'') or simply ''Sambal''. History The Sambal are the original Austronesian inhabitants of the province of Zambales in the Philippines. They speak mainly Sambal and Botolan, as well as Kapampangan, Tagalog, Ilocano, Bolinao, and Pangasinense. The Sambalic languages are most closely related to the Kapampangan language and Sinauna and archaic form of Tagalog still spoken in Tanay in the province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
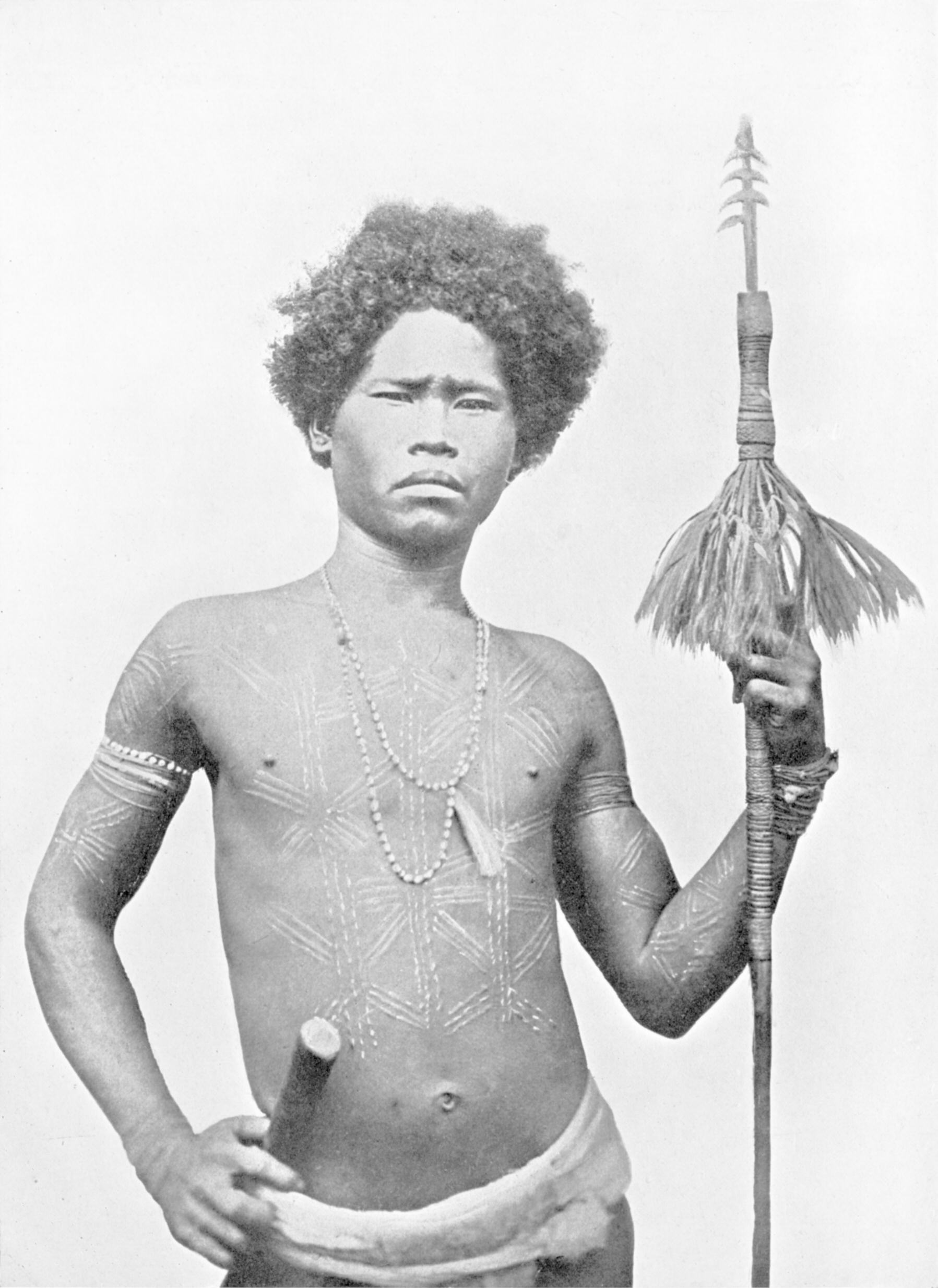
Aeta
Aeta (Ayta ), Agta and Dumagat, are collective terms for several indigenous peoples who live in various parts of Luzon islands in the Philippines. They are included in the wider Negrito grouping of the Philippines and the rest of Southeast Asia, with whom they share superficial common physical characteristics such as: dark skin tones; short statures; frizzy to curly hair; and a higher frequency of naturally lighter hair colour ( blondism) relative to the general population. They are thought to be among the earliest inhabitants of the Philippines—preceding the Austronesian migrations. Regardless, the modern Aeta populations have significant Austronesian admixture, and speak Austronesian languages. Aeta communities were historically nomadic hunter-gatherers, typically consisting of approximately one to five families per mobile group. Groups under the "Aeta" umbrella term are normally referred to after their geographic locations or their common languages. Etymology The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the List of islands by population, 4th most populous island in the world. It is the List of islands by area, 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary Island groups of the Philippines, island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon Mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan Islands, Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Philippines
There are some 130 to 195 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole language, creole varieties generally called Chavacano along with some local varieties of Chinese are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino language, Filipino, a de facto standardized version of Tagalog language, Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English language, English. Filipino is regulated by Commission on the Filipino Language and serves as a ''lingua franca'' used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds. Republic Act 11106 declares Filipino Sign Language or FSL as the country's official sign language and as the Philippine government's official language in communicating with the Filipino Deaf. While Filipino is used for communication across the country's diverse linguistic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian Language
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken by about 328 million people (4.4% of the world population). This makes it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages include Malay language, Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named "Indonesian language, Indonesian"), Javanese language, Javanese, Sundanese language, Sundanese, Tagalog language, Tagalog (standardized as Filipino language, Filipino), Malagasy language, Malagasy and Cebuano language, Cebuano. According to some estimates, the family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family. In 1706, the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland first observed similarities between the languages spoken in the Malay Archipelago and by people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komisyon Sa Wikang Filipino
The Commission on the Filipino Language (CFL), also referred to as the (KWF), is the official regulating body of the Filipino language and the official government institution tasked with developing, preserving, and promoting the various local Philippine languages. The commission was established in accordance with the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines. Established by Republic Act No. 7104 in 1991, the commission is a replacement for the Institute of Philippine Languages (IPL; ''Linangan ng mga Wika sa Pilipinas'') that was set up in 1987 which was a replacement of the older Institute of National Language (INL; ''Surian ng Wikang Pambansa''), established in 1937 as the first government agency to foster the development of a Philippine national language. History The 1st National Assembly of the Philippines passed Commonwealth Act No. 184 of 1936, establishing the Institute of National Language (''Surian ng Wikang Pambansa''). On January 12, 1937, President Manuel L. Quezon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Language
* A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area. Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, "''regional or minority languages''" ''means languages that are:'' #''traditionally used within a given territory of a State by nationals of that State who form a group numerically smaller than the rest of the State's population and'' #''different from the official language(s) of that State'' Recognition of regional or minority languages must not be confused with recognition as an official language. Relationship with official languages In some cases, a regional language may be closely related to the state's main language or official language. For example: *The Frisian languages spoken in the Netherlands and Germany, which belong to the Germanic family. *The Gutnish language, a regional language spoken in Gotland and related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baybayin
Baybayin (,), also sometimes erroneously referred to as alibata, is a Suyat, Philippine script widely used primarily in Luzon during the 16th and 17th centuries and prior to write Tagalog language, Tagalog and to a lesser extent Visayan languages, Kapampangan language, Kampampangan, Ilocano language, Ilocano, and several other Philippine languages. Baybayin is an abugida belonging to the family of the Brahmic scripts. Its use was gradually replaced by the Latin alphabet during Spanish Colonization in the Philippines, Spanish rule, though it has seen limited modern usage in the Philippines. The script is encoded in Unicode as Tagalog (Unicode block), Tagalog block since 1998 alongside Buhid script, Buhid, Hanunoo script, Hanunoo, and Tagbanwa scripts. The Archives of the University of Santo Tomas in Manila holds the largest collection of extant writings using Baybayin. Baybayin has seen increasing modern usage in the Philippines. Today, Baybayin is often used for cultural and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |