|
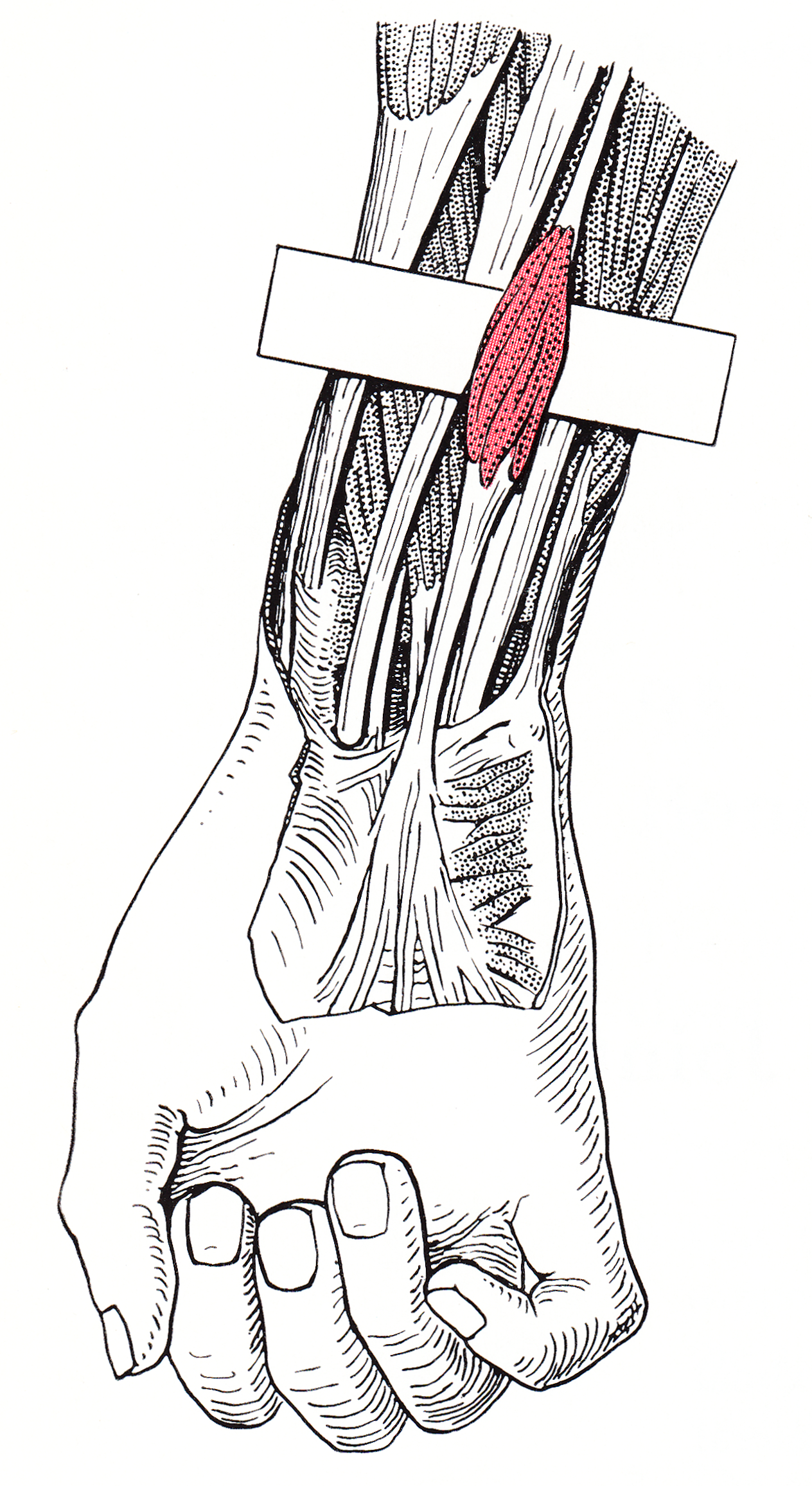
Palmaris Longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; however, the rate varies in different ethnic groups. Absence of the palmaris longus does not have an effect on grip strength. The lack of palmaris longus muscle does result in decreased pinch strength in fourth and fifth fingers. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is more prevalent in females than males. The palmaris longus muscle can be observed by touching the pads of the fourth finger and thumb and flexing the wrist. The tendon, if present, will be visible in the midline of the anterior wrist. Structure Palmaris longus is a slender, elongated, spindle shaped muscle, lying on the medial side of the flexor carpi radialis. It is widest in the middle, and narrowest at the proximal and distal attachments.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Epicondyle Of Humerus
The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used. The medial epicondyle gives attachment to the ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint, to the pronator teres, and to a common tendon of origin (the common flexor tendon) of some of the flexor muscles of the forearm: the flexor carpi radialis, the flexor carpi ulnaris, the flexor digitorum superficialis, and the palmaris longus. The medial epicondyle is located on the distal end of the humerus. Additionally, the medial epicondyle is inferior to the medial supracondylar ridge. It is also proximal to the olecranon fossa. The medial epicondyle protects the ulna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Carpi Radialis Muscle
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist. Origin and insertion The flexor carpi radialis is one of four muscles in the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm. This muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus as part of the common flexor tendon. It runs just laterally of flexor digitorum superficialis and inserts on the anterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal, and has small slips to both the third metacarpal and trapezium tuberosity. The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis is visible on the anterior surface of the forearm, just proximal to the wrist, when the wrist is flexed. It is the tendon seen most lateral, closest to the thumb. Nerve and artery Like most flexors of the anterior compartment of the forearm, FCR is innervated by the median nerve, specifically by axons from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Pollicis Longus
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population. Human anatomy Origin and insertion It arises from the grooved anterior (side of palm) surface of the body of the radius, extending from immediately below the radial tuberosity and oblique line to within a short distance of the pronator quadratus muscle.Gray 1918, ''Flexor Pollicis Longus'', paras 20, 25 An occasionally present accessory long head of the flexor pollicis longus muscle is called 'Gantzer's muscle'. It may cause compression of the anterior interosseous nerve. It arises also from the adjacent part of the interosseous membrane of the forearm, and genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Finger
The little finger or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger. Etymology The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''pink'', meaning "little finger". The earliest recorded use of the term "pinkie" is from Scotland in 1808. The term (sometimes spelled "pinky") is common in Scottish English and American English, and is also used extensively in other Commonwealth countries such as New Zealand, Canada, and Australia. Nerves and muscles There are nine muscles that control the fifth digit: Three in the hypothenar eminence, two extrinsic flexors, two extrinsic extensors, and two more intrinsic muscles: * Hypothenar eminence: ** Opponens digiti minimi muscle ** Abductor minimi digiti muscle (adduction from third palmar interossei) ** Flexor digiti minimi brevis (the "longus" is absent in most humans) * Two extrinsic flexors: ** Flexor digitorum superficialis ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaphoid
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew nut. Structure The scaphoid is situated between the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones. It is located on the radial side of the wrist, adjacent to the styloid process of the radius. It articulates with the radius, lunate, trapezoid, trapezium, and capitate. Over 80% of the bone is covered in articular cartilage. Bone The palmar surface of the scaphoid is concave, and forming a distal tubercle, giving attachment to the transverse carpal ligament. The proximal surface is triangular, smooth and convex. The lateral surface is narrow and gives attachm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform Bone
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisiformis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist ( carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Process Of The Ulna
The coronoid process of the ulna is a triangular process projecting forward from the anterior proximal portion of the ulna. Structure Its ''base'' is continuous with the body of the bone, and of considerable strength. Its ''apex'' is pointed, slightly curved upward, and in flexion of the forearm is received into the coronoid fossa of the humerus. Its ''upper surface'' is smooth, convex, and forms the lower part of the semilunar notch. Its ''antero-inferior'' surface is concave, and marked by a rough impression for the insertion of the brachialis muscle. At the junction of this surface with the front of the body is a rough eminence, the tuberosity of the ulna, which gives insertion to a part of the brachialis; to the lateral border of this tuberosity the oblique cord is attached. Its ''lateral surface'' presents a narrow, oblong, articular depression, the radial notch. Its ''medial surface'', by its prominent, free margin, serves for the attachment of part of the ulnar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant 1962 97 D
Grant or Grants may refer to: People * Grant (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Grant (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters ** Ulysses S. Grant (1822–1885), the 18th president of the United States and general of the Union during the American Civil War ** Cary Grant (1904–1986), British-American actor ** Hugh Grant (born 1960), British actor ** Richard E. Grant (born 1957), British-Swazi actor ** Justice Grant (other), judges named Grant * Clan Grant, a Highland Scottish clan Law and philanthropy *Grant (money), an award usually funded by a government, business, or foundation, often with not-for-profit preconditions *Grant (law), a term in conveyancing * Spanish and Mexican land grants in New Mexico * Spanish land grants in Florida *'' Grant v Torstar Corp'', a leading Supreme Court of Canada case on responsible communication in the public interest as a defence against defamation Places *Grant County (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
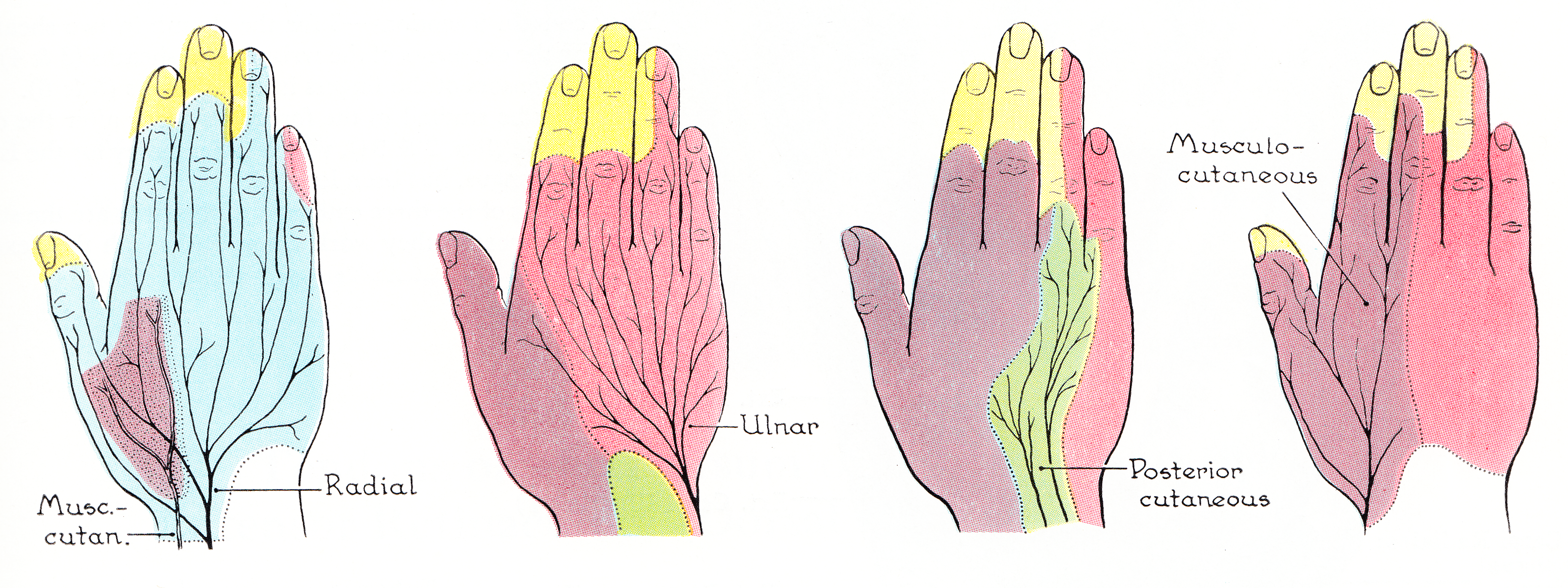
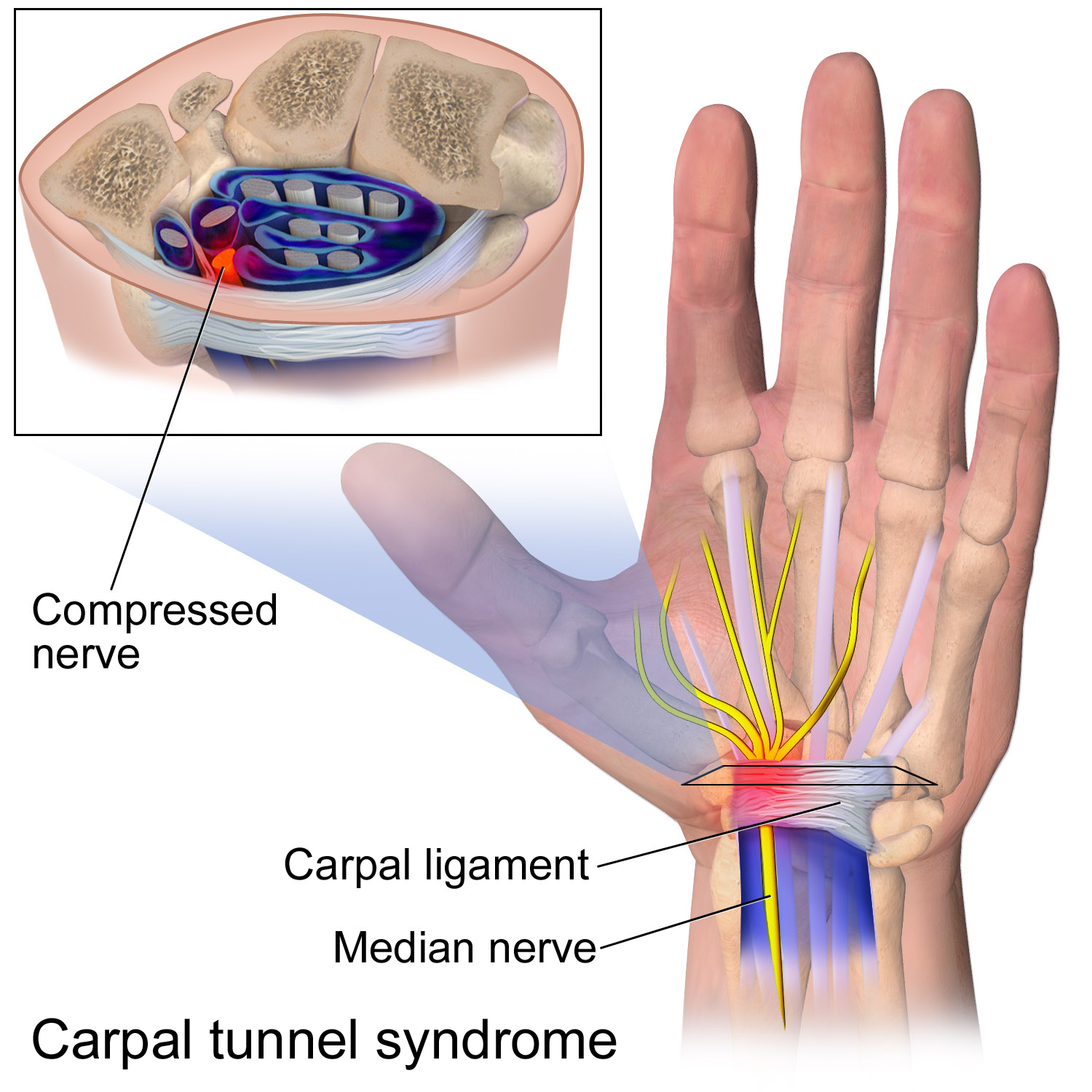
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C6-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmar Aponeurosis
The palmar aponeurosis (palmar fascia) Deep fascia, invests the muscles of the palm, and consists of central, lateral, and medial portions. Structure The central portion occupies the middle of the palm, is triangular in shape, and of great strength Its apex is continuous with the lower margin of the transverse carpal ligament, and receives the expanded tendon of the palmaris longus. Its base divides below into four slips, one for each finger. Each slip gives off superficial fibers to the skin of the palm and finger, those to the palm joining the skin at the furrow corresponding to the metacarpophalangeal articulations, and those to the fingers passing into the skin at the transverse fold at the bases of the fingers. The deeper part of each slip subdivides into two processes, which are inserted into the fibrous sheaths of the flexor tendons. From the sides of these processes offsets are attached to the transverse metacarpal ligament (other), transverse metacarpal ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel. Structure The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone. The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |