|
Palkinsky District
Palkinsky District () is an administrativeLaw #833-oz and municipalLaw #420-oz district (raion), one of the twenty-four in Pskov Oblast, Russia. It is located in the west of the oblast and borders with Pskovsky District in the northwest, Ostrovsky District in the southeast, Pytalovsky District in the south, Viļaka and Alūksne Municipalities of Latvia in the southwest, and with Pechorsky District in the northwest. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the urban locality (a work settlement) of Palkino. Population: 10,520 ( 2002 Census); The population of Palkino accounts for 33.1% of the district's total population. Geography The district lies in the basin of the Velikaya River. The Velikaya itself crosses the district from south to north. The principal tributary of the Velikaya in the limits of the district is the Vyada, which forms the border with Ostrovsky District. The largest lake, Lake Belaya Struga, has an area of . About 5% of the district's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
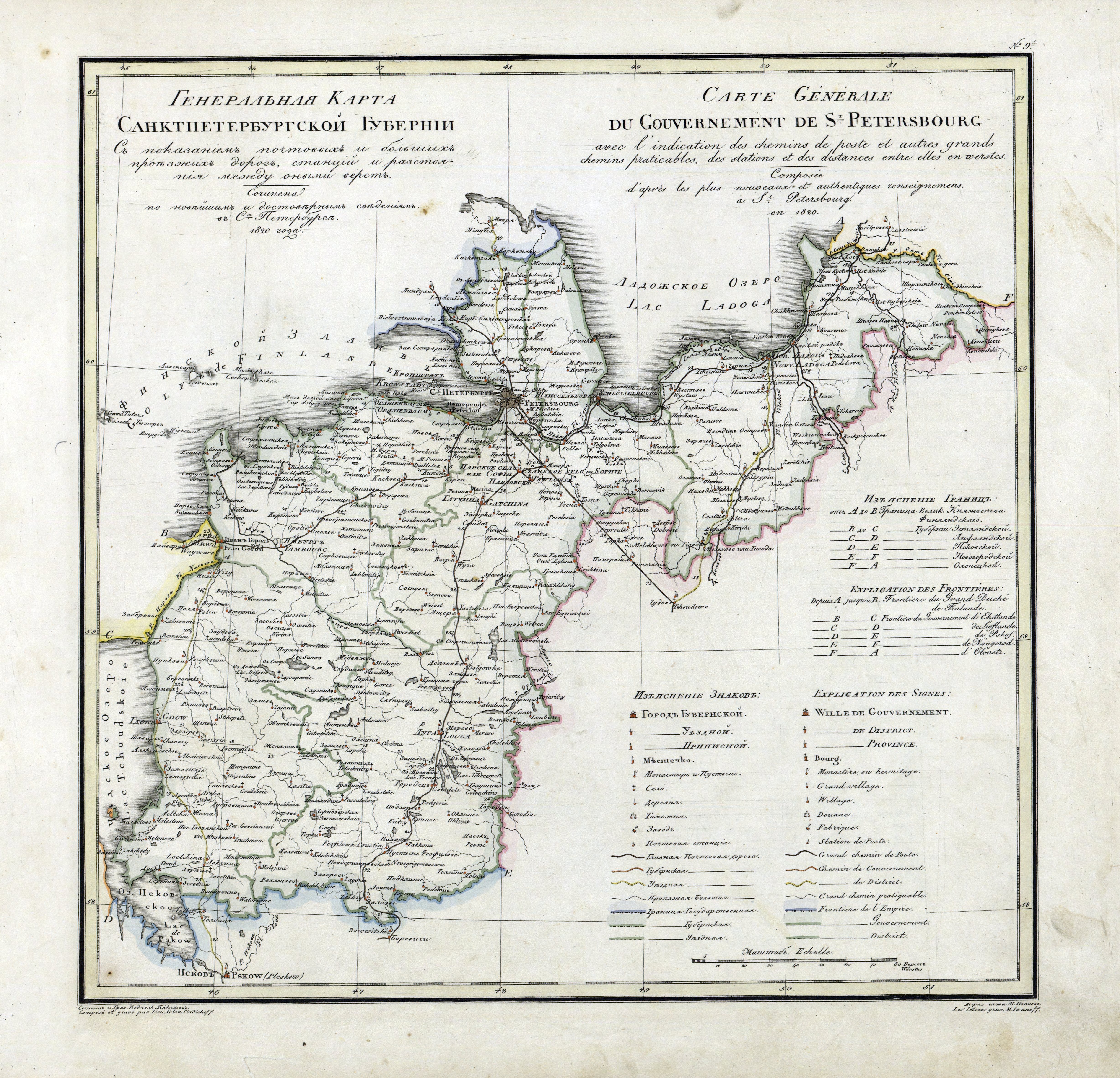
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast () is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the west of the country. Its administrative center is the Classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Pskov. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, its population was 599,084. Geography Pskov Oblast is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of contiguous Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast, while located further to the west, is an enclave and exclave, exclave).1september.ru. Д. В. Заяц (D. V. Zayats).Псковская область (''Pskov Oblast''). It borders with Leningrad Oblast in the north, Novgorod Oblast in the east, Tver Oblast, Tver and Smolensk Oblasts in the southeast, Vitebsk Region, Vitebsk Oblast of Belarus in the south, and with the counties of Latvia (Alūksne Municipality, Balvi Municipality, and Ludza Municipality) and Estonia (Võru County) in the west. In the northwest, Pskov Oblast is limited by Lake Peipus, which ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''village'', from Latin ''villāticus'', ultimately from Latin ''villa'' (English ''vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov Viceroyalty
Pskov Viceroyalty () was an administrative-territorial unit ('' namestnichestvo'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1777–1796. The seat of the Viceroyalty was located in Pskov. Both the predecessor and the successor of the viceroyalty was Pskov Governorate. In terms of modern administrative division of Russia, the area of the viceroyalty is currently split between Pskov, Leningrad, Tver, and Novgorod Oblasts. History Pskov Governorate with the seat in the town of Opochka was established in 1772 to accommodate vast areas transferred to the Russian Empire as the result of the First Partition of Poland. The governorate was too big for practical governance, and in 1776, it was divided into Pskov (with the seat in Pskov) and Polotsk Governorates. According to the general line of the administrative reforms by Catherine the Great, on 23 August 1777 the governorate was transformed into viceroyalty. Simultaneously, Luga (newly founded), Kholm, and Novorzhev (formerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov Governorate
Pskov Governorate () was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, which existed in 1772–1777 and 1796–1927. Its seat was located in Opochka between 1772 and 1776, and in Pskov after 1776. The governorate was located in the west of the Russian Empire and bordered (after 1796) Saint Petersburg Governorate in the north, Novgorod Governorate in the northeast, Tver Governorate in the east, Smolensk Governorate in the southeast, Belarusian Governorate (since 1802, Vitebsk Governorate) in the south, and Governorate of Livonia in the west. In terms of modern administrative division of Russia, the area of the governorate is currently split between the Pskov Oblast, Pskov, Tver Oblast, Tver, and Novgorod Oblast, Novgorod oblasts. The former border between Pskov Governorate and Governorate of Livonia still largely corresponds to the state border between Russia in the east and Estonia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novgorod Governorate
Novgorod Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, which existed from 1727 to 1776 and from 1796 to 1927. Its administrative center was in the city of Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod. The governorate was located in the northwest of the European part of the Russian Empire. History The governorate was established in 1727 from Belozersk, Novgorod, Pskov, Tver and Velikiye Luki Provinces of Saint Petersburg Governorate, St. Petersburg Governorate. It was abolished by a decree (''ukase'') of Catherine II of Russia, Catherine II on , 1776, which established Novgorod Viceroyalty, Novgorod and Tver Viceroyalty, Tver Viceroyalties instead. Novgorod Viceroyalty included Novgorod Oblast, Russian Empire, Novgorod and Olonets Oblast, whereas Tver Viceroyalty was made of the former Tver Province. The viceroyalty was never formally abolished, however, after a number of administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate was a province (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Saint Petersburg. The governorate was composed of of area and 2,112,033 inhabitants. It was bordered by Governorate of Estonia, Estonian and Governorate of Livonia, Livonian Governorates to the west, Pskov Governorate to the south, Novgorod Governorate to the east, Olonets Governorate to the northeast, and Viipuri Province, Vyborg Governorate of the Grand Duchy of Finland to the north. The governorate covered most of the areas of modern Leningrad Oblast and Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru, Jõgeva County, Jõgeva, Tartu County, Tartu, Põlva County, Põlva, and Võru County, Võru counties of Estonia. Establishment Ingermanland Governorate (, ''Ingermanlandskaya guberniya'') was created from the territories reconquered from the Swedish Empire in the Great Northern War. In 1704 prince Alexander Menshikov was appointed as its first governor, and in 1706 it was first Russian region des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Russia In 1708–1710
The administrative division reform of 1708 was carried out by Russian Tsar Peter the Great in an attempt to improve the manageability of the vast territory of Russia. Prior to the reform, the country was subdivided into uyezds and volost Volost (; ; ) was a traditional administrative subdivision in Kievan Rus', the Grand Duchy of Moscow, and the Russian Empire. History The '' Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary'' (1890–1907) states that the origins of the concept is unc ...s, and in the 17th century the number of the uyezds was 166. Creation On , 1708, Peter issued an edict dividing Russia into eight governorates ('' guberniyas'').Указ об учреждении губерний и о росписании к ним горо ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Moscow
The Grand Principality of Moscow, or Muscovy, known as the Principality of Moscow until 1389, was a late medieval Russian monarchy. Its capital was the city of Moscow. Originally established as a minor principality in the 13th century, the grand principality was transformed into a centralized Russian state in the late 15th century. Moscow became a separate principality when Daniel of Moscow, Daniel (), the youngest son of Alexander Nevsky, received the city and surrounding area as an appanage. By the end of the 13th century, Moscow had become one of the leading principalities within the Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir grand principality, alongside Principality of Tver, Tver. A struggle between the princes of Moscow and Tver began after Mikhail of Tver became Grand Prince of Vladimir, grand prince in 1304. Yury of Moscow, Yury () contested the title and was later made grand prince in 1318 by the Khan (title), khan of the Golden Horde, who held suzerainty over the princes. However, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the Volkhov River just downstream from its outflow from Lake Ilmen and is situated on the M10 federal highway connecting Moscow and Saint Petersburg. UNESCO recognized Novgorod as a World Heritage Site in 1992. The city has a population of At its peak during the 14th century, the city was the capital of the Novgorod Republic and was one of Europe's largest cities. The "Великий" part was added to the city's name in 1999. Climate Veliky Novgorod has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfb''). The city has warm summers with temperatures reaching over 30 °C (86 °F) and relatively cold winters with frequent snowfall. The lowest air temperature ever recorded is -45 °C (-49 °F). The warmest month is July with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Belaya Struga
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |