|
Pan Pan (kingdom)
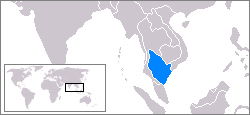
Pan Pan or Panpan was a small Hindu kingdom believed to have existed around the 3rd to 7th century CE. It is believed to have been located on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula, with opinion varying from somewhere in Kelantan or Terengganu, in modern-day Malaysia to the vicinity of Phunphin district, Surat Thani province, in modern Thailand. According to the Chinese text ''Jiu Tang Shu'', Pan Pan was bordered in the south with Langkasuka, and in the north with Tun Sun near the Kra Isthmus. Jacq-Hergoualc'h speculates that the border may have been south of Nakhon Si Thammarat, possibly near Songkhla. After the northern neighbor Tun Sun gained independence from Funan and became ''Lang-chia'' or ''Lang-ya-hsiu'' in the late 5th century CE, its southern part joined Pan Pan in the 6th century, while the northern territory became Dvaravati. It is speculated to be related to the Patani Kingdom, which occupied the same area many centuries later, and has some differences in culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering parts of present-day Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam that existed from the first to sixth century CE. The name is found in Chinese historical texts describing the kingdom, and the most extensive descriptions a name the people of Funan gave to their polity. Some scholars argued that ancient Chinese scholars has found the records from Yuán Shǐ, the history records of Yuan Dynasty. "Syam Kok and Lo Hu Kok, formerly the Kingdom of Funan, were located to the west of Linyi Kok (Champa Kingdom in central Vietnam). The maritime distance was from the capital of Linyi Kok to the capital of Funan Kok. They are separated by about 3,000 li." Like the name of the kingdom, the ethno-linguistic nature of the people is the subject of much discussion am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Kedah
Archeological digs suggest a settlement existed on the northern bank of the Merbok River by the 1st millennium CE. The Merbok settlement, Sungai Batu was built near the river's estuary. The early history of Kedah can be traced from various sources, from the prehistoric period, most famously the archaeological site of Bujang Valley, the early maritime trade of India, Persia, and the Arabs to the written works of early Chinese pilgrims and early Chinese records, and later to the partly-historical '' Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa'' and the ''Al-Tarikh Salasilah Negeri Kedah''. Around 170 CE groups of people of the Hindu faith arrived at Kedah, joining them soon were peoples from nearby islands and those from the northern Mon-Khmer region. Traders from India, Persia and Arabia arrived in the Malacca Strait, using Gunung Jerai as a landmark point in their travels. After the 7th century, Srivijaya gained Kedah as one of its vassals. In trade, Kedah supplied its own tin, and jungle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bujang Valley
The Bujang Valley () is a sprawling historical complex and has an area of approximately , with the discovery of a set of new iron smelting sites, Sungai Batu site enlarging the settlement area to . Bujang Valley situated near Merbok, Kedah, between 1,217-metre Mount Jerai in the north and Muda River in the south. It is the richest archaeological area in Malaysia. The area consists of ruins that may date more than 1,500 years old. More than 50 ancient pagoda temples, called '' candi'' (pronounced as "chandi"), have also been unearthed. The most impressive and well-preserved of these is located in Pengkalan Bujang, Merbok. The Bujang Valley Archaeological Museum is also located that known as Sungai Batu, excavations have revealed jetty remains, iron-smelting sites, and a clay brick monument dating back to 110 AD, making it the oldest man-made structure to be recorded in Southeast Asia. The local rulers adopted Hindu-Buddhist Indian cultural and political models earlier tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharmasetu
Dharmasetu was an 8th-century Maharaja of Srivijaya. Under his reign, he successfully incorporated Pan Pan, a kingdom located in the north of the Malay Peninsula, into the Srivijayan sphere of influence before 775 CE. At an old monastery of Nakhon Si Thammarat in modern-day Thailand, there is a stele indicating that Dharmasetu ordered the construction of three sanctuaries dedicated to Bodhisattvas Padmapani, Vajrapani, and Buddha in Ligor. The inscription further states that Dharmasetu was the head of the Sailendra dynasty that ruled Java Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje .... This is the first instance of a relationship known to have existed between Srivijaya and the Sailendra. Dewi Tara, the daughter of Dharmasetu, later married a member of the Sailendra dynasty b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srivijaya
Srivijaya (), also spelled Sri Vijaya, was a Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia) that influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th to 11th century AD. Srivijaya was the first polity to dominate much of western Maritime Southeast Asia. Due to its location, Srivijaya developed complex technology utilizing maritime resources. In addition, its economy became progressively reliant on Maritime Silk Road, the booming trade in the region, thus transforming it into a luxury good, prestige goods-based economy. The earliest reference to it dates from the 7th century. A Tang dynasty Chinese people, Chinese Bhikkhu, monk, Yijing (monk), Yijing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for six months. The earliest known inscription in which the name Srivijaya appears also dates from the 7th century in the Kedukan Bukit inscription fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Dynasty
The Chen dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Chen (南陳 / 南朝陳) in historiography, was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty and the fourth and last of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Southern dynasties, Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. Following the Liang dynasty, the Chen dynasty was founded by Emperor Wu of Chen, Chen Baxian (Emperor Wu). The Chen dynasty further strengthened and revitalized the economy and culture of southern China, and made territorial expansions northward, laying the foundation for future dynasties. It was conquered by the Sui dynasty in 589, marking an end to the Northern and Southern dynasties period in Chinese history. The descendants of the Chen imperial family continued to hold powerful high-ranking positions in the imperial courts of both the Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang dynasties. History Founding and expansion: Chen Baxian In the twilight of the Liang dynasty (548–55 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () or Xiao Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the Southern Qi dynasty and succeeded by the Chen dynasty. The rump state of Western Liang existed until it was conquered in 587 by the Sui dynasty. Rule During the Liang dynasty, in 547 a Persian embassy paid tribute to the Liang, amber was recorded as originating from Persia by the '' Book of Liang''. In 548, the Prince of Henan Hou Jing started a rebellion with Xiao Zhengde, the Prince of Linhe, nephew and a former heir of the Emperor Wu of Liang, and installed Xiao Zhengde as emperor. In 549, Hou sacked Jiankang, deposed and killed Xiao Zhengde, seized power and put Emperor Wu effectively under house arrest. He dismissed the armies opposed to him in the name of Emperor Wu. In 549, Emperor Wu died; Emperor Wu's third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Siam
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in length and up to in width, and has a surface area of . The gulf is surrounded on the north, west and southwest by the coastlines of Thailand (hence the name), on the northeast by Cambodia and the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, and opens to the South China Sea in the southeast. Names The modern Thai language, Thai name of the gulf is ''Ao Thai'' (, , 'Thai Gulf') and "Gulf of Thailand" has been adopted as the official name of the body by the International Hydrographic Organization. Its name in Malay language, Malay is "Gulf of Siam", ''Teluk Siam'' or in Jawi script: , and in '', Chhoung Samut Siem''. In Thai, the gulf is historically known as ''Ao Sayam'' (). In Vietnamese language, Vietnamese it is known as ''Vịn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartography, Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Greater India#Indianized kingdoms of South East Asia, Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''(Mandala (Southeast Asian political model), Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering parts of present-day Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam that existed from the first to sixth century CE. The name is found in Twenty-Four Histories, Chinese historical texts describing the kingdom, and the most extensive descriptions a name the people of Funan gave to their polity. Some scholars argued that ancient Chinese scholars has found the records from History of Yuan, Yuán Shǐ, the history records of Yuan Dynasty. "Syam Kok and Lo Hu Kok, formerly the Kingdom of Funan, were located to the west of Linyi Kok (Champa Kingdom in central Vietnam). The maritime distance was from the capital of Linyi Kok to the capital of Funan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaundinya II
Kaundinya II (, ), was a ruler from the house of Kaudinya, Varman dynasty of the Phnom or Funan kingdom. Biography He was the son of King Candana (), who was descended from King Kaundinya I Kaundinya I (, , ), also known as Kaundanya in Odia (), Hùntián ( zh, 混塡), Hỗn Điền () and Preah Thong (), was the second monarch of Funan (reigned c. 1st century) which comprises much of Cambodia located in mainland Southeast Asia ce .... During his reign about 410 AD, he married to his queen. The son born to her was Kaundinyajayavarman (Khmer: ព្រះបទកៅណ្ឌិន្យជ័យវរ្ម័ន, Latin: ''Kaundinya jayavarman)'' and died in 434 AD. References 6th-century Cambodian monarchs Monarchs of Funan {{Cambodia-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |