|
Paleontology In Missouri
Paleontology in Missouri refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ... state of Missouri. The geologic column of Missouri spans all of geologic history from the Precambrian to present with the exception of the Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic. Brachiopods are probably the most common fossils in Missouri. During the early Paleozoic, Missouri was covered by a warm shallow sea that would come to be home to creatures like ''Archimedes (bryozoan), Archimedes'', brachiopods, shelled cephalopods, conodonts, corals, crinoids, armored fishes, and trilobites. During the Carboniferous a rich flora developed on land. Primitive tetrapods left behind Fossil footprints, footprints that would later fossiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of USA MO
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
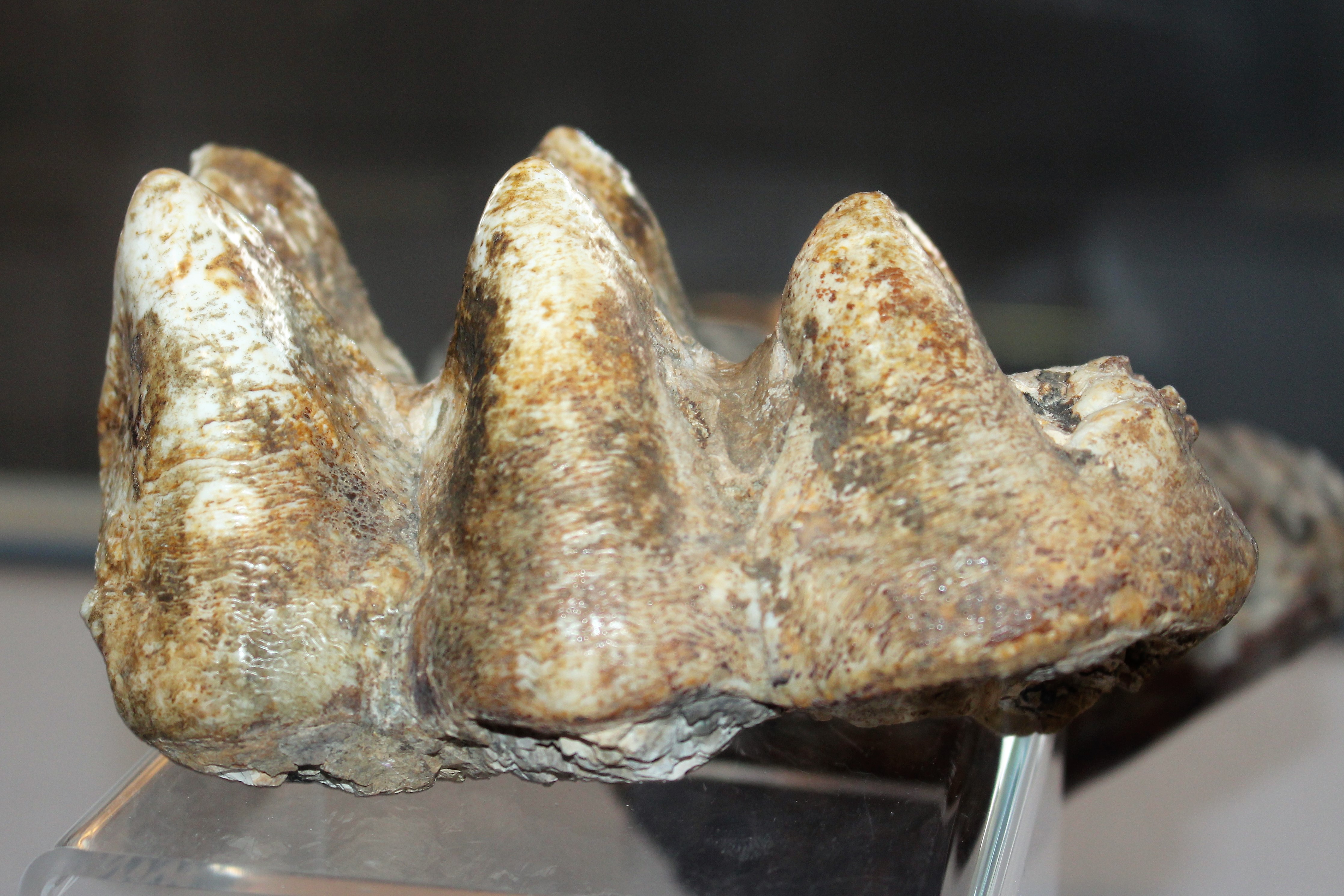
Mastodons
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to the early Holocene. Mastodons belong to the order Proboscidea, the same order as elephants and mammoths (which belong to the family Elephantidae). ''Mammut'' is the type genus of the extinct family Mammutidae, which diverged from the ancestors of modern elephants at least 27–25 million years ago, during the Oligocene. Like other members of Mammutidae, the molar teeth of mastodons have zygodont morphology (where parallel pairs of cusps are merged into sharp ridges), which strongly differ from those of elephantids. In comparison to its likely ancestor '' Zygolophodon'', ''Mammut'' is characterized by particularly long and upward curving upper tusks, reduced or absent tusks on the lower jaw, as well as the shortening of the mandibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoths
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabiting Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Mammoths are distinguished from living elephants by their (typically large) spirally twisted tusks and in some later species, the development of numerous adaptions to living in cold environments, including a thick layer of fur. Mammoths and Asian elephants are more closely related to each other than they are to African elephants. The oldest mammoth representative, '' Mammuthus subplanifrons'', appeared around 6 million years ago during the late Miocene in what is now southern and Eastern Africa.'''' Later in the Pliocene, by about three million years ago, mammoths dispersed into Eurasia, eventually covering most of Eurasia before migrating into North America around 1.5–1.3 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camels
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provide food (camel milk and meat) and textiles (fiber and felt from camel hair). Camels are working animals especially suited to their desert habitat and are a vital means of transport for passengers and cargo. There are three surviving species of camel. The one-humped dromedary makes up 94% of the world's camel population, and the two-humped Bactrian camel makes up 6%. The wild Bactrian camel is a distinct species that is not ancestral to the domestic Bactrian camel, and is now critically endangered, with fewer than 1,000 individuals. The word ''camel'' is also used informally in a wider sense, where the more correct term is "camelid", to include all seven species of the family Camelidae: the true camels (the above three species), along with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe this entire period up to the present as an "ice age", in popular culture this term usually refers to the Last Glacial Period, most recent glacial period, or to the Pleistocene epoch in general. Since Earth still has polar Ice sheet, ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, though currently in an interglacial period. During the Quaternary glaciation, ice sheets appeared, expanding during glacial periods and contracting during interglacial periods. Since the end of the last glacial period, only the Antarctic ice sheet, Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets have survived, while other sheets formed during glacial periods, such as the Laurentide Ice Sheet, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Record
The geologic record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata. That is, deposits laid down by volcanism or by deposition of sediment derived from weathering detritus (clays, sands etc.). This includes all its fossil content and the information it yields about the history of the Earth: its past climate, geography, geology and the evolution of life on its surface. According to the law of superposition, sedimentary and volcanic rock layers are deposited on top of each other. They harden over time to become a solidified ( competent) rock column, that may be intruded by igneous rocks and disrupted by tectonic events. Correlating the rock record At a certain locality on the Earth's surface, the rock column provides a cross section of the natural history in the area during the time covered by the age of the rocks. This is sometimes called the ''rock history'' and gives a window into the natural history of the location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Footprints
A fossil track or ichnite (Greek "''ιχνιον''" (''ichnion'') – a track, trace or footstep) is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the years, many ichnites have been found, around the world, giving important clues about the behaviour (and foot structure and stride) of the animals that made them. For instance, multiple ichnites of a single species, close together, suggest 'herd' or 'pack' behaviour of that species. Combinations of footprints of different species provide clues about the interactions of those species. Even a set of footprints of a single animal gives important clues, as to whether it was bipedal or quadrupedal. In this way, it has been suggested that some pterosaurs, when on the ground, used their forelimbs in an unexpected quadrupedal action. Special conditions are required, in order to preserve a footprint made in soft ground (such as an alluvial plain or a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapods
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four- limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn evolving into two major clades, the sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, some lizards, kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of vestigial spurs that are remnants of the hindlimbs. Tetrapods evolved from a group of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the tetrapodomorphs which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish ( sarcopterygians) aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |